Method for judging alpine meadow degradation degree based on root-soil ratio
A technology based on the degree of degradation and root soil, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of lack of grassland type-specific methods, and achieve the effects of promoting sustainable development, improving grassland utilization rate and grassland restoration efficiency, and reducing restoration costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for judging the degradation degree of alpine meadow based on root-to-soil ratio, comprising the following steps:
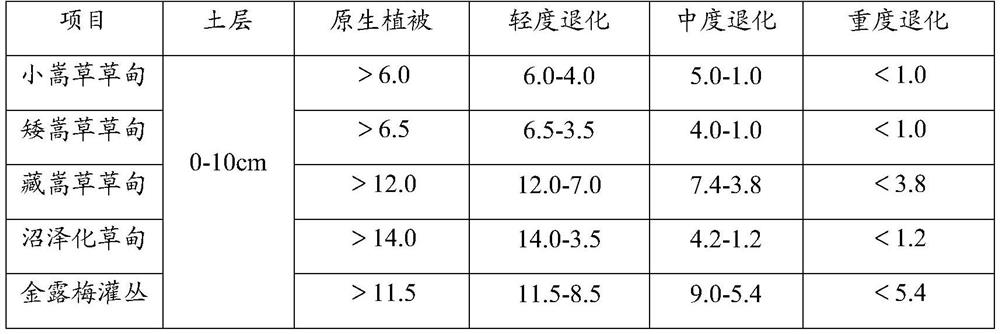
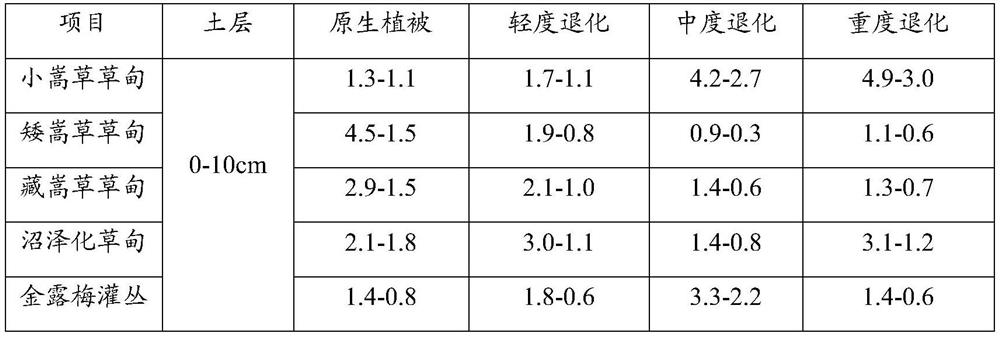
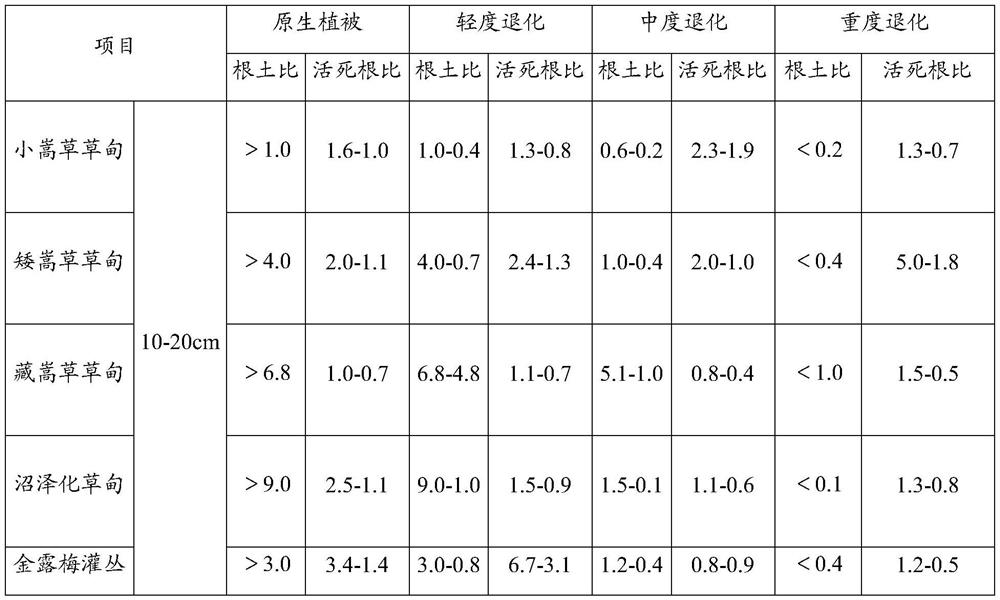
[0034] Step 1. Collect the soil samples that need to be measured. The measured points are required to be evenly distributed. The aboveground vegetation is representative in the area, and the sampling points are not less than 5. The larger the sample size, the higher the representativeness;
[0035] Among them, representative means that its plant community status is consistent with the overall area, such as the coverage and height of the plant community at the sampling point area are not significantly lower or higher than the overall status of the area (below or higher than 10% of the overall status of the area), The number of plant species shall not be less than 80% of the region as a whole.
[0036] When collecting soil samples, it should be noted that the soil samples are all from the same depth range, and the soil sample volume is not less than ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The root-to-soil ratio was used to determine the alpine meadow degradation gradient, which was verified in Zoige alpine swamp meadow with different degradation gradients in August 2018. The verification method is as follows:
[0060] 1. Determine the degradation gradient of swamp meadows in advance through the grading indicators of natural grassland degradation, desertification, and salinization (GB 19377-2003). It is determined that the sampling points contain two degraded gradients, original and moderate.
[0061] 2. Select a more representative community area to collect soil and root mixed samples. The samples are collected using the soil drill method (inner diameter 5cm), and the samples are collected at 0-10cm and 10-20cm respectively. 10 replicates per degradation gradient.
[0062] 3. Bring the mixed sample back to the laboratory, and through the combination of manual selection and sieving, the soil and root system are separated, and the live roots and dead roo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com