Stator of a thin-plate frame structure linear ultrasonic motor with fins and its excitation method
A technology of linear ultrasonic motor and frame structure, applied in the direction of piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motor, generator/motor, electrical components, etc., can solve the limitation of length or width direction, and the vibrator structure is not easy to miniaturize , bending vibration node bending deformation and other problems, to achieve the effect of large driving force and driving speed, simple fixing method, and degeneracy of frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
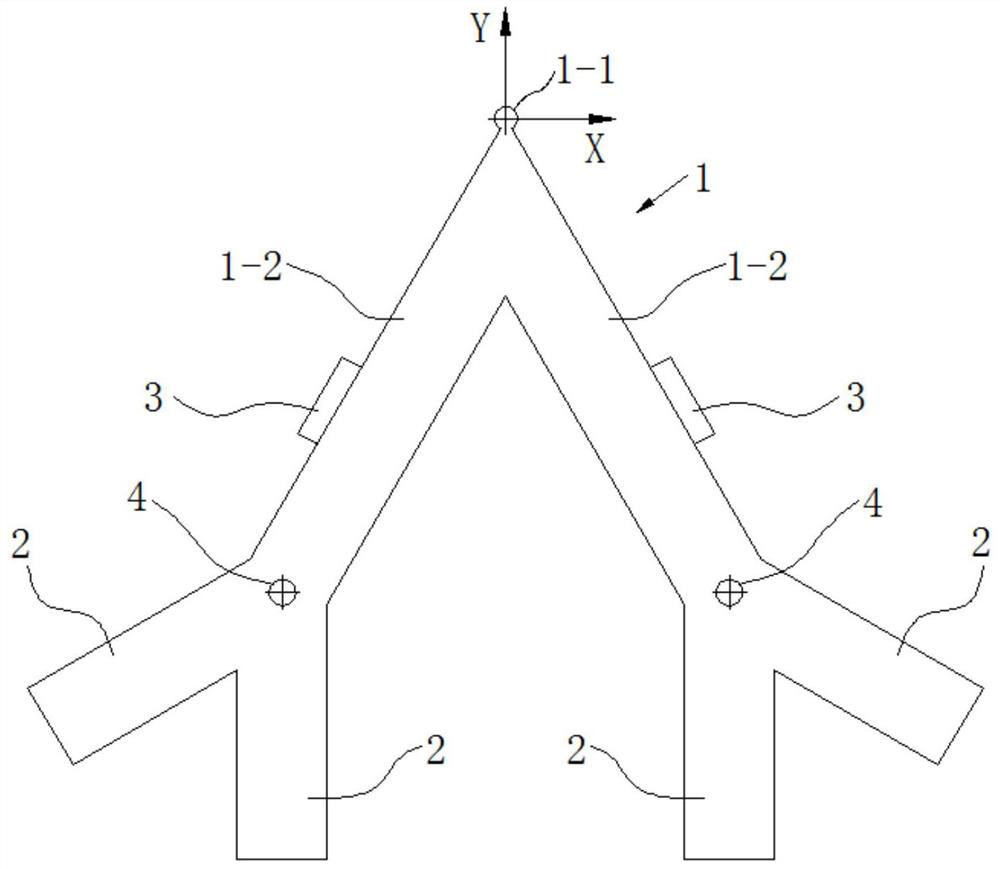
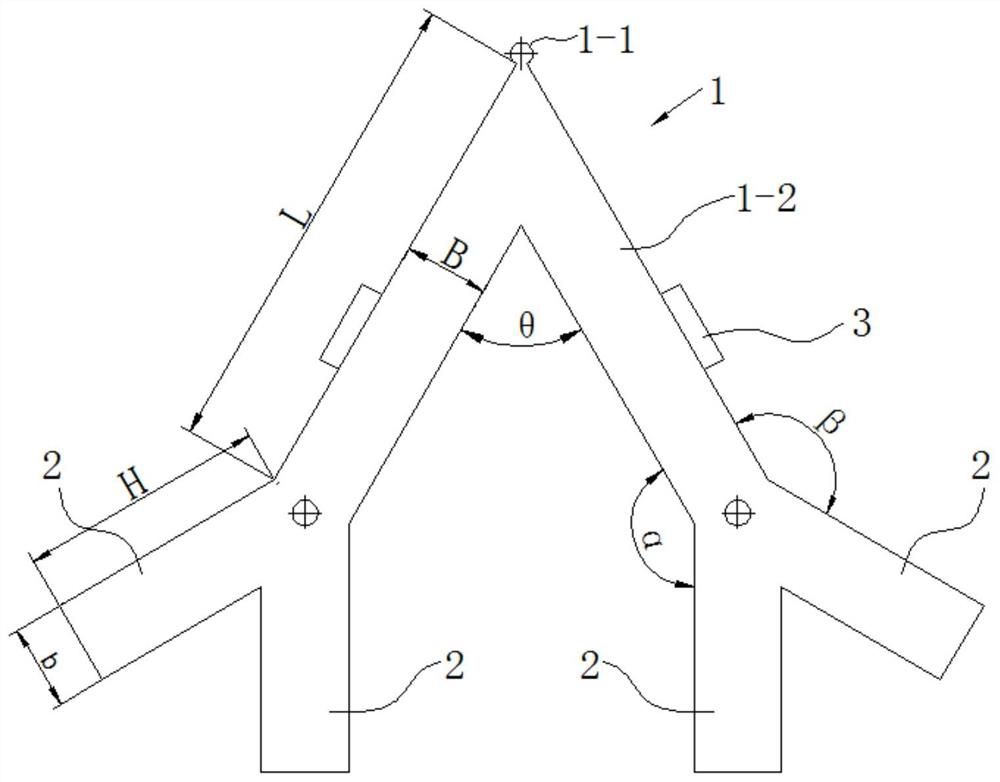
[0060] Embodiment 1, the quantity of the thin-plate empennage 2 of the present embodiment is 4, and two thin-plate empennages 2 are respectively arranged on both sides 1-2 of the V-shaped frame 1, as Image 6 As shown, the side length L=11.5mm of the V-shaped frame 1, the width B=2mm, and the included angle θ=60°. The mounting hole 4 is circular, located at the junction of the V-shaped side and the empennage, and fixed with a pin. The thin-plate empennage 2 is located at the end of the V-shaped side, and the structural size of the thin-plate empennage is completely symmetrical, and the two thin-plate empennages 2 are arranged symmetrically with the center line of the mounting hole. The length H=5.7mm of single thin-plate tail 2, width b=2mm, the thickness of both sides 1-2 of V-shaped frame 1 and thin-plate tail 2 are 0.5-2mm, the thin-plate tail 2 of the outside and V-shaped frame side angle 150 °, the angle between the inner tail fin and the V-shaped side is 150°, and two pi...
Embodiment 2
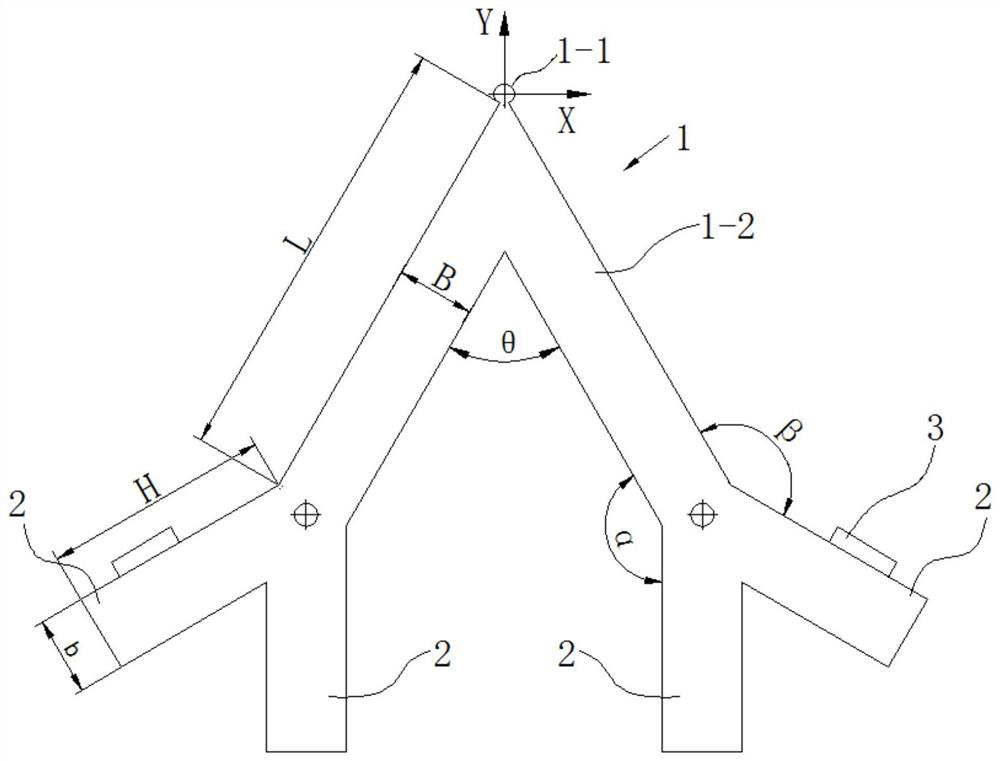
[0061] Embodiment 2. In this embodiment, on the basis of the V-shaped frame 1 described in Embodiment 1, the arrangement position and included angle of the thin-plate empennage 2 are adjusted. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that α=180°, β=90°, θ=90°, get as Figure 9 As shown in the stator structure, designing a circular drive at the driving point 1-1 is sufficient to increase the amplitude, and the symmetrical mode is as Figure 10 As shown, the antisymmetric mode is as Figure 11 As shown, the two modes are orthogonally superimposed at the driving point to form an elliptical motion and drive the guide rail to move.
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3, on the basis of the V-shaped frame described in Embodiment 1, the arrangement position and the included angle of the thin plate empennage 2 are adjusted. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that α=90°, β=180°, and θ=90 °, get as Figure 12 As shown in the stator structure, designing a circular drive at the driving point 1-1 is sufficient to increase the amplitude, and the symmetrical mode is as Figure 13 As shown, the antisymmetric mode is as Figure 14 As shown, the two modes are orthogonally superimposed at the driving point to form an elliptical motion and drive the guide rail to move.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com