Optical system, imaging module and electronic equipment
An optical system and optical axis technology, applied in the field of photography, can solve problems such as insufficient effective focal length and difficulty in telephoto performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
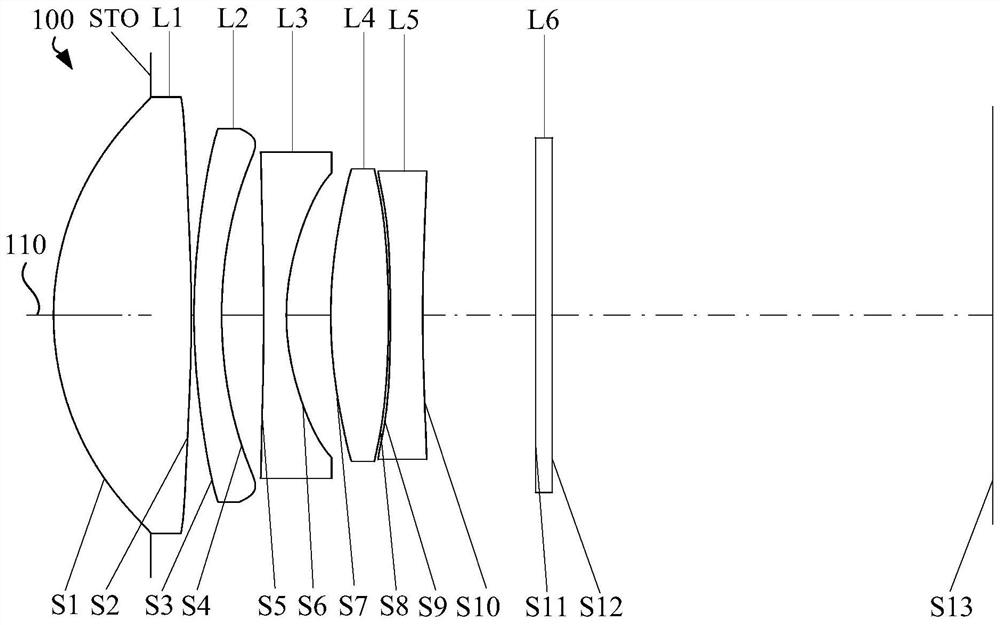
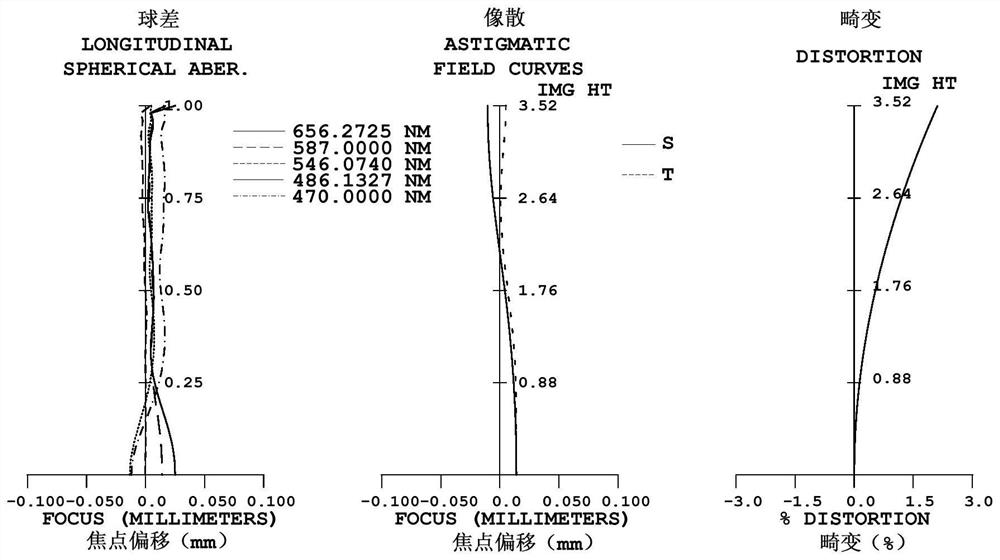
[0091] See figure 1 and figure 2 , figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of the optical system 100 in the first embodiment. The optical system 100 sequentially includes an aperture stop STO, a first lens L1 with positive refractive power, a second lens L2 with negative refractive power, and an aperture stop STO from the object side to the image side. A third lens L3 having a negative refractive power, a fourth lens L4 having a positive refractive power, and a fifth lens L5 having a negative refractive power. figure 2 From left to right are graphs of longitudinal spherical aberration, astigmatism, and distortion of the optical system 100 in the first embodiment, wherein the reference wavelength of the astigmatism graph and the distortion graph is 587 nm, and the other embodiments are the same.
[0092] The object side surface S1 of the first lens L1 is a convex surface at the near optical axis 110, and is a convex surface at the circumference;
[0093] The image si...
no. 2 example
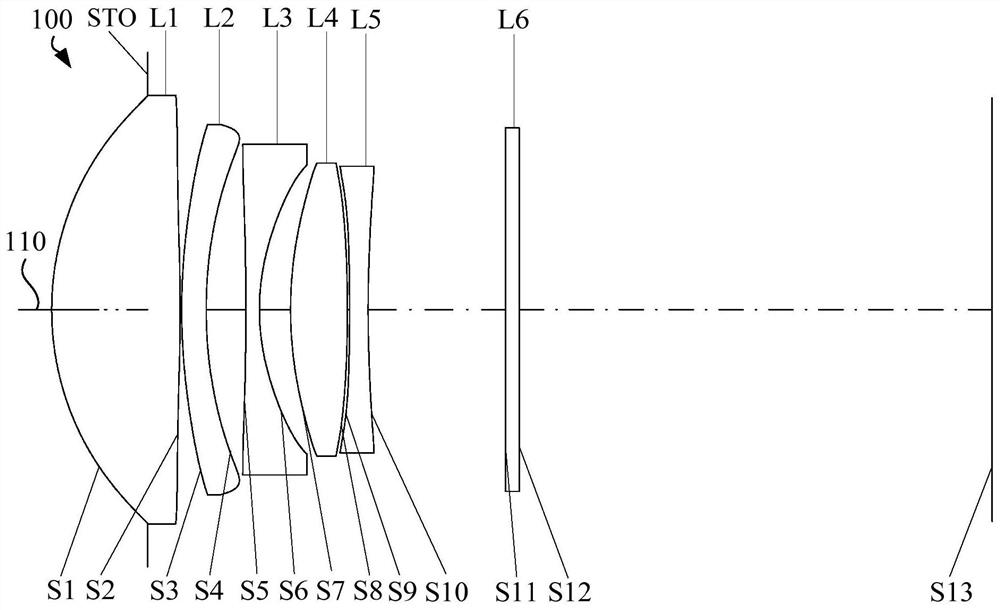
[0129] See image 3 and Figure 4 , image 3 It is a schematic structural diagram of the optical system 100 in the second embodiment. The optical system 100 sequentially includes an aperture stop STO, a first lens L1 with positive refractive power, a second lens L2 with negative refractive power, and an aperture stop STO from the object side to the image side. A third lens L3 having a negative refractive power, a fourth lens L4 having a positive refractive power, and a fifth lens L5 having a negative refractive power. Figure 4 From left to right are graphs of longitudinal spherical aberration, astigmatism and distortion of the optical system 100 in the second embodiment.
[0130] The object side surface S1 of the first lens L1 is a convex surface at the near optical axis 110, and is a convex surface at the circumference;
[0131] The image side surface S2 of the first lens L1 is a convex surface at the near optical axis 110, and is a convex surface at the circumference;
...
no. 3 example
[0153] See Figure 5 and Image 6 , Figure 5It is a schematic structural diagram of the optical system 100 in the third embodiment. The optical system 100 sequentially includes an aperture stop STO, a first lens L1 with positive refractive power, a second lens L2 with positive refractive power, and an aperture stop STO from the object side to the image side. A third lens L3 having a negative refractive power, a fourth lens L4 having a positive refractive power, and a fifth lens L5 having a negative refractive power. Image 6 From left to right are graphs of longitudinal spherical aberration, astigmatism and distortion of the optical system 100 in the third embodiment.
[0154] The object side surface S1 of the first lens L1 is a convex surface at the near optical axis 110, and is a convex surface at the circumference;
[0155] The image side surface S2 of the first lens L1 is a convex surface at the near optical axis 110 and a concave surface at the circumference;
[0156...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com