Molten salt impurity removal method suitable for chemical tempering production and method for improving glass strength
A technology of chemical tempering and molten salt, which is applied in the purification of alkali metal nitrate, etc., and can solve problems such as unsatisfactory results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
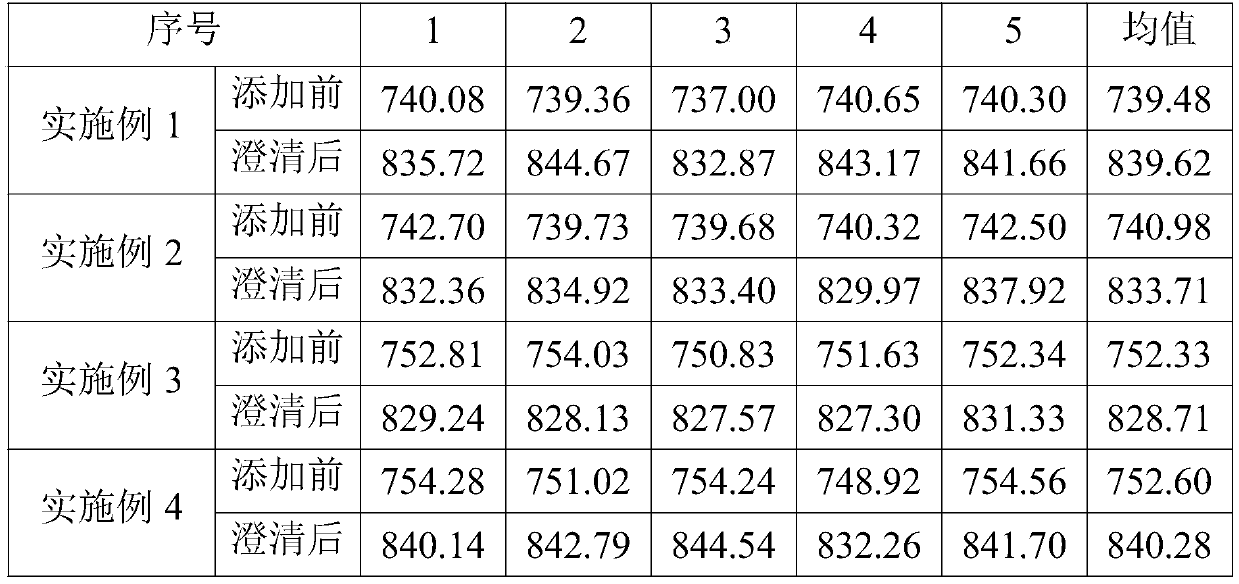
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for improving the strength of glass by chemical tempering, comprising the following steps:
[0047] Step 1) Use a stress tester to measure and record the stress value of each batch of tempered glass, if it is less than 770MPa, stop the tempering operation.
[0048] Step 2) adding 0.5% KOH to the mass percentage of the molten salt to adjust the pH value of the molten salt to 9.
[0049] Step 3) adding 0.5% potassium carbonate and 0.5% potassium phosphate accounting for the mass percentage of the molten salt, and fully stirring at the same time.
[0050] Step 4) adding 0.5% potassium pyroantimonate solution accounting for the mass percentage of the molten salt, and fully stirring at the same time.
[0051] Step 5) adding 1% silicic acid to the mass percentage of the molten salt to adjust the pH value of the molten salt to 7.
[0052] Step 6) Adding 0.5% aluminum oxide based on the mass percentage of the molten salt.
[0053] Step 7) Clarify for 4h.
[0054] S...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A method for improving the strength of glass by chemical tempering, comprising the following steps:
[0057] Step 1) Use a stress tester to measure and record the stress value of each furnace of tempered glass, if it is less than 770MPa, stop the tempering operation.
[0058] Step 2) adding 0.1% KOH to the mass percentage of the molten salt to adjust the pH value of the molten salt to 9.
[0059] Step 3) adding 0.5% potassium carbonate and 0.5% potassium phosphate accounting for the mass percentage of the molten salt, and fully stirring at the same time.
[0060] Step 4) adding 0.5% potassium pyroantimonate to the mass percentage of the molten salt, and fully stirring at the same time.
[0061] Step 5) adding 2% silicic acid to the mass percentage of the molten salt to adjust the pH value of the molten salt to 7.
[0062] Step 6) Adding 0.5% aluminum oxide based on the mass percentage of the molten salt.
[0063] Step 7) Clarify for 4h.
[0064] Step 8) Tempering op...
Embodiment 3
[0066] A method for improving the strength of glass by chemical tempering, comprising the following steps:
[0067] Step 1) Use a stress tester to measure and record the stress value of each batch of tempered glass, if it is less than 770MPa, stop the tempering operation.
[0068] Step 2) adding 0.5% KOH to the mass percentage of the molten salt to adjust the pH value of the molten salt to 13.
[0069] Step 3) adding 1% potassium carbonate and 1% potassium phosphate accounting for the mass percentage of the molten salt, while fully stirring.
[0070] Step 4) adding 0.5% potassium pyroantimonate to the mass percentage of the molten salt, and fully stirring at the same time.
[0071] Step 5) adding 1% silicic acid to the mass percentage of the molten salt to adjust the pH value of the molten salt to 7.
[0072] Step 6) Adding 0.5% aluminum oxide based on the mass percentage of the molten salt.
[0073] Step 7) Clarify for 4h.
[0074] Step 8) Tempering operation, using a str...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com