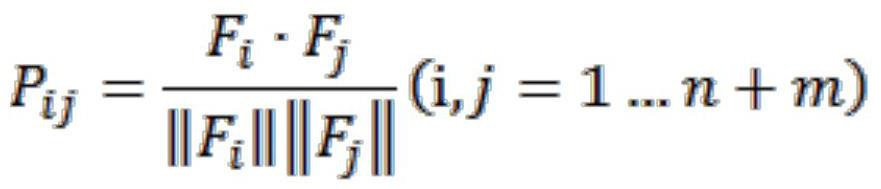Computed tomography spinal fracture auxiliary diagnosis system
A tomography, auxiliary diagnosis technology, applied in computer-aided medical procedures, computer parts, computing and other directions, can solve the problems of inconspicuous symptoms, small scope, hidden features, etc., to reduce learning difficulty, improve model performance, and improve accuracy. rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
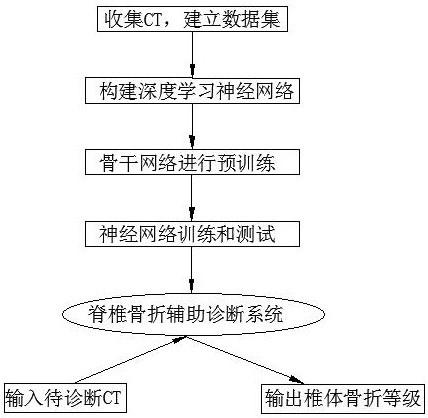
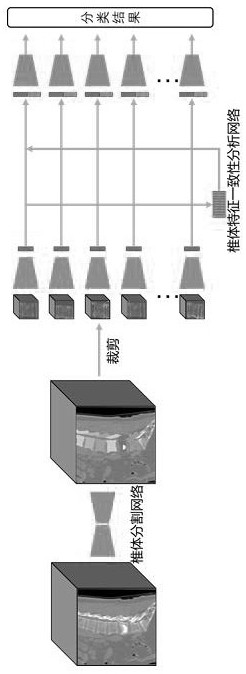
[0032] The auxiliary diagnosis system takes the original CT image containing the spine as input, and fuses and compares and analyzes the feature images of multiple vertebral bodies through a neural network, so as to help the model identify vertebral bodies with abnormal features. At the same time, the feature information of vertebral bodies with known fracture levels is introduced as a reference for neural network fusion and comparison. The above design effectively utilizes the information of multiple vertebral bodies of the spine in CT images, so that the model can play a good role in the diagnosis of spinal fractures based on CT images.
[0033] Because CT images have the characteristics of high resolution and large amount of information, this model uses a two-stage network to analyze CT images. The analysis process includes two stages of vertebral body positioning and segmentation and classification and diagnosis.
[0034] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a computeri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com