Obtaining method and application of SNP related to milk buffalo milk production traits
A technology of milk buffaloes and traits, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial determination/inspection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: Buffalo Genotyping
[0046] A total of 309 Mediterranean buffalo individuals were used for simplified genome sequencing analysis. The GATK4 software package was used for SNP typing, and the reference genome was the Mediterranean buffalo genome ((UOA_WB_1). The plink software was used for SNP quality control, and the standard was: SNP detection rate -6 . In addition, chromosomally unknown or duplicated SNPs were also removed. After quality control, a total of 274 individuals and 142326 SNPs were used for subsequent analysis.
[0047] Result analysis:
[0048] Table 1 SNP distribution statistics of buffalo based on simplified genome sequencing
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] It can be seen from Table 1 that a total of 142,326 SNPs were detected based on the simplified genome sequencing technology, covering the size of the buffalo genome of about 2.62Gb. The number of SNPs per chromosome ranged from 2661 to 10976. The average density of SNPs is one SNP per ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Calculation of regression breeding values for milk production traits
[0053] 1) Calculate the estimated breeding value (EBV) formula of each individual milk production trait according to the animal model with the Asreml-R4 software package as follows:
[0054] the y ijklmn =u+Herd i +Year j +Season k +Parity l +Age m +a n +e ijklmn
[0055] Among them, y ijklmn is the observed value of phenotype; u is the overall mean; Herd i is the field fixed effect (4 levels); Year j Year fixed effect (≤2007 and 2008-2016); Season k is the seasonal fixed effect (2 levels); Parity l Parity effect (1 to 7 and≥8); Age m is the fixed effect of calving age; a n is the individual additive effect; e ijklmn is a random error;
[0056] 2) For the calculation of DEBV for each individual milk production trait, first use R language to calculate the weighted value. The formula is (Garrick et al.2009) where c is assumed to be 0.4 (Saatchi et al.2014); h 2 is the he...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3: Genome-wide association (GWAS) analysis of milk production traits
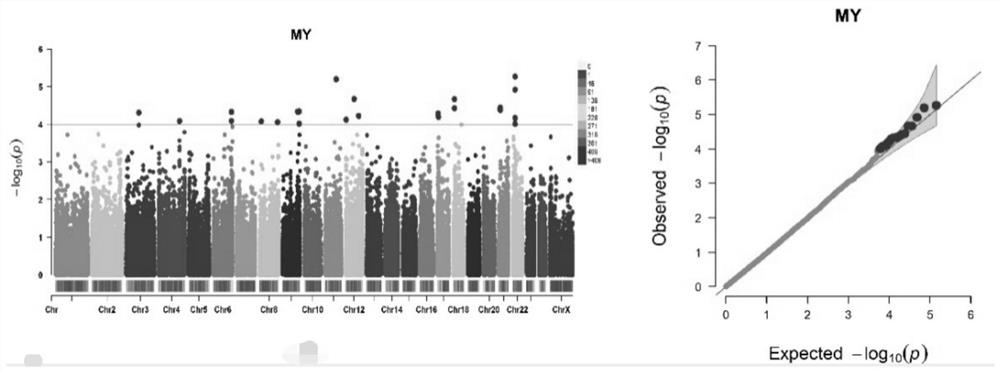
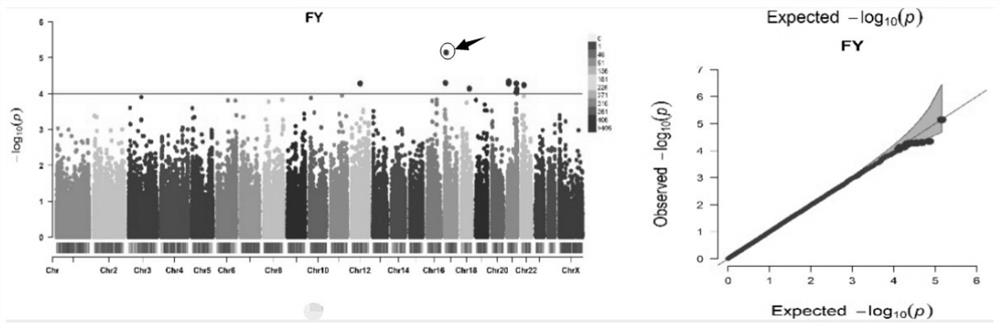
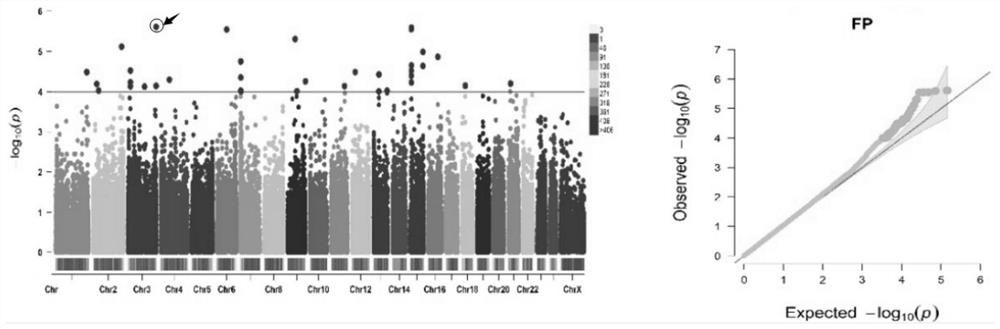
[0058] The association analysis between SNPs and milk production traits was carried out using the FarmCPU method in the rMVP R package. The threshold for significant SNP screening is P-4 . The results are shown in the table below:
[0059] Table 2 GWAS analysis results of buffalo milk production traits
[0060]
[0061]
[0062]
[0063]
[0064] Remarks: Significant marker level is P value-4 .
[0065] It can be seen from Table 2 that a total of 128 SNPs passed the selection threshold and can be regarded as SNPs significantly related to milk production traits. Among them, there are 24 SNPs related to milk production, and 11, 42, 22 and 29 SNPs related to milk fat amount, milk fat percentage, milk protein amount and milk protein percentage, respectively. The important ones are snp16586372 (p-value 5.39E-06 this locus is on chromosome 22), snp6752954 (p-value 7.16E-06 this locu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com