Satellite on-orbit fault propagation and sweep effect modeling and prediction method and system
A technology of fault propagation and prediction method, which is applied in special data processing applications, design optimization/simulation, and constraint-based CAD, etc. It can solve problems such as gyroscope measurement output out-of-tolerance, control system losing the chance of autonomous fault judgment, satellite attitude deviation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
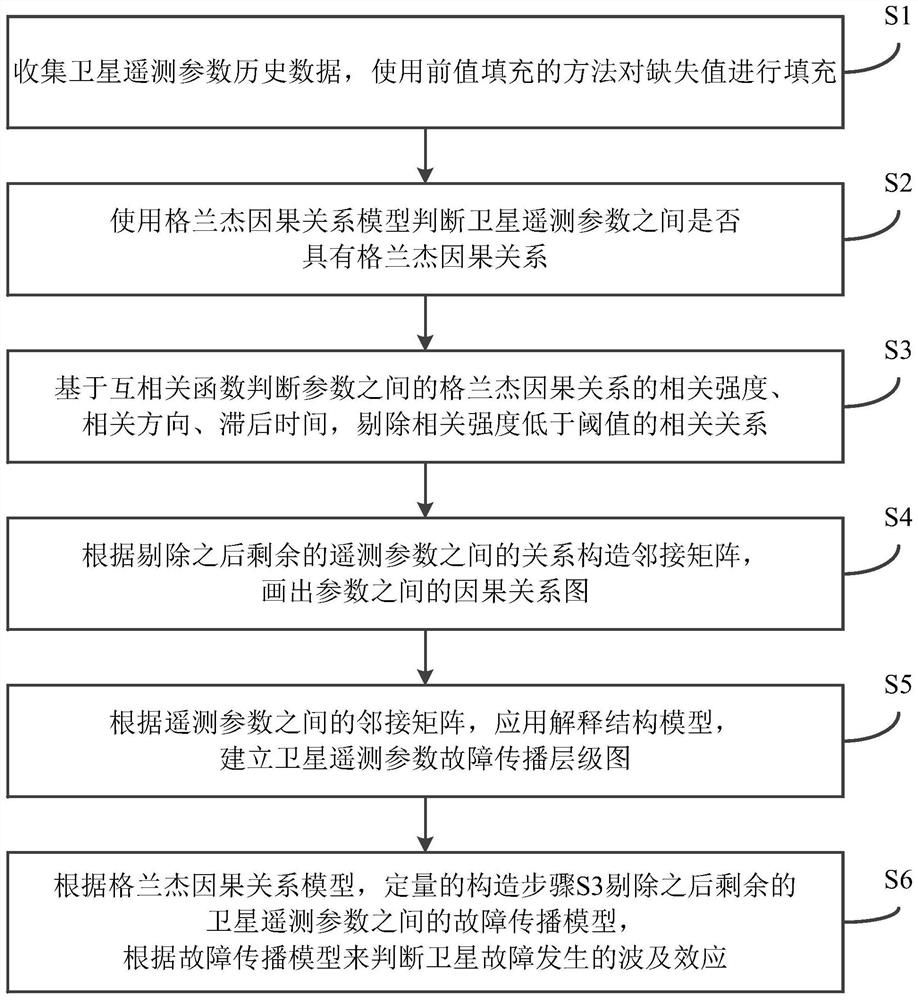
[0129] This embodiment discloses a satellite on-orbit fault propagation and ripple effect modeling and prediction method, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0130] Step S1. Collect the historical data of the satellite telemetry parameters, and fill in the missing values by using the previous value filling method.
[0131] Step S2, using the Granger causality model to judge whether there is a Granger causality between the satellite telemetry parameters.
[0132] In this step, the determination of Granger causality between telemetry parameters includes the following steps:
[0133] Step S21, performing mean value removal processing on the telemetry data. In this way, it is ensured that the satellite telemetry data meets the requirement of data fluctuation around the y-axis in the Granger causality test.
[0134] Step S22, selecting the ADF to perform a unit root test on the telemetry data. In order to determine whether the satellite telemetry data mee...
Embodiment 2
[0243] Relying on the methods in the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment discloses a specific calculation example of a satellite in-orbit fault propagation and ripple effect modeling and prediction method, including the following steps:
[0244] S11: Collect historical data of satellite telemetry parameters; use the previous value filling method to fill in missing values.
[0245] The parameter data includes telemetry parameters such as temperature, current, voltage, etc., because during the operation of the satellite in orbit, various physical quantities of its components need to be measured. These physical quantities are telemetry parameters, and the obtained data are telemetry data. is a time series, specifically expressed as t is the length of the time series, and n is the number of parameters.
[0246] S12: Use the Granger causality model to determine whether there is a Granger causality between the satellite telemetry parameters. The Granger causality between...
Embodiment 3
[0262] This embodiment discloses a satellite on-orbit fault propagation and ripple effect modeling and prediction system based on the improved Granger causality model, including a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and operable on the processor When the processor executes the computer program, the steps of the corresponding methods in the above two embodiments are implemented.
[0263] To sum up, the methods and systems for modeling and predicting satellite on-orbit fault propagation and spillover effects disclosed in the above-mentioned embodiments of the present invention have at least the following beneficial effects:
[0264] The present invention judges the correlation strength, correlation direction, and lag time of the Granger causality between parameters based on the cross-correlation function, and eliminates correlations whose correlation strength is lower than the threshold, and solves the problem that traditional causality modeling canno...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com