Medium and method for proliferation and differentiation of alveolus organoids
A technology of proliferation medium and differentiation medium, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as hindering the development of precision medicine, unable to reflect individual differences, and easy to lose phenotype, so as to facilitate precision medicine and high-throughput drug screening, and save research and development costs. And the effect of time-consuming research and development and good operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
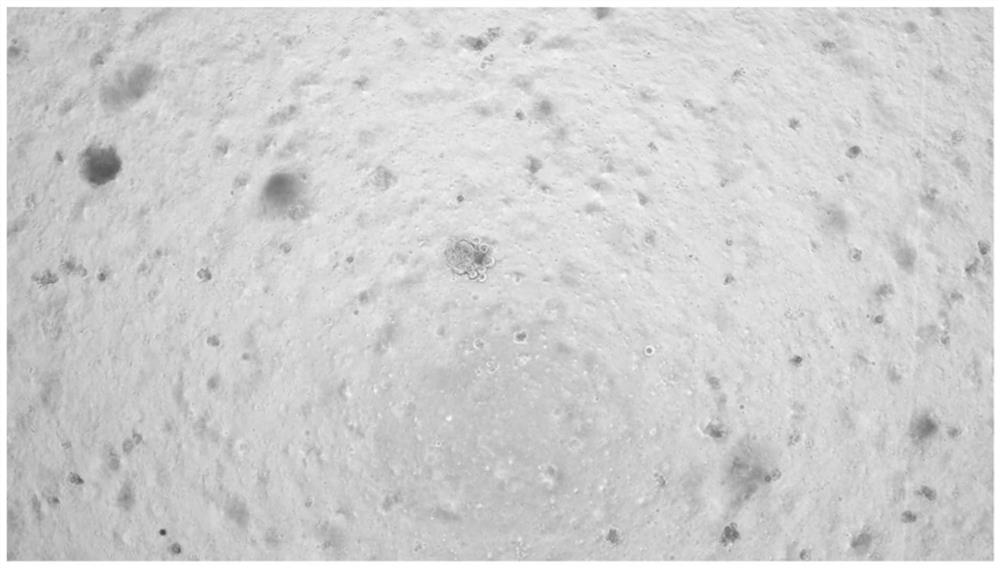
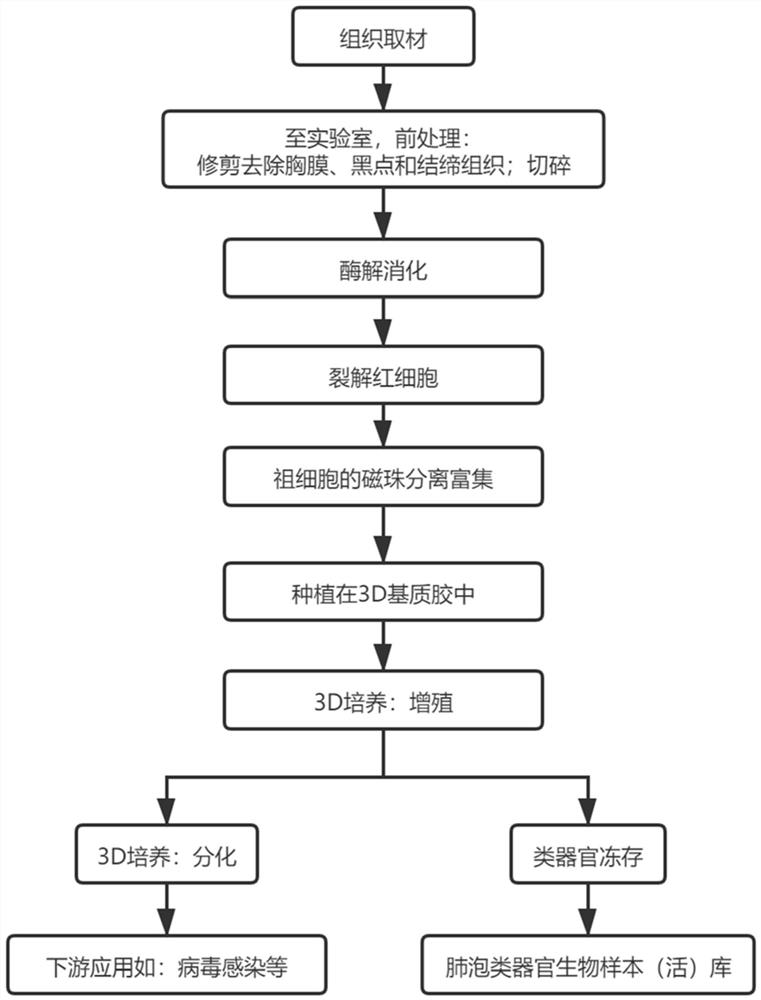
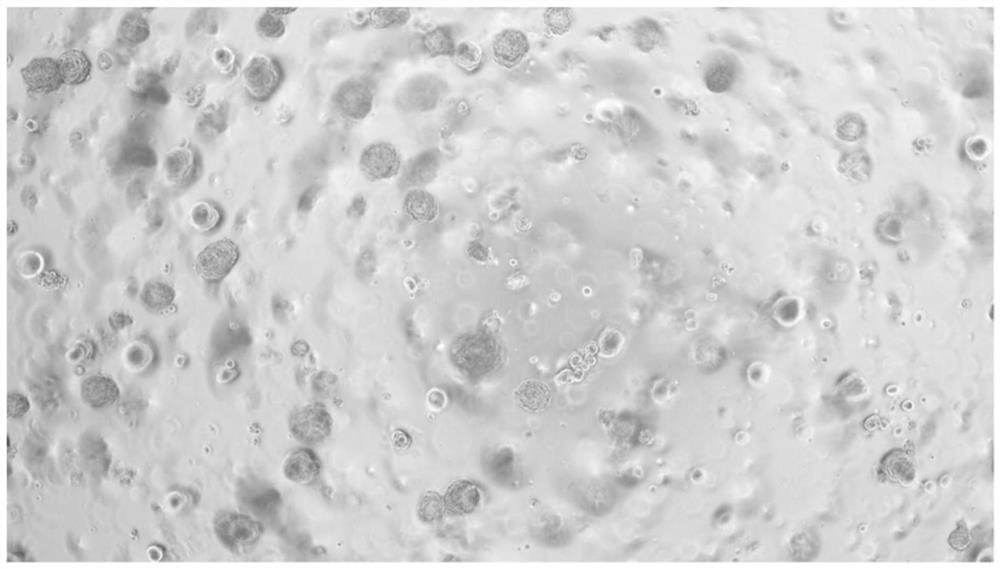
[0044] The whole process steps of culturing human tissue-derived alveolar organoids are as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0045] 1. The collection and transfer of lung resection tissue in the operating room.
[0046]Tissues for healthy alveolar organoid use can usually be normal lung tissue that has been extensively resected during radical lung cancer surgery, or normal lung tissue remaining after pruning from a lung transplant donor. The tissues used for disease alveolar organoids can be determined according to the needs of different diseases. Unless required by a specific disease model, it is not recommended to use lung tissue from long-term smokers, patients with current pulmonary infection, patients with chronic pulmonary obstruction, and other underlying lung diseases as the starting material for culture. Avoid the airway and cancer focus tissue when collecting materials, try to take the distal lung tissue, and only take the part with good activity (reddish, soft, relativel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com