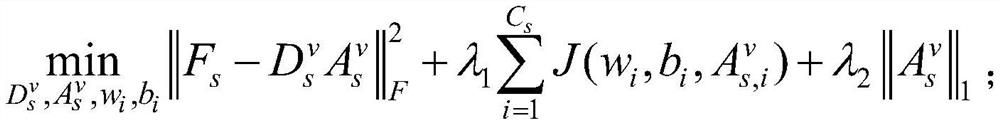Zero sample identification method and system based on discriminative visual attributes
A visual attribute, discriminative technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, computer parts, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of lack of semantic information of feature representation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
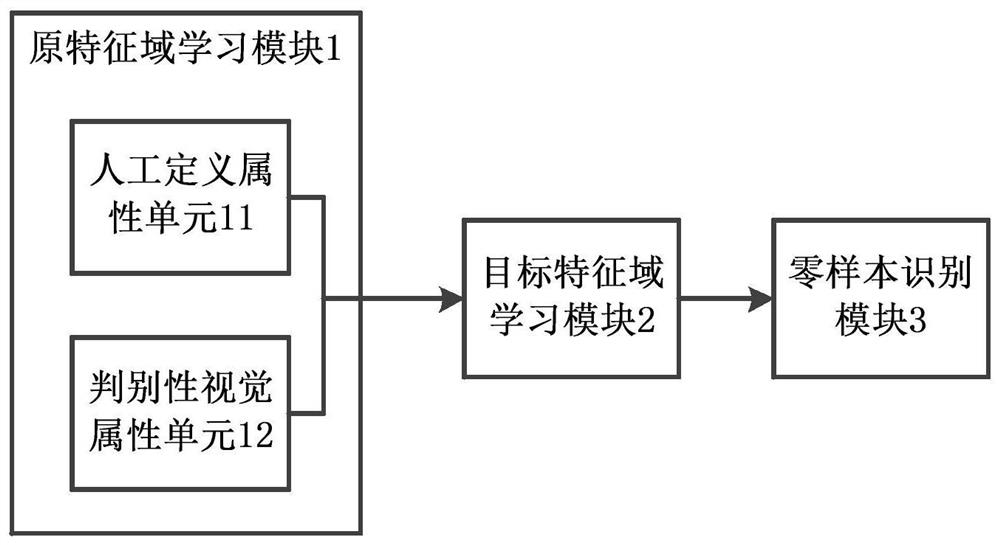
[0056] refer to figure 1 , is a schematic structural diagram of an embodiment of a zero-shot recognition system based on discriminative visual attributes in the present invention; specifically, the system includes: an original feature domain learning module 1, a target feature domain learning module 2, and a zero-shot recognition module 3;
[0057] The association between the visual feature space and the semantic embedding space plays an important role in zero-shot visual recognition. The present invention decomposes the learning of the above feature space association information into two parts: the original feature domain learning (known object category) and the target feature Domain learning (unknown object category), zero-shot recognition problem in which object categories are disjoint between the original feature domain and the target feature domain.
[0058] Specifically, the original feature domain learning module 1 includes a manually defined attribute unit 11 and a dis...
Embodiment 2
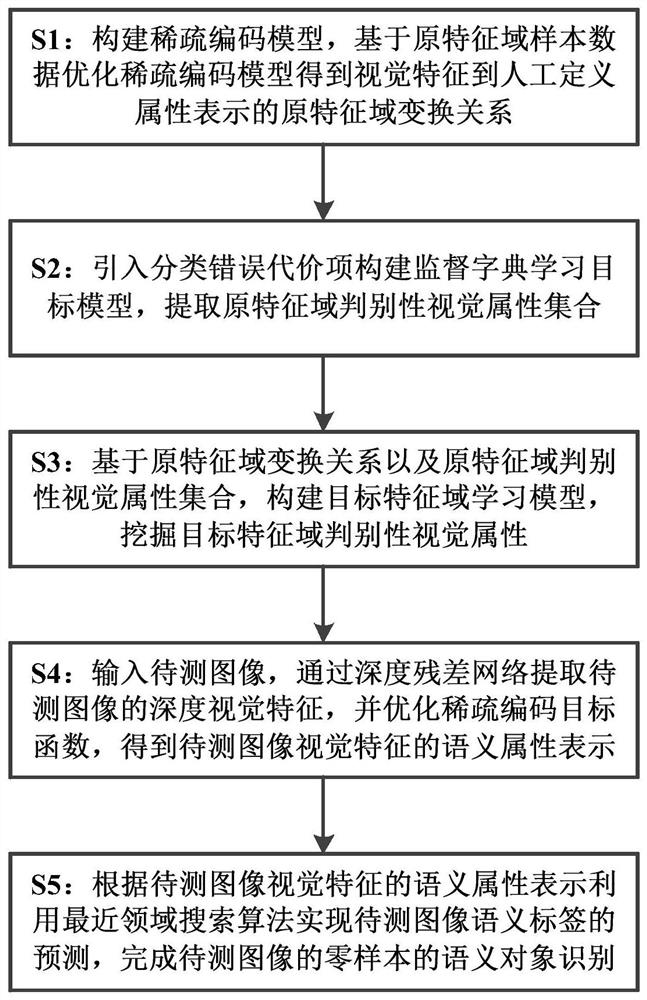
[0081] Based on the system in Embodiment 1, the present invention also provides a zero-sample recognition method based on discriminative visual attributes, the flowchart can refer to figure 2 , specifically, a zero-shot recognition method based on discriminative visual attributes, comprising the following steps:
[0082] S1: Construct a sparse coding model, optimize the sparse coding model based on the sample data of the original feature domain to obtain the transformation relationship of the original feature domain from the visual feature to the manually defined attribute representation;
[0083]In this step, using the original feature domain sample data, by optimizing the following sparse coding model, the transformation relationship from visual features to manually defined attribute representations is obtained. Further, the sparse coding model in step S1 is:
[0084]
[0085] Among them, F s Represents the visual feature set of the original feature domain image sample....
Embodiment 3
[0110] In the present embodiment, the inspection data to the system in the embodiment 1 and the method in the embodiment 2 are also provided, specifically, select aPY, AwA2 reference database, wherein, the data statistics of the zero sample recognition database in the aPY, AwA2 database are as follows 1:
[0111] Table 1 Statistics of the current benchmark aPY and AwA2 zero-sample recognition databases
[0112]
[0113] Then, select existing several zero-sample methods and compare the accuracy of the method in the present invention on the benchmark zero-sample recognition database. The existing zero-sample methods for selection include: the zero-sample method proposed by M. Method CONSE; the zero-sample method LATEM proposed by Y.Xian et al. in 2016, and the zero-sample method DLFZRL proposed by Bin Tong et al. in 2019. The final accuracy is shown in Table 2 below:
[0114] Table 2 Accuracy of different part recognition methods on the benchmark zero-sample recognition data...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com