Method and equipment for data transmission in relay network
A relay network, data transmission technology, applied in the field of communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
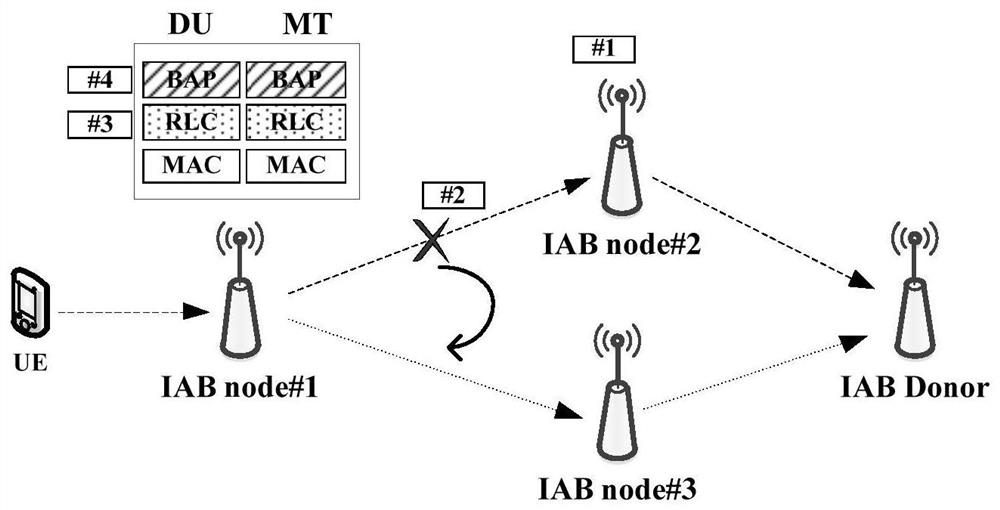
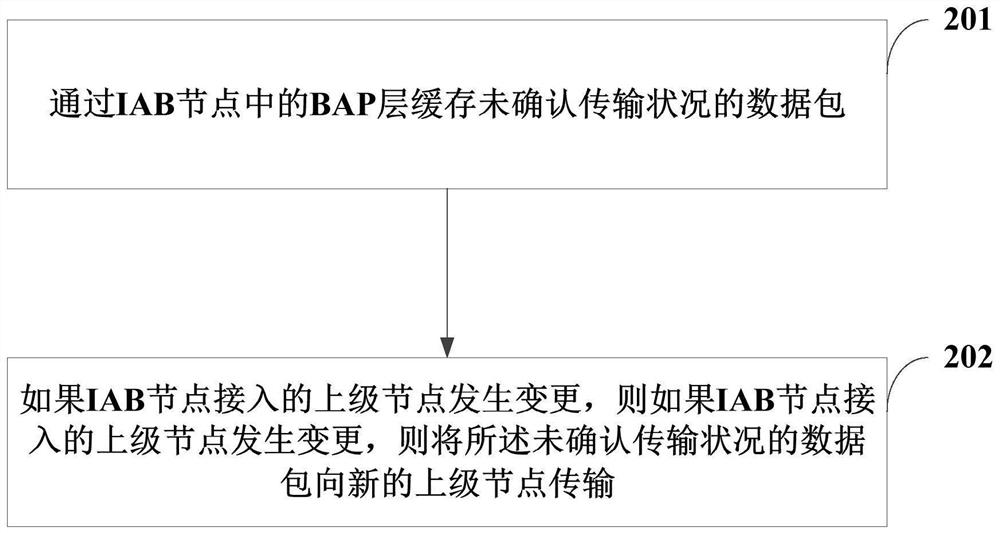
[0099] Embodiment 1: Data transmission when IAB node changes the access node, see Figure 5 .
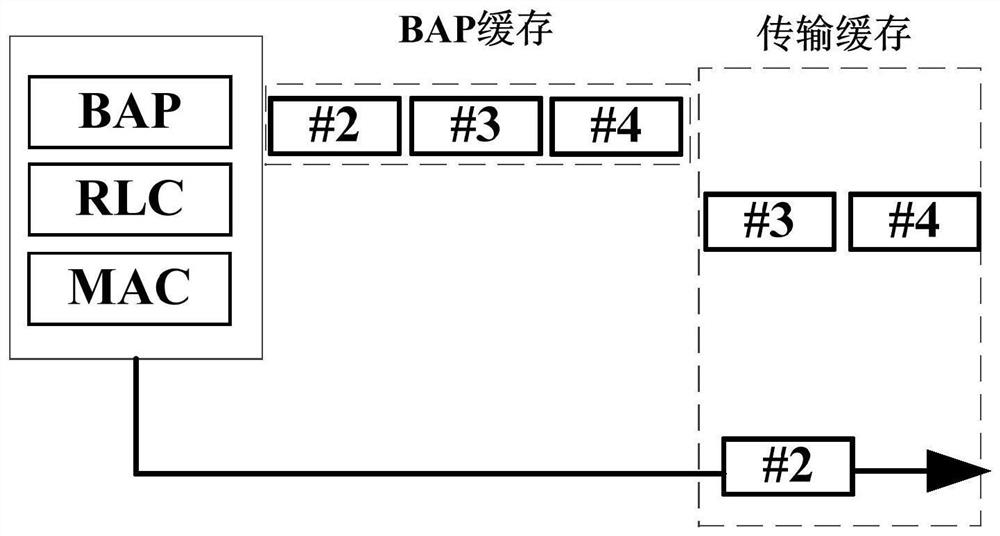
[0100] Step 1: The BAP layer in the IAB node1 caches data packets to be transmitted (or data packets with unconfirmed transmission status), including: data packets not submitted to the RLC layer, submitted to the RLC layer (and / or MAC layer) data packets, data packets that have been transmitted to the upper node on the air interface;
[0101] For example, a data packet to be transmitted is buffered by a redundant buffer (Redundant buffer) and / or a transmission buffer (Transmission buffer).
[0102] Step 2: If the conditions for deleting the BAP cache are met, delete the data packets in the BAP cache, for example, delete data packet #2, data packet #3 and data packet #4;
[0103] It can be understood that, for the specific process of deleting the data packets in the BAP cache, reference may be made to Embodiments 2-6.
[0104] Step 3: If the IAB node is connected to another upper-le...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Embodiment 2: RLC feeds back successfully transmitted data packets to BAP according to PDCP SN, see Figure 6 .
[0108] Step 1: The BAP layer analyzes the identification mark carried by the data packet, such as the PDCP SN, and the BAP layer submits the data packet to the RLC layer. Optionally, the identification mark also includes: a terminal identification and / or a bearer identification;
[0109] Step 2: The RLC layer receives the data packet submitted by the BAP layer, organizes it into an RLC PDU for air interface transmission, and parses the identification mark carried by the data packet, such as the PDCP SN. Optionally, the identification mark also includes a terminal identification and / or Bearer ID;
[0110] Step 3: The RLC layer receives the RLC feedback sent by the opposite end, and for the data packet that receives the RLC ACK, feeds back to the BAP the identifier of the data packet that the BAP layer can recognize, specifically the feedback PDCP SN, and opt...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Embodiment 3: RLC feeds back successfully transmitted data packets to BAP according to BAP SN, see Figure 6 .
[0114] Step 1: The BAP layer submits the data packet to the RLC layer, and assigns the BAP SN to the data packet;
[0115] Step 2: The RLC layer receives the data packet submitted by the BAP layer and the BAP SN corresponding to the data packet. The RLC layer can strip the BAP SN and not include it in the RLC PDU, or the BAP SN can also be included in the RLC PDU middle;
[0116] Step 3: The RLC layer receives the RLC feedback sent by the opposite end, and feeds back to the BAP the BAP SN of the data packet that successfully received the RLC ACK;
[0117] For example, an indication of successful reception of data packet #2 and data packet #3 is fed back, or an indication of successful reception of data packet #4 and data packet #5 is fed back.
[0118] Step 4: The BAP layer deletes the successfully sent data packets in the BAP cache according to the feedba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com