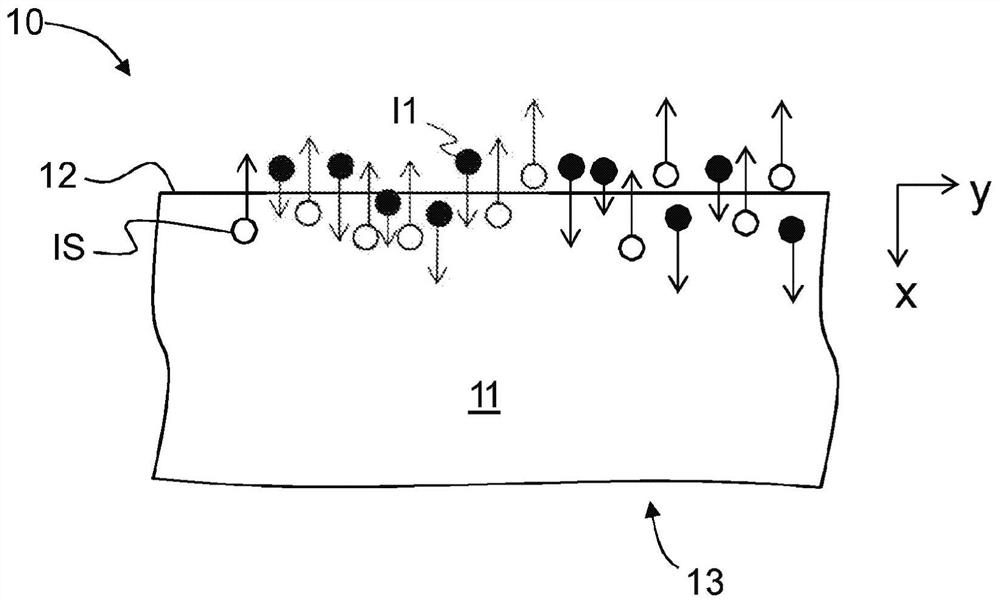
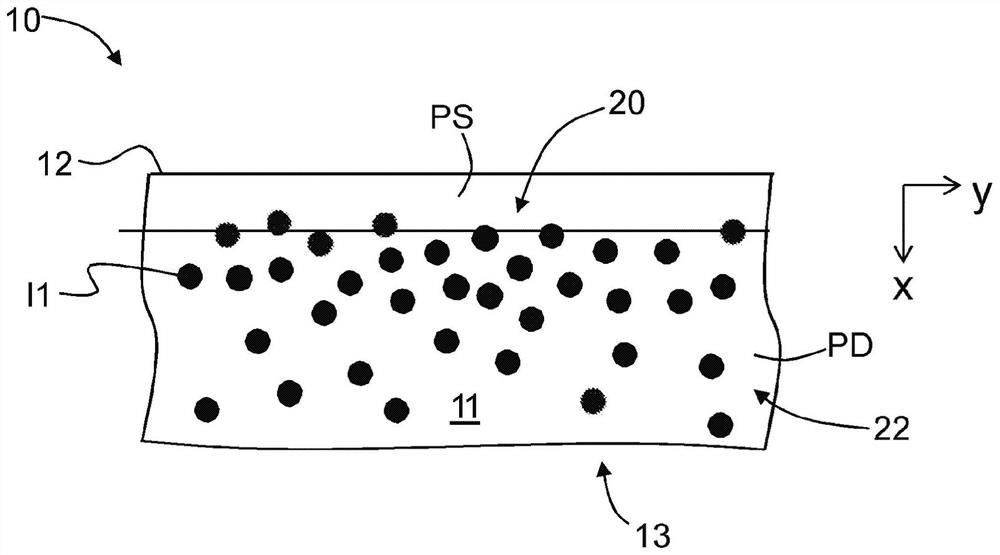
Prism coupling methods of characterizing stress in glass-based ion-exchanged articles having problematic refractive index profiles
A technology of refractive index distribution and ion exchange, which is applied in the field of glass-based ion exchange products, can solve problems such as blurred resolution of the prism coupler measurement system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] Various embodiments of the present disclosure are described in detail below, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Wherever possible, the same or similar reference numbers and symbols will be used throughout the drawings to refer to the same or similar parts. The drawings are not necessarily to scale and those skilled in the art will appreciate that the drawings are simplified to show key aspects of the invention.
[0031] The acronym IOX can mean "ion exchanged" or "ion exchanged", depending on the context of the discussion.
[0032] The term "glass-based" is used herein to describe a material, article, matrix, substrate, etc., which means that the material, article, matrix, material, substrate, etc. may comprise or consist of glass or glass-ceramic.
[0033] The compressive stress distribution of the pristine 10X article is denoted CS(x) and may also be referred to herein simply as the stress distribution. The surface compressive stress or ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com