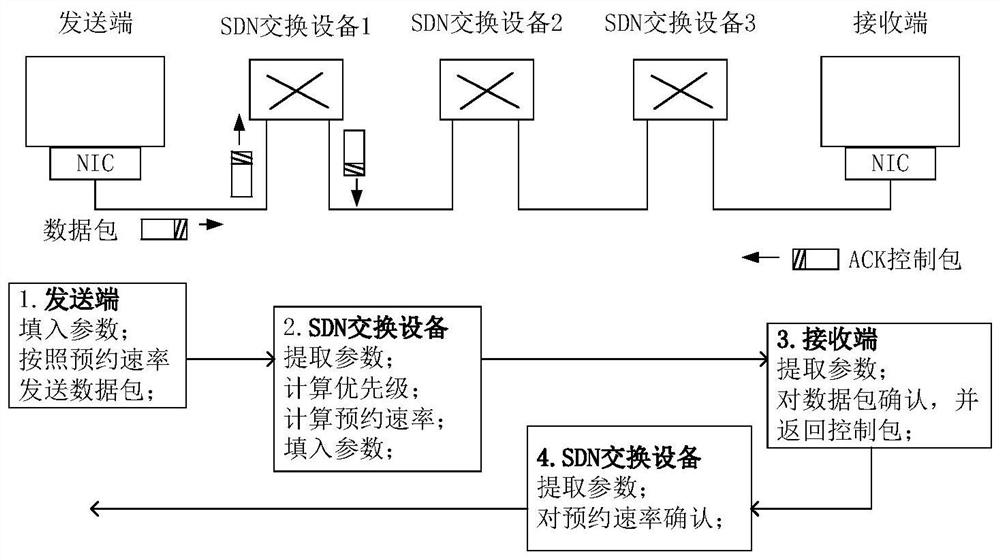
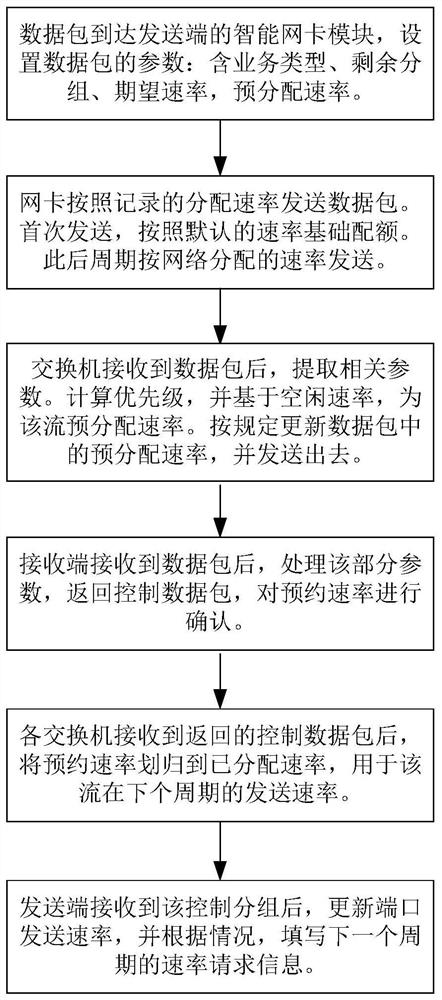
Dynamic priority congestion control method for programmable switching network
A dynamic priority and congestion control technology, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as inability to complete, fixed functions, and lack of flexible parameter modification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
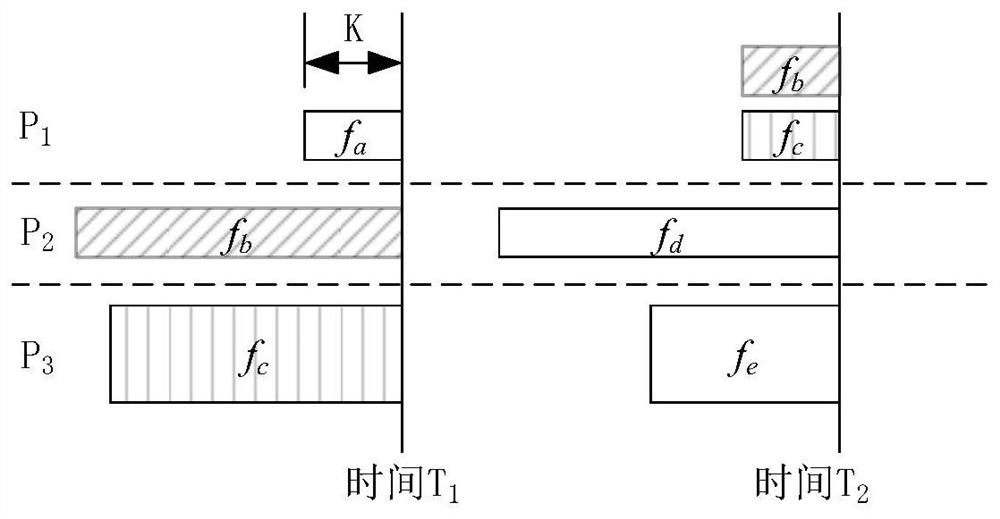
[0060] Embodiment 1: as image 3 An example of dynamic priority adjustment is shown
[0061] If time T 1 When, the flow f in a link b and f c Delay-sensitive services and non-delay-sensitive services are respectively set to priority P 2 and P 3 , while flow f a Because the number of remaining packets is small, it is set to priority P 1 . When the link rate is allocated, the priority is to satisfy the flow f a , then satisfies the flow f b , and finally if there is a surplus, the flow f is satisfied c .
[0062] If the remaining link rate is 500Mbps, flow f a , f b , f c The expected rates are 120Mbps, 120Mbps, and 200Mbps respectively. Since there are currently no other stream requests, the final allocated rates are 120Mbps, 120Mbps, and 260Mbps.
[0063] As time goes by, reaching time T 2 , at this time flow f b and f c There are fewer packets left to be transmitted, so they are assigned to priority P 1 . To this end, during link rate allocation, the flow f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com