Spatial semantic similarity calculation method based on sliding window sampling
A technology of semantic similarity and sliding window, which is applied in computing, instrumentation, text database query, etc., and can solve problems such as insufficient accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
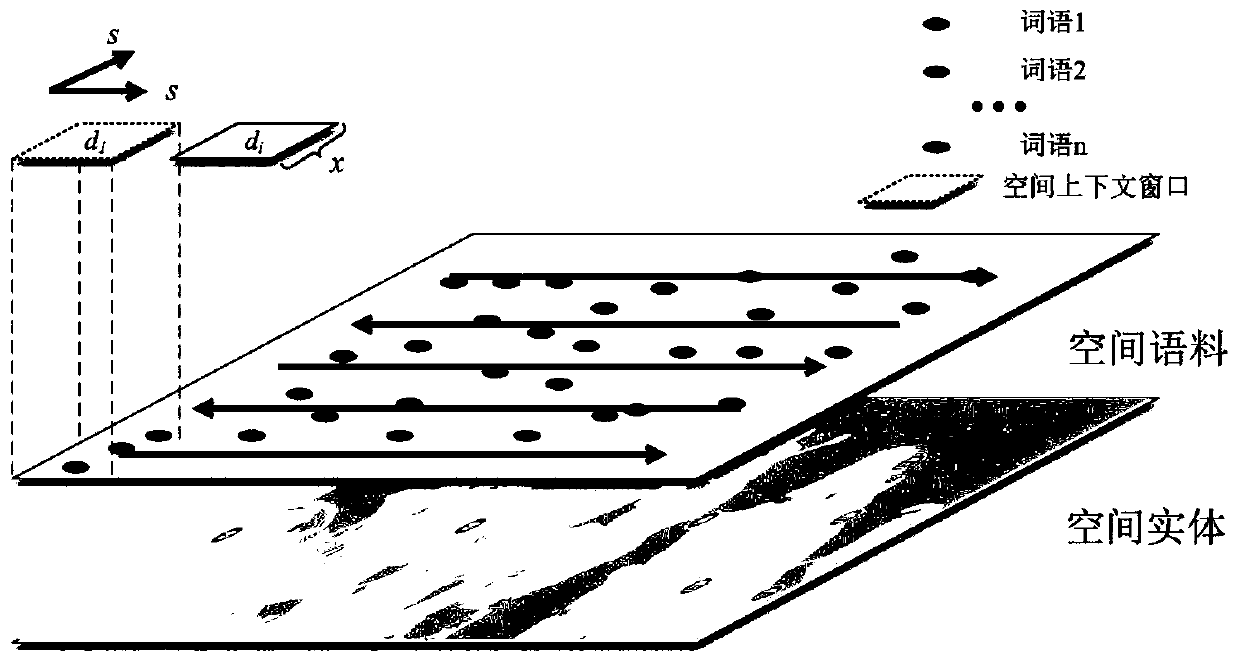
[0039] The present invention aims at the technical problem that the method in the prior art has insufficient accuracy when processing information containing spatial relationship information and subject fuzzy, and provides a spatial semantic similarity calculation method based on crowdsourced geographic big data and sliding window sampling, Mining the spatial semantic similarity relationship between words, constructing a model that can measure the spatial semantic similarity of words, as a new perspective to understand human natural language by integrating human spatial thinking and spatial perception, the traditional natural semantic similarity model is carried out It is an effective supplement to effectively improve the accuracy of intelligent geographic information retrieval and recommendation systems.
[0040] In order to achieve the above object, the main idea of the present invention is as follows:
[0041]Based on the spatial semantic similarity calculation method of c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com