Piece-orange-like structure composite fiber with controllable bond strength and its preparation process
A composite fiber, bonding strength technology, applied in fiber processing, textiles and papermaking, filament/thread forming, etc. Difficulty in precision strength and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
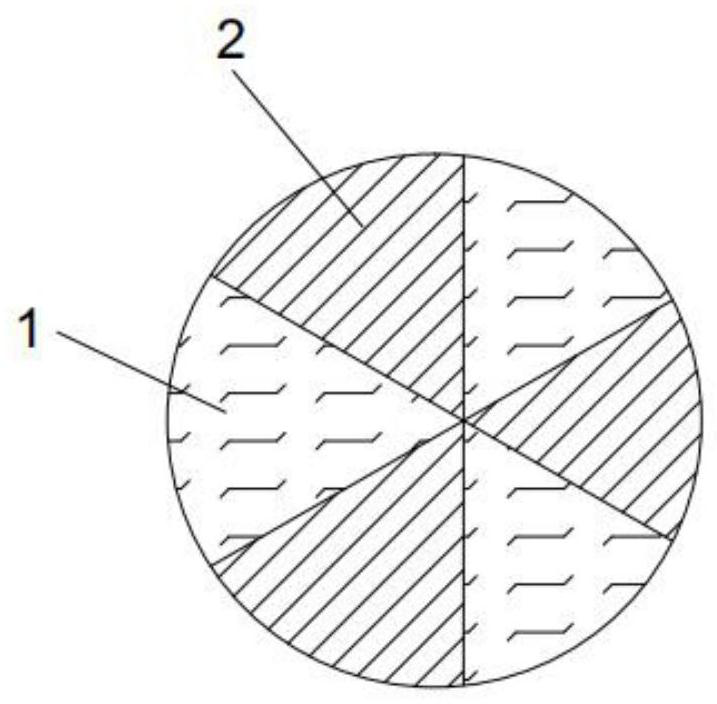
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, the composite fiber with a pierced-orange structure with controllable bond strength, the composite fiber is composed of high melting point high polymer 2 polypropylene (PP) with a melting point of 175 °C and low melting point high polymer 1 polyethylene with a melting point of 130 °C (PE) The cross section is set at intervals to form a hot-melt fiber with an asymmetric orange segment structure consisting of six segments of different sizes. Each orange segment is a high polymer, and 6 orange segments together form a circular structure. The ratio of the eccentricity in the cross-section of the composite fiber to the diameter of the composite fiber is the eccentricity ratio, and the eccentricity ratio of the composite fiber cross-section is 1. / 20, the fineness is 0.8D, and the ratio of the minimum and maximum orange segment area of polyethylene (PE) is 1:1.05.
[0030] The present invention also includes a process for preparing composite fibe...
Embodiment 2
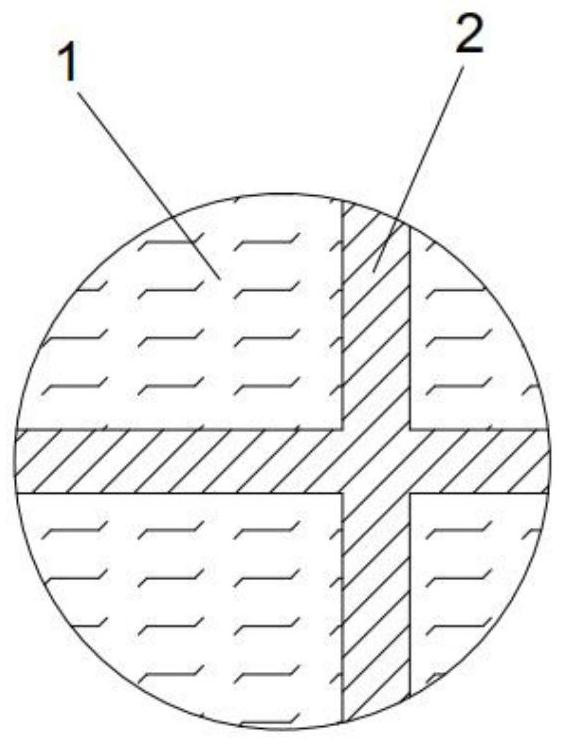
[0036] Such as figure 2 As shown, the composite fiber with a pierced-orange structure with controllable bond strength, the composite fiber is copolymerized by low-melting high polymer 1 polyamide (PA) with a melting point of 160°C and high-melting high polymer 2 with a melting point of 265°C The ester amine (COPA) cross interval is set, and the cross-section formed is a circular structure composed of 4 orange segments of different sizes and a cross-shaped skeleton. All the orange segments are polyamide (PA), and the cross-shaped skeleton is copolyesteramine (COPA). The ratio of the eccentricity in the cross-section of the composite fiber to the diameter of the composite fiber is the eccentricity ratio, and the eccentricity of the cross-section of the composite fiber is The ratio is 1 / 2, the denier is 100D, and the ratio of the minimum and maximum pie area of polyamide (PA) is 1:6.
[0037] The present invention also includes a process for preparing composite fibers with a ...
Embodiment 3
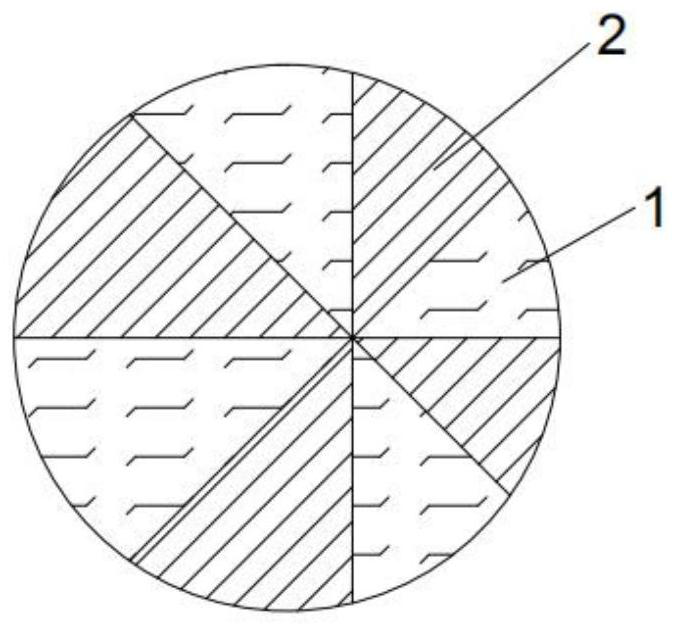
[0043] Such as image 3 As shown, the composite fiber with a pierced-orange structure with controllable bond strength, the composite fiber is copolymerized by the high-melting point high polymer 2 polyester (PET) with a melting point of 285 °C and the low-melting point high polymer 1 with a melting point of 160 °C Ester (COPET) is set at cross intervals to form a hot-melt fiber with an asymmetric orange segment structure whose cross section consists of 8 segments of different sizes. Each orange segment is a high polymer, and 8 orange segments together form a circular structure. The ratio of the eccentricity in the cross-section of the composite fiber to the diameter of the composite fiber is the eccentricity ratio, and the eccentricity ratio of the cross-section of the composite fiber is 1 / 10 , the denier is 50D, and the ratio of the minimum and maximum orange segment area of copolyester (COPET) is 1:3.
[0044] The present invention also includes a process for preparing co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com