Composition for ameliorating human skin cell damage caused by ultraviolet rays containing hydrangea chinensis extract
A technology of skin cells and extracts, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, skin care preparations, applications, etc., can solve problems such as the mechanism research of human epidermal cells and dermal cells, to prevent skin aging and inhibit secretion , increase the effect of secretion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Preparation of extracts utilizing ethanol
[0036]The hydrangea crassa extract contained in the composition of the present invention is prepared by the following procedure. First, buy a one-year-old hydrangea that grows on Jeju Island, wash it with distilled water, and dry it completely in a cool place without sunlight until there is no change in weight. After that, the completely dried dry product was pulverized with a homogenizer to obtain the pulverized product, and then 50 g of the pulverized product was added after mixing ethanol:distilled water at a weight ratio of 7:3 to prepare 400 g of each extraction solvent. At this time, the mixing ratio of the pulverized product and the extraction solvent was 1:8 by weight. Next, the extraction solvent mixed with the pulverized product was put into a shaking constant temperature water tank, and stirred and extracted at 50° C. for 2 hours. The substances obtained by extraction were extracted with Whatman (No 2....
experiment example 1
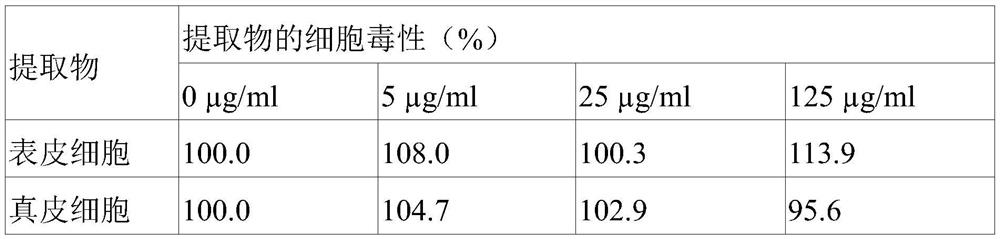
[0037] Experimental example 1: Cytotoxicity evaluation of the ethanol extract of Hydrangea coarse tooth
[0038] It was determined whether the extract obtained in Example 1 above had cytotoxicity to skin cells. In this experiment, HaCaT Keratinocytes were used as keratinocytes, and HS68 fibroblasts were used as dermal cells. In order to confirm whether there is cytotoxicity, 1.0X10 4 The individual cells of the number of cells were dispensed on a 96-well plate, adhered for 24 hours, and stabilized, and then treated with ethanol extracts of Hydrangea dentata at concentrations of 0, 5, 25, and 125 ppm (μg / ml). After 24 hours, the degree of cell viability was determined by MTT assay. The MTT assay is a method for measuring the amount of formazan formed from MTT reduced by the mitochondria of surviving cells. Each cell was treated with 50 µl of a 5 mg / ml MTT solution, and after culturing for 4 hours, the solution was completely removed, and the plate dissolved in dimethyl sul...
experiment example 2
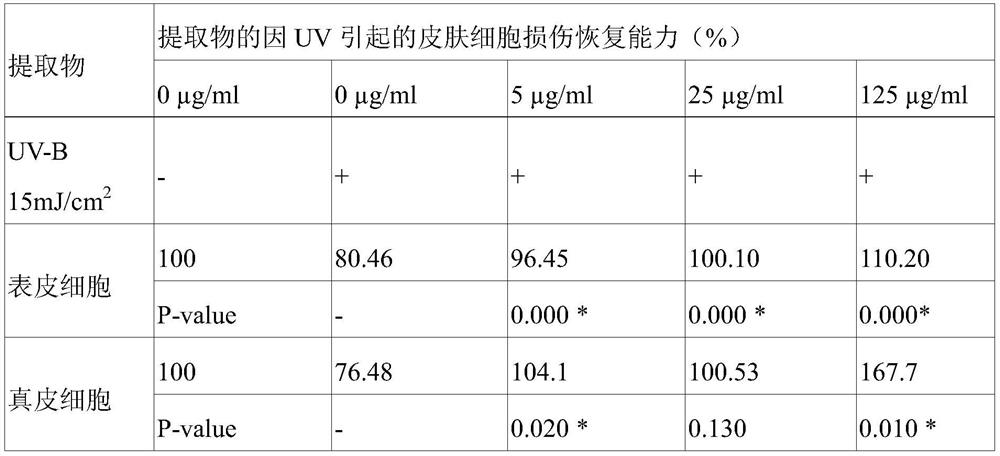
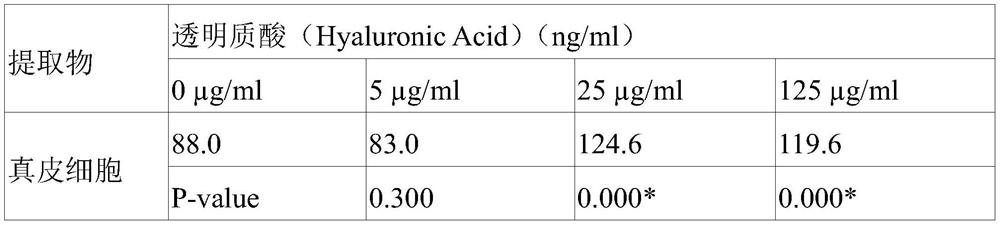
[0042] Experimental example 2: Evaluation of recovery from cell damage caused by UV-B of the ethanol extract of Hydrangea japonica
[0043] With respect to the extract obtained in Example 1 above, it was determined whether the damage of skin cells exposed to UV-B could be restored. In this experiment, HaCaT Keratinocyte was used as keratinocytes, and HS68fibroblast was used as dermal cells. In order to confirm whether there is a cell recovery effect, 1.0X10 4 Each cell of the cell number was dispensed on a 96-well plate, adhered for 24 hours, and after stabilization, 15mJ / cm 2 UV-B irradiation. Afterwards, the medium was replaced with the medium treated with the ethanol extract of Hydrangea crachydenta at concentrations of 0, 5, 25, and 125 ppm (μg / ml), and the degree of cell survival was determined by MTT assay. The MTT assay is a method for measuring the amount of formazan formed from MTT reduced by the mitochondria of surviving cells. More specifically, each cell was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com