Methods for terpenoid production
A terpene synthase and terpene technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, oxidoreductase, lyase, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient activity and limitation of terpene synthase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0148] Engineering E. coli strains for TPS characterization
[0149] Wild-type E. coli BL21 produces small amounts of terpene precursors (GPP and FPP), therefore, it is not suitable as a TPS characterization platform. In order to improve the sensitivity and accuracy of detection, DXS and IDI were overexpressed to increase the intracellular precursor ( image 3 ). Unlike existing methods, two DXS mutants (SL3 and SL5) were identified based on random mutagenesis and screening. As shown in Figure 2, SL3 and SL5 have higher solubility and thus higher activity than wild-type DXS compared to wild-type DXS. More importantly, SL5 had higher specific activity than wild-type DXS ( Figure 2B ). Therefore, the lycopene production of strains overexpressing SL3 or SL5 was higher than that of wild-type DXS. Here, lycopene was used as an indicator to demonstrate that GPP and FPP were higher in the strains (SL3 and SL5). Using DXS mutants, the detection sensitivity of the cell platform ...
Embodiment 2
[0151] Analysis of terpenes produced in Amanita cylindrica
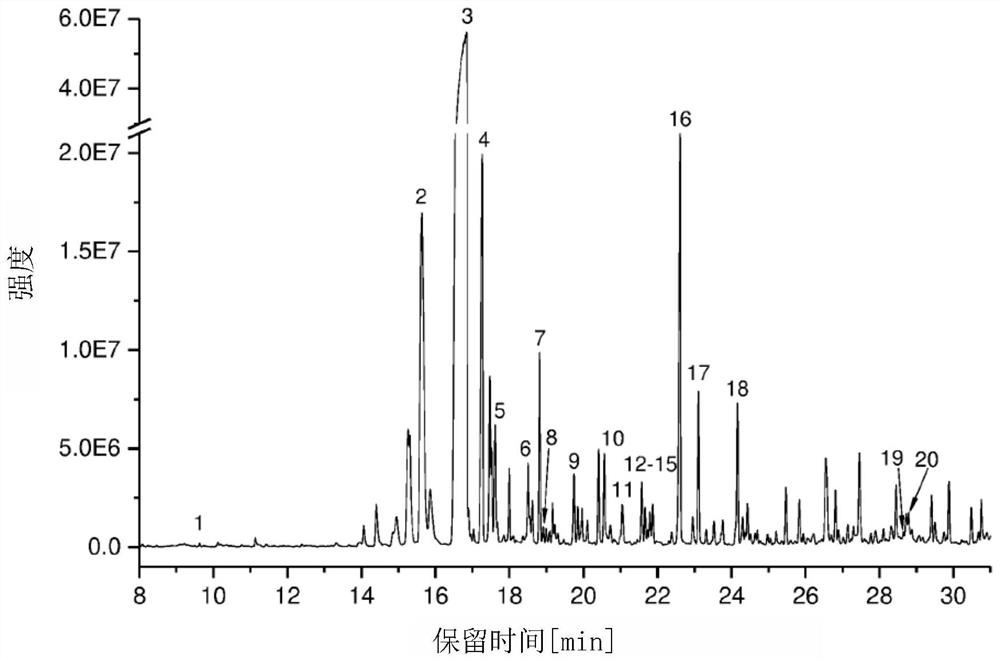
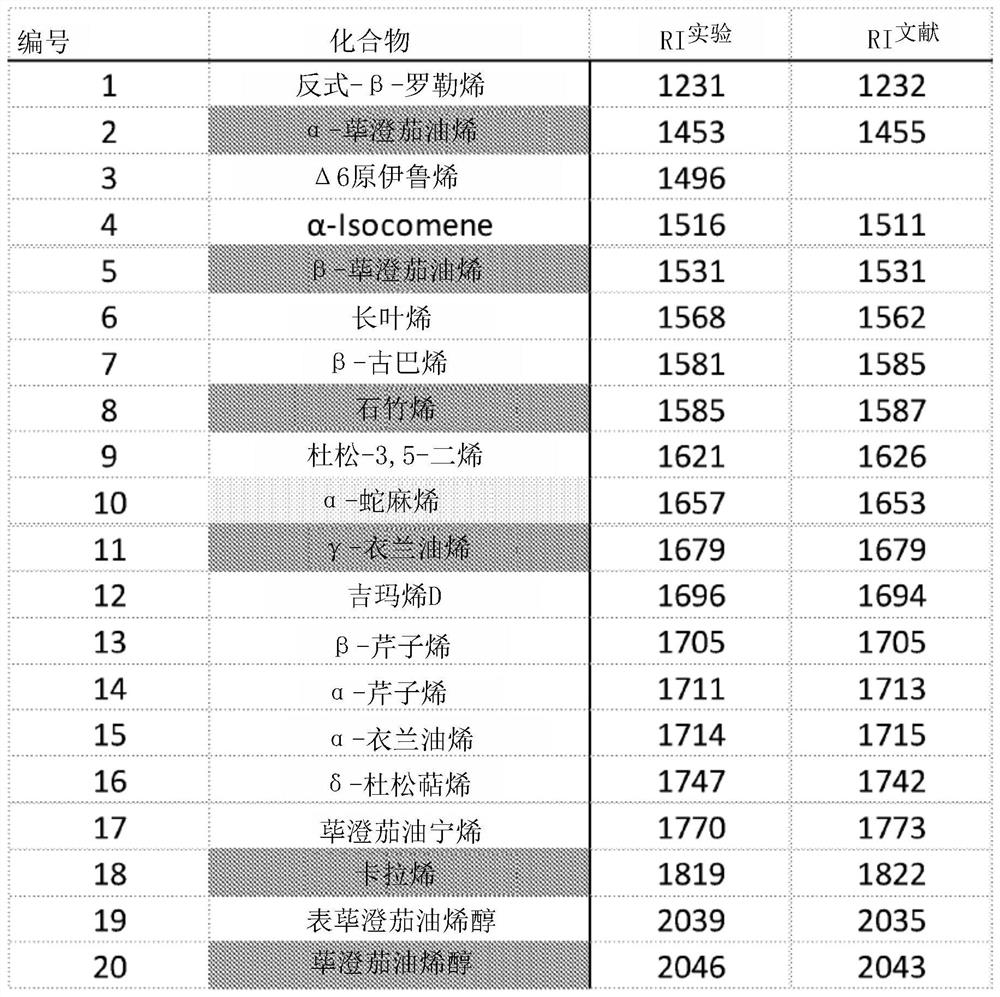
[0152] To obtain an assessment of the terpenes produced in Amanita cylindrosum, the volatile compounds produced by its liquid cultures were analyzed. The illudin precursor Δ(6)protoilurene 1 is the main metabolite produced in A. cylindrica ( figure 1 ). In addition, after 26 days of culture, a small amount of α-iocomene was observed # , α-, β-piperene, β-cubene, γ-ylangolene 2, δ-junipene 4, β-celerene # 9. Piper cubeba oleinol, epipiperumba oleenol 10 and Piper cubeba oleinol ( Figure 4 and Figure 5 chemical structures and mass spectra of all terpenes identified in the study, respectively). The results indicated that the mushroom Acromanus cylindrica produced structurally diverse terpenes.
Embodiment 3
[0154] Sesquiterpene Alcohols from Amanita cylindrica
[0155] Twenty putative terpenoids were detected by GC / MS analysis during fruiting of Amanita cylindrica, among which the experimentally identified Δ6-protoilurene # is the most prominent compound ( figure 1 ). Other major compounds are α-piperene, α-isocomene # , β-piperene and δ-juniperene ( Figure 4 The compound structure in Figure 5 mass spectrometry in ). A blastp search of putative STSs present in the A. cylindrica genome revealed 11 genes (Table 2 and Figure 6 ). Seven TPS clustered into at least 3 distinct groups with known Basidiomycete TPS. Four putative TPSs (AAE3_09008, AAE3_06743, AAE3_04444, and AAE3_05024) compile into a cluster ( Figure 6 ). Four of the STS genes (AAE3_10454, AAE3_12839, AAE3_04120 and AAE3_13291) were part of a cluster that included two to five P450 monooxygenases.
[0156] Table 2 Details of the STS gene of Amanitula cylindrica
[0157] protein ID bracket gene...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com