A biobasic flame retardant epoxy resin precursor based on natural flavonoids and its preparation method and application
A technology of flavonoids and epoxy resins, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of harsh curing conditions, complicated preparation process, etc., and achieve the effects of simple operation, simple process and saving oil resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] The invention discloses a preparation method of a biobasic flame retardant epoxy resin precursor based on natural flavonoids, comprising: subjecting natural flavonoids, epichlorohydrin and potassium carbonate to glycidol under the action of a phase transfer catalyst Etherification reaction to prepare biobasic flame retardant epoxy resin precursor.
[0039] The invention mixes and heats natural flavonoids, epichlorohydrin, alkali and a phase transfer catalyst to carry out glycidyl etherification reaction, and then after post-treatment, the precursor of the biobasic flame-retardant epoxy resin can be prepared.
[0040] All the raw materials of the present invention have no special limitation on their sources, they can be purchased in the market. Wherein, the natural flavonoids are myricetin (Myricetin, CAS number: 529-44-2), quercetin (Quercetin, CAS number: 117-39-5), kaempferol (Kaempferol, CAS number: 520- 18-3), luteolin (Luteolin, CAS number: 491-70-3), apigenin (Ap...
Embodiment 1
[0056] React 1mol genistein and 6mol epichlorohydrin in the presence of 10mol potassium carbonate and 0.2mol tetrabutylammonium bromide at 80°C for 24 hours, then filter and vacuum rotary evaporation to remove excess epichlorohydrin propane, washed with water and dried to obtain glycidyl ether genistein.
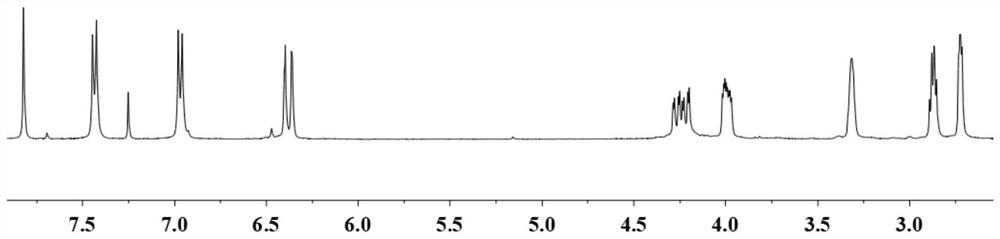
[0057] Calculate the productive rate of product to be 89%, its proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum 1 H-NMR such as figure 1 As shown, each peak on the figure is in one-to-one correspondence with the hydrogen atoms on the glycidyl ether genistein structure.
[0058] Mix the obtained glycidyl ether genistein with the curing agent DDM (diaminodiphenylmethane) according to the molar ratio of epoxy and NH one to one, then heat and cure in a blast oven, and finally completely cure at 180°C , to obtain glycidyl ether genistein-DDM epoxy resin.
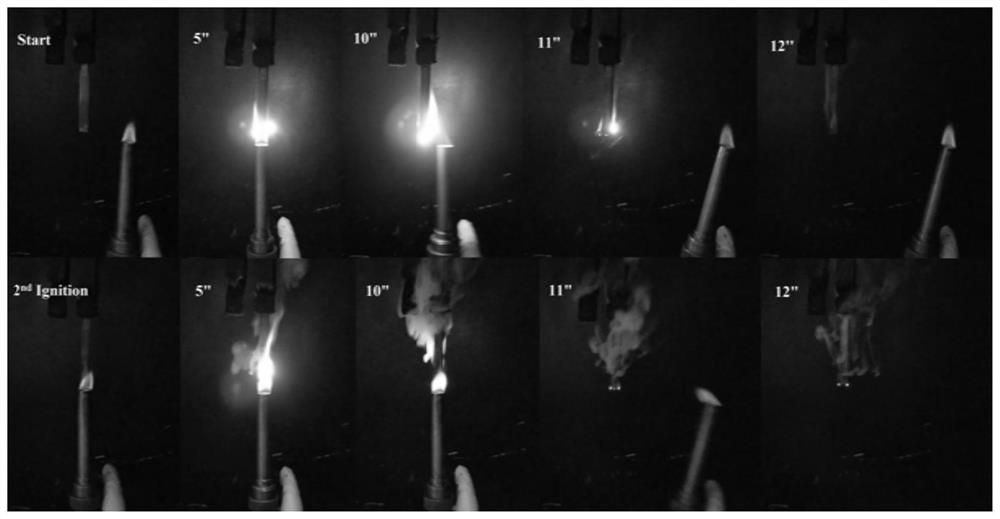
[0059] The glass transition of the cured product obtained by testing and curing is 223° C., and the bending strength is 141 Mpa,...
Embodiment 2
[0061] React 1 mol of chrysin and 5 mol of epichlorohydrin in the presence of 15 mol of potassium carbonate and 0.3 mol of tetrabutylammonium bromide at 90°C for 18 hours, then remove excess epichlorohydrin by filtration and rotary evaporation under reduced pressure , washed with water and dried to obtain glycidyl ether chrysin with a yield of 78%.
[0062] Mix the obtained glycidyl ether chrysin and the curing agent DDM (diaminodiphenylmethane) according to the molar ratio of epoxy and NH one to one, then heat and cure in a blast oven, and finally completely cure at 180°C. A glycidyl ether chrysin-DDM epoxy resin was obtained. The obtained cured product had a glass transition of 205° C., a bending strength of 131 MPa, and a flame retardancy level of V0.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com