Laser radar auxiliary control method based on impeller equivalent wind speed correction
A technology equivalent to wind speed and laser radar, which is applied in the control of wind turbines, monitoring of wind turbines, engine control, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate time and achieve the effect of reducing numerical deviations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0065] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment:
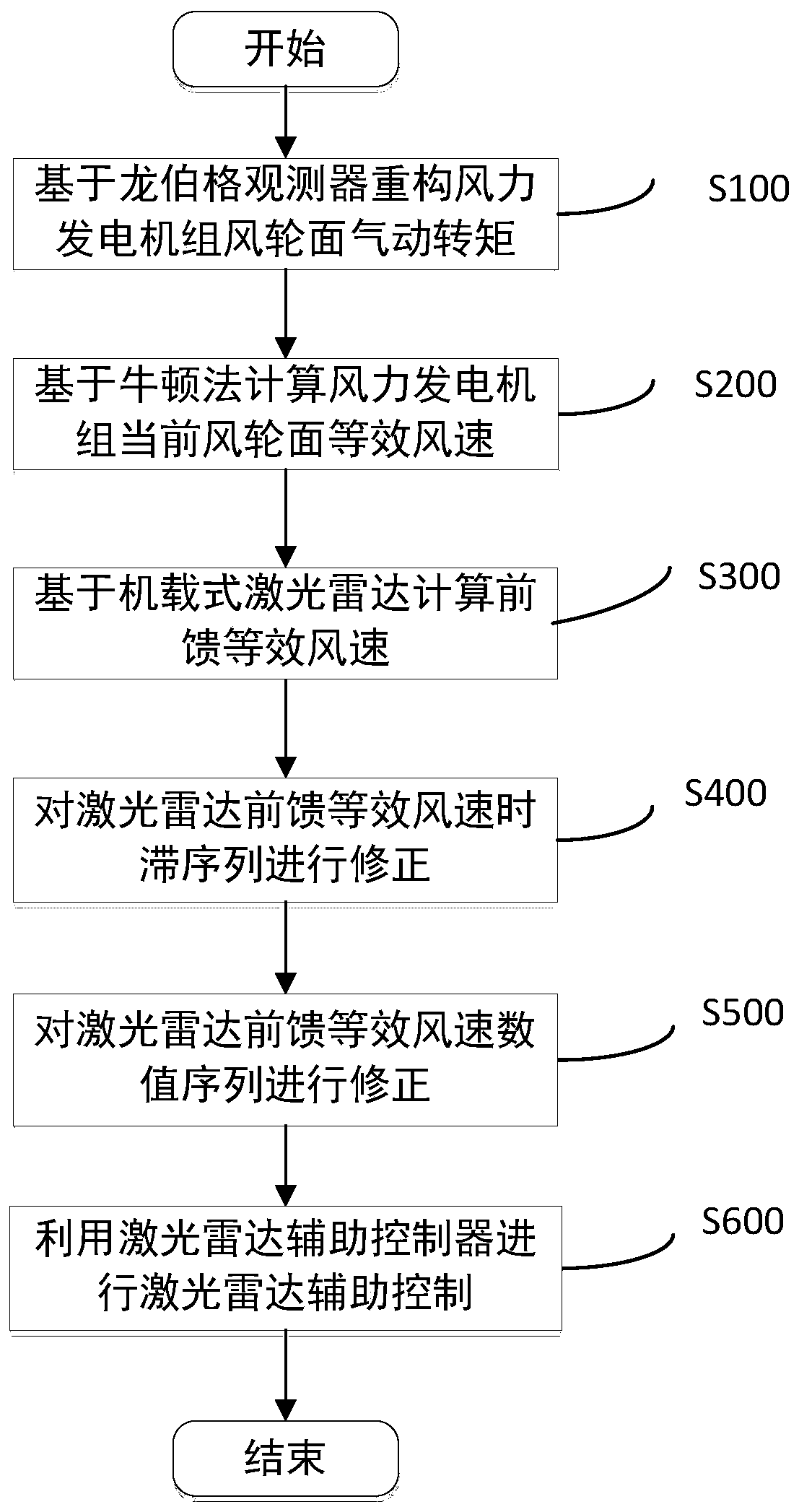
[0066] like figure 1 The illustrated embodiment is a lidar-assisted control method based on impeller equivalent wind speed correction, including the following steps:
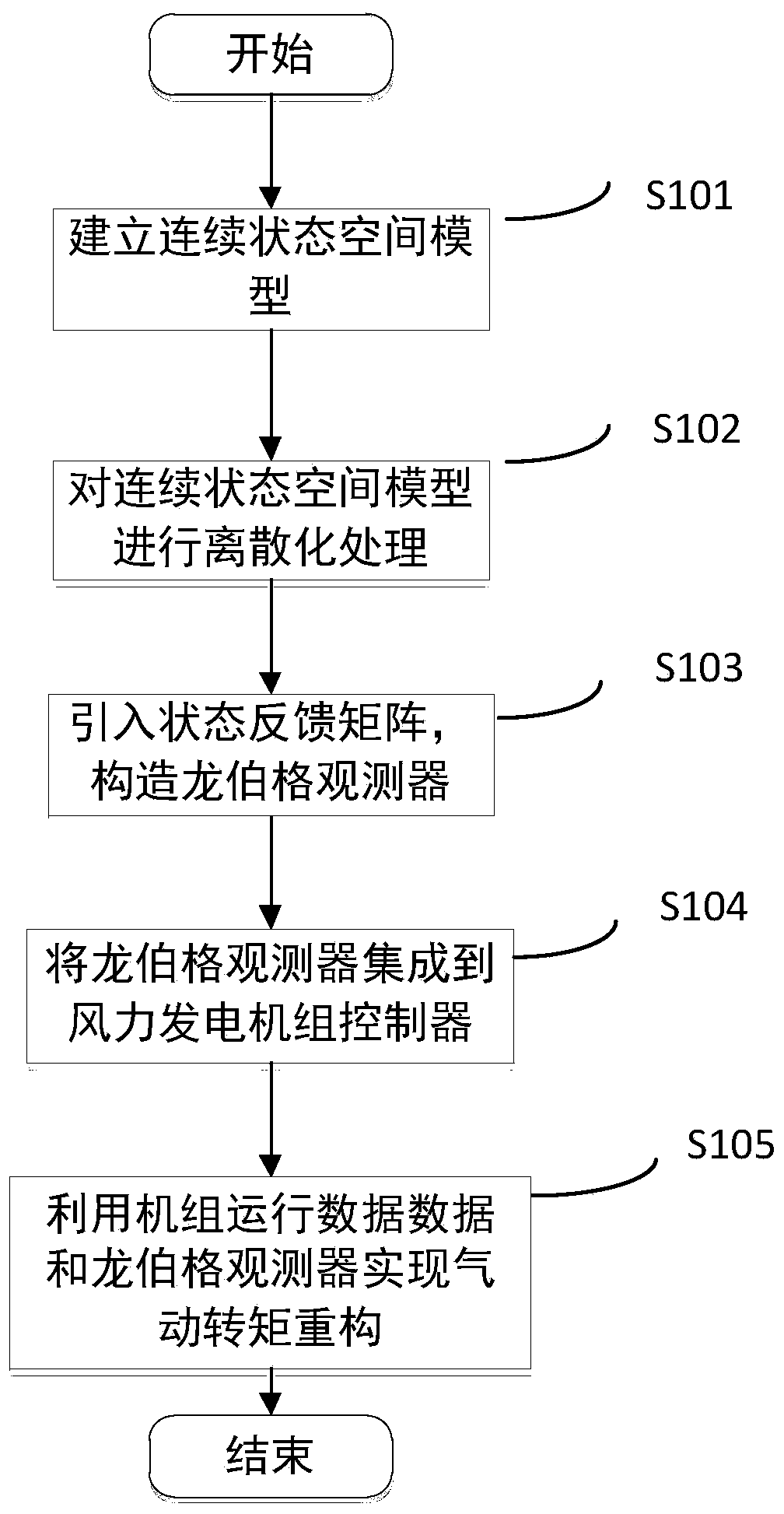
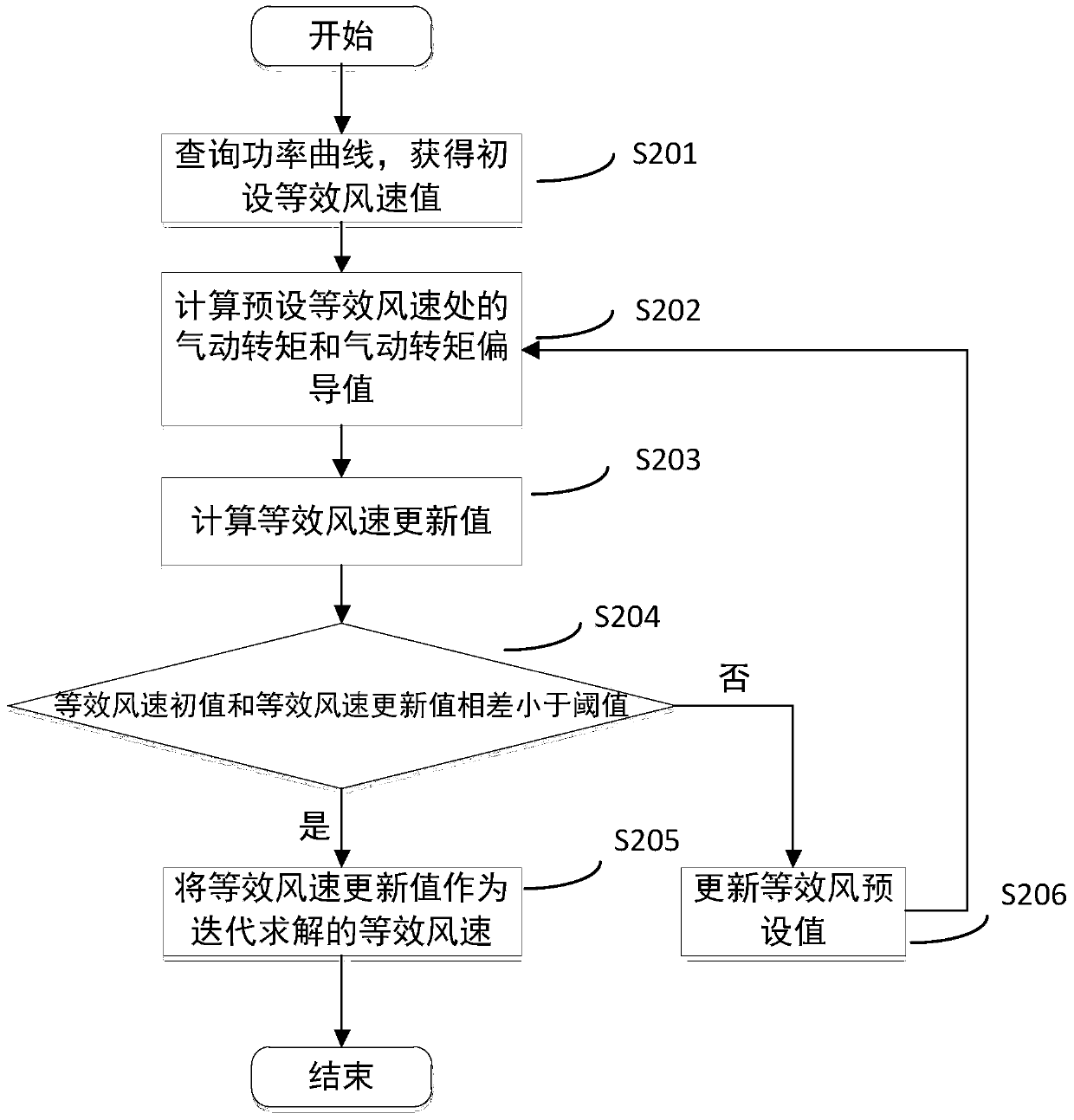
[0067] Step S100, such as figure 2 As shown, the aerodynamic torque of the wind turbine rotor surface is reconstructed based on the Lomberg observer;
[0068] Step S101, based on the double-mass model, regards the aerodynamic torque as the equivalent disturbance, selects the design parameters and operating parameters of the wind turbine, and takes the wind rotor speed ω r , generator speed ω g , low-speed shaft torque T ls is the state variable of the observer, and the generator electromagnetic torque T e As an input quantity, a state-space model of the wind turbine is established
[0069]
[0070] In the formula, C d is the low-speed shaft stiffness, k d is low-speed shaft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com