Equipment, kits and analysis systems for simultaneous prenatal screening of chromosomal and single gene diseases
A prenatal screening and equipment technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, genomics, sequence analysis, etc., can solve the problem of low hybridization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
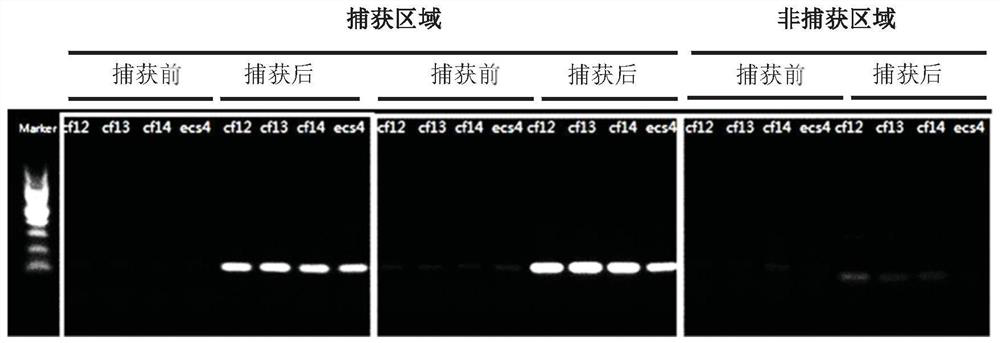
[0375] Example 1: Targeting probe captures DNA
[0376] a. Plasma separation and cell-free DNA extraction:
[0377] Place the blood collection tube in a centrifuge and centrifuge at 1600g for 10 minutes for EDTA anticoagulant tubes and 15 minutes for Streck tubes. After the centrifugation is completed, slowly draw the supernatant from top to bottom into a 5mL transfer tube, and centrifuge again at 16000g for 10min. The purpose of the second centrifugation of the plasma is to remove all cellular pollutants. Use TIANGEN Magnetic Bead Method Large Volume Free Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit for free DNA extraction, including proteinase K treatment of plasma samples, 60°C water bath for 20 minutes, add MagAttract Suspension E, Buffer GHH and Carrier RNA, vortex and mix for 30 seconds, and then incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes. Magnetic beads adsorb nucleic acids. Use the washing solution Buffer PWG, and vortex to mix well to fully suspend the magnetic beads. Finally, the...
Embodiment 2
[0455] Example 2: Sequencing
[0456] Sequencing was performed using the Huada high-throughput sequencing platform MGISEQ-2000 and supporting reagents high-throughput sequencing kit (PE100). The principle of sequencing is to use combined probe-anchored aggregation technology (cPAS), by polymerizing DNA molecular anchors and fluorescent probes on DNA nanoballs (DNB), and using a high-resolution imaging system to collect optical signals, optical signals After digital processing, high-quality and high-accuracy sample sequence information is obtained. The post-capture amplified library needs to go through the following steps to complete the sequencing output fastq file, library quantification, circularization, DNB preparation, high-throughput sequencing, and data splitting and comparison:
[0457] 1. Carry out the quality control of the concentration and fragment length. The concentration is determined using the invitrogen Qubit Fluorometer and the supporting reagent Qubit 1X dsD...
Embodiment 3
[0466] Example 3: Oligonucleotide probe synergistic allelic target enrichment method improves the capture uniformity of alleles in the target region
[0467] We employed the oligonucleotide probe cooperative allelic target enrichment method (COATE) to reduce the hybridization annealing temperature difference (ΔTm) between the probe and the target including the reference and mutant alleles. Different from traditional probe design, the probe design method provided by the present invention does not require the designed probes to be complementary to the reference genome sequence or mutant sequence, and these probes may or may not be complementary to the reference or mutant allele , it is only required that the ΔTm of the probe to the reference gene sequence (wild type) and the mutant sequence (mutant type) in the capture region be the smallest.
[0468] The following is an example of SNP capture probe design: for the SNP site rs7321990 (chr13: 20257054-20257054) on chromosome 13, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com