Motion optimizing method for redundant degree-of-freedom robot
An optimization method and robot technology, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as poor optimization results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0156] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the configuration of a humanoid robot. This type of robot includes 7 movable joints, joint 1 to joint 7.
[0157] Such as figure 2 Shown is the kinematics construction method of the robot. In order to simplify the calculation process, both the base coordinate system and the first joint coordinate system are translated to the second joint; the tool coordinate system is represented by the seventh joint coordinate system, and it is translated to the sixth joint.
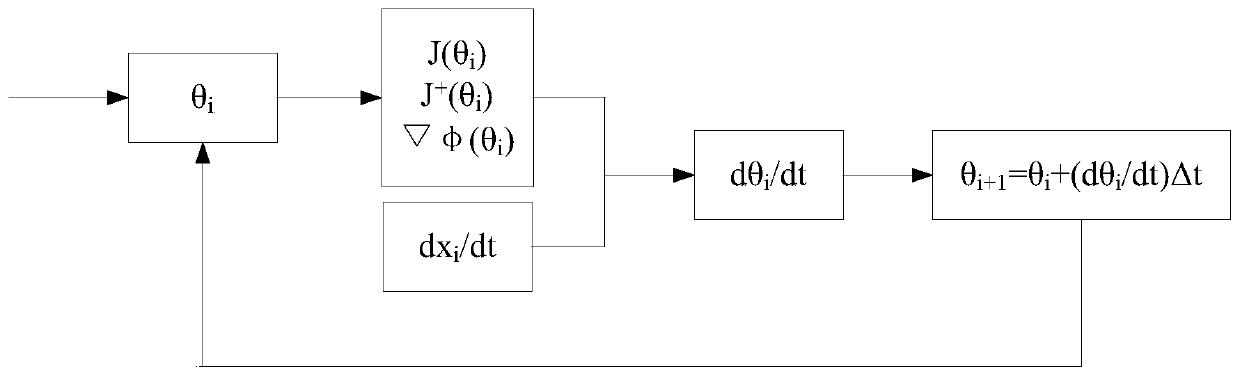
[0158] The general solution of the inverse Jacobian kinematics problem for redundant robots is:
[0159]
[0160] in, Indicates the joint space velocity, J is the Jacobian matrix, J + is the P-M pseudo-inverse matrix of the Jacobian matrix, y is an arbitrary vector, is the Cartesian space velocity of the robot, is the minimum norm solution, and defines the end motion of the robot; I is the identity matrix, (I-J + J) y is a homogeneous solution,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com