Access control method, client and server
An access control and client-side technology, applied in the field of network security, can solve the problems of complex operation and setting learning costs, users cannot log in normally, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing learning costs, high use efficiency, and high positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
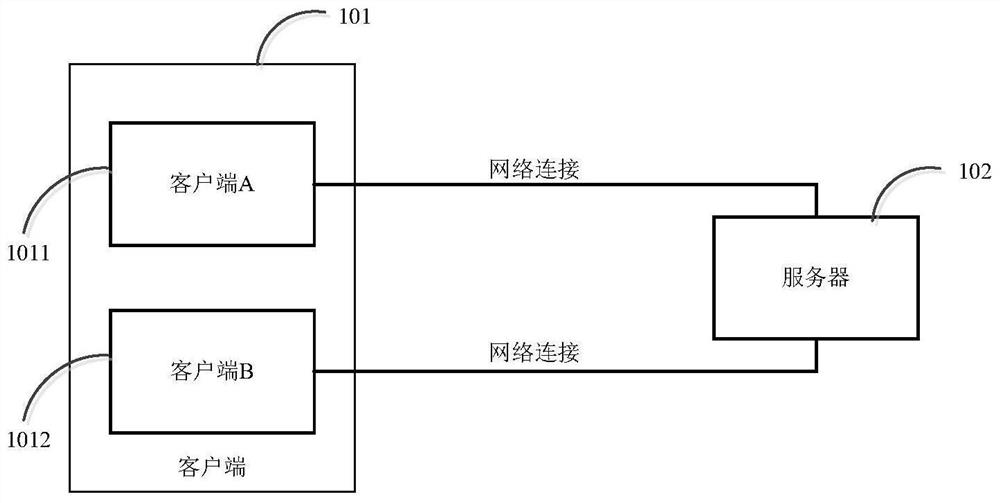
[0051] see figure 1 , is a schematic diagram of a connection between a client and a server provided in the embodiment of this application.
[0052] The client 101 includes a client terminal A (1011) and a client terminal B (1012). The client A and the client B are connected to the server 102 through a network to realize mutual communication.
[0053] It should be noted that the geographical location of the client A and the client B are the same, so that the actual geographic location information of the user can be obtained through the client A.
[0054] Preferably, client A runs on a mobile device, and can scan the login QR code on client B through the camera.
[0055] Preferably, the client B runs on a personal computer PC. When the user is going to log in to the server, the login preparation is first made on client B. If the client B finds that the user has already logged in, it will prompt that the user has logged in, and no further login operation through the client A i...
Embodiment 2
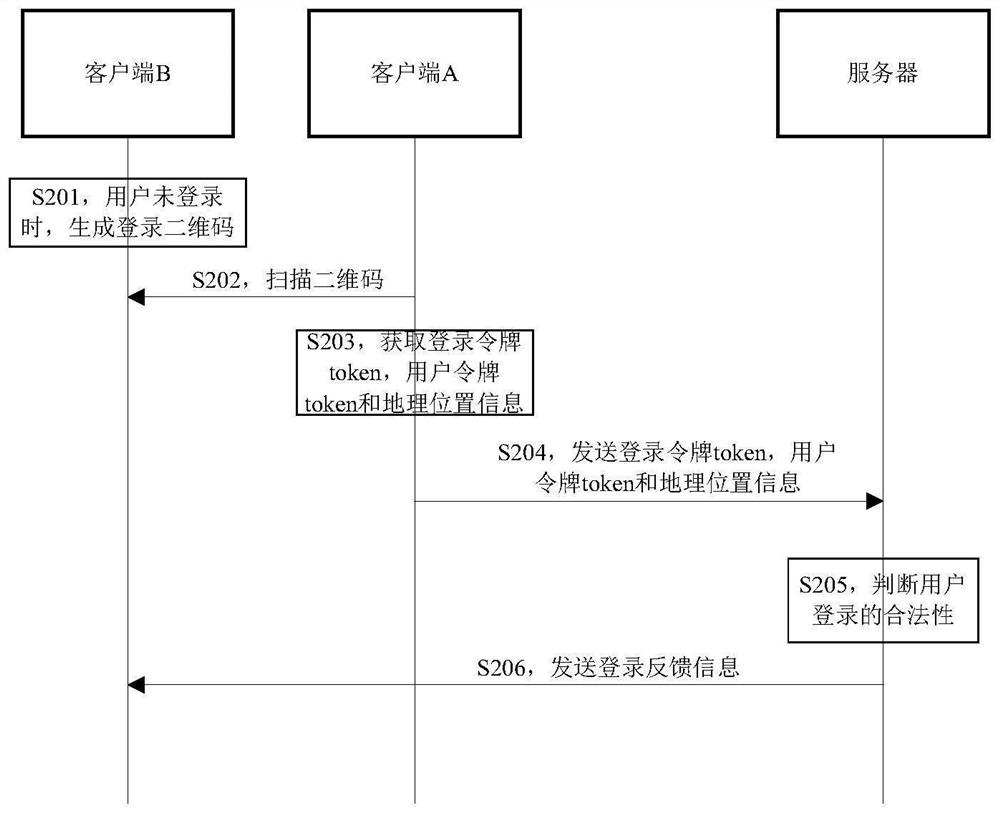
[0060] like figure 2 , this embodiment also provides an access control method, the method comprising:
[0061] S201. When the client B determines that the user is not logged in, generate a login QR code of the user.
[0062] When the user is about to log in to the server, he operates through the client B, and the client B checks the user's login status, and if it finds that the user is not logged in, it generates the user's login QR code. If client B finds that the user has logged in, the user can normally access the server through client B.
[0063] It should be noted that the client B checks the login status of the user, which may be specifically determined based on the login information of the user recorded locally. Preferably, it is determined that the user has logged in when the time of the user's operation is not more than time N from the last log-in time of the user. If time N is exceeded, client B logs out the user and records that the user is not logged in.
[00...
Embodiment 3
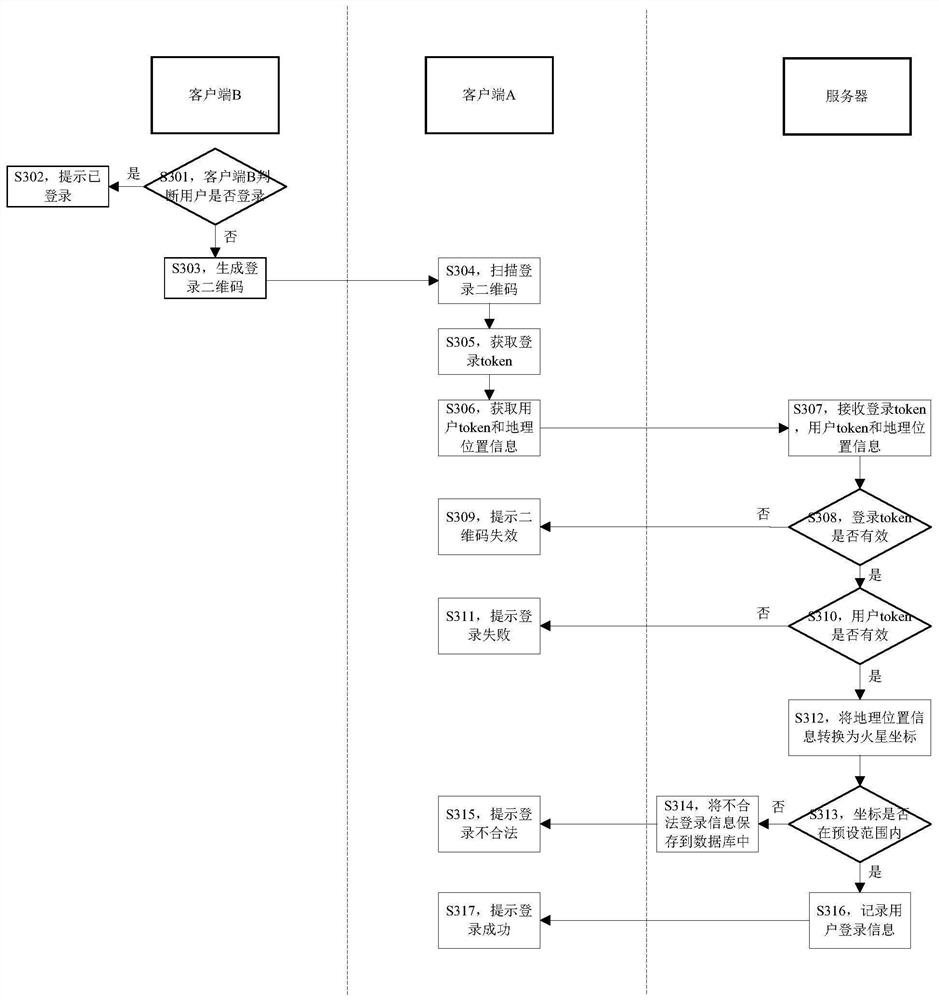
[0080] like image 3 As shown, this embodiment also provides an access control method, which specifically includes:
[0081] S301, client B judges whether the user is logged in, if the user has logged in, execute S302, otherwise execute S303.
[0082] The method for judging whether the user logs in in this step is the same as that in Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here.
[0083] S302, the client B prompts that the user has logged in.
[0084] When client B judges that the user has logged in, it allows the user to access the server normally and use the corresponding service.
[0085] S303, generating a login QR code of the user.
[0086] Client B generates the user's login QR code, and prompts the user to scan the QR code through client A to log in.
[0087] S304, the client A scans the login QR code.
[0088] The method for scanning the two-dimensional code in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here.
[0089] S305. Clien...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com