Bone cement filler suite
A technology of bone cement and filler, applied in the field of medical devices, to achieve the effects of reducing diffusion, improving injection efficiency, and increasing the mixing range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
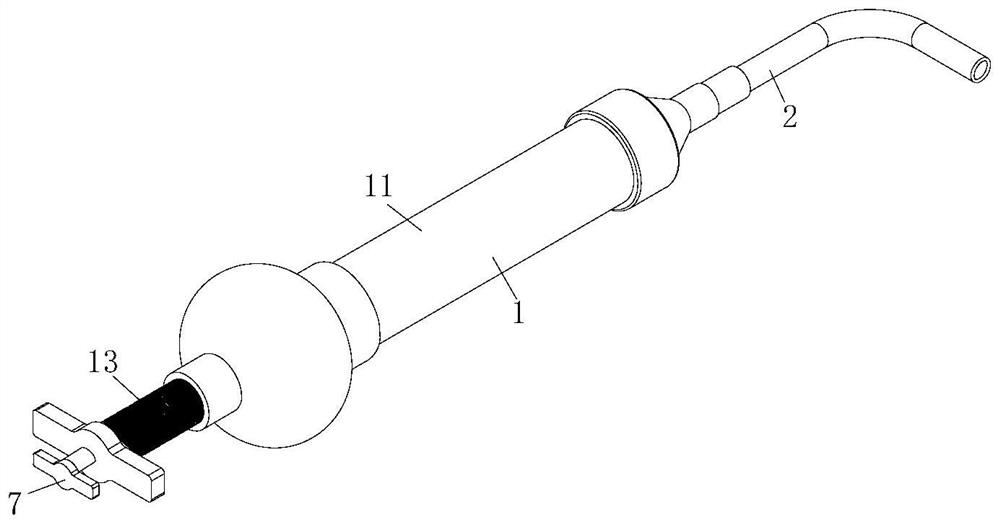
[0039] A bone cement filler kit such as Figure 1-3 As shown, it includes a sleeve set 1 and an extension tube set 2; the sleeve set 1 includes a mixer body 11, a bone cement mixer O-ring, an inner push rod 12 and a T-shaped outer push rod 13; the extension Tube set 2 is a long extension tube set or a short extension tube set; also includes:
[0040] Elastic push block 3, the elastic push block 3 is used to push the bone cement in the mixer barrel 11;
[0041] Groove 31, described groove 31 is provided on the elastic push block 3;
[0042] No. 1 channel 4, said No. 1 channel 4 is set in the elastic push block 3, inner push rod 12 and T-shaped outer push rod 13 connected in sequence;
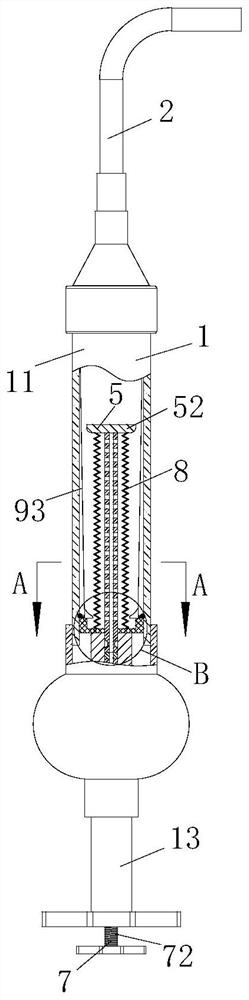
[0043] Stirring group 5, described stirring group 5 comprises stirring rod 51, stirring block 52, No. 1 magnetic block 53 and clamping module 6; One end of described stirring rod 51 is connected with stirring block 52 placed in groove 31, and the other end Connect with the No. 1 magnetic block...
Embodiment 2
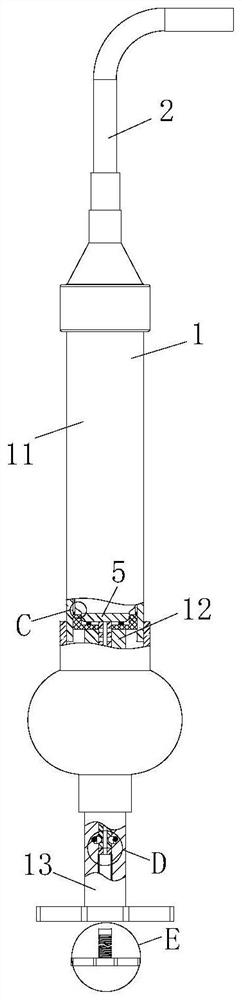
[0049] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that, as image 3 and Figure 7 As shown, the engaging module 6 includes a clamping block 61, an annular clamping groove 62 and a clamping groove 63; the inner wall of the No. 1 channel 4 is provided with a clamping groove 63; the outer ring of the stirring rod 51 There is an annular snap-in groove 62 on the top, and in the initial state, the snap-in slot 63 corresponds to the annular snap-in slot 62; Inside;
[0050] Through the mutual cooperation between the clamping block 61 and the annular clamping groove 62, the engagement and fixation of the stirring rod 51 can be realized, and the force of the pushing rod 72 can be pushed outward to realize the engagement between the clamping block 61 and the annular clamping groove 62. Detachment does not need to add an additional driving source, and at the same time, the operation is simple and stable;
[0051] The difference from the specific working process of Embodiment 1 is that when t...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The difference from the second embodiment is that, if image 3 as well as Figure 7-Figure 8 As shown, a group of balls 41 are arranged on the inner wall of the No. 1 channel 4 located at the bottom of the No. 1 magnetic block 53, and the inner diameter formed between the corresponding balls 41 on the inner wall of the No. 1 channel 4 is much larger than that of the No. 2 magnet. The width of piece 71; Described push rod 72 is made up of rod one 721 and rod two 722, and rod one 721 connects No. 2 magnetic block 71, and rod one 721 and rod two 722 are rotationally connected, and the outer ring of rod one 721 is opened There is a spiral groove 723 matching with the ball 41;
[0054] By setting the push rod 72 composed of rod one 721 and rod two 722, and on the rod one 721, a spiral groove 723 matching the ball 41 is provided, and the spiral groove 723 cooperates with the ball 41, thereby realizing the stirring rod 51 and the stirring The rotation of the block 52 increas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com