A device and method for improving the DNA detection performance of an optical addressable potential sensor using zno nanorods
A potentiometric sensor and optical addressing technology, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming trace DNA, complicated detection process, high production cost, etc., and achieve the effect of short detection time, high sensitivity and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
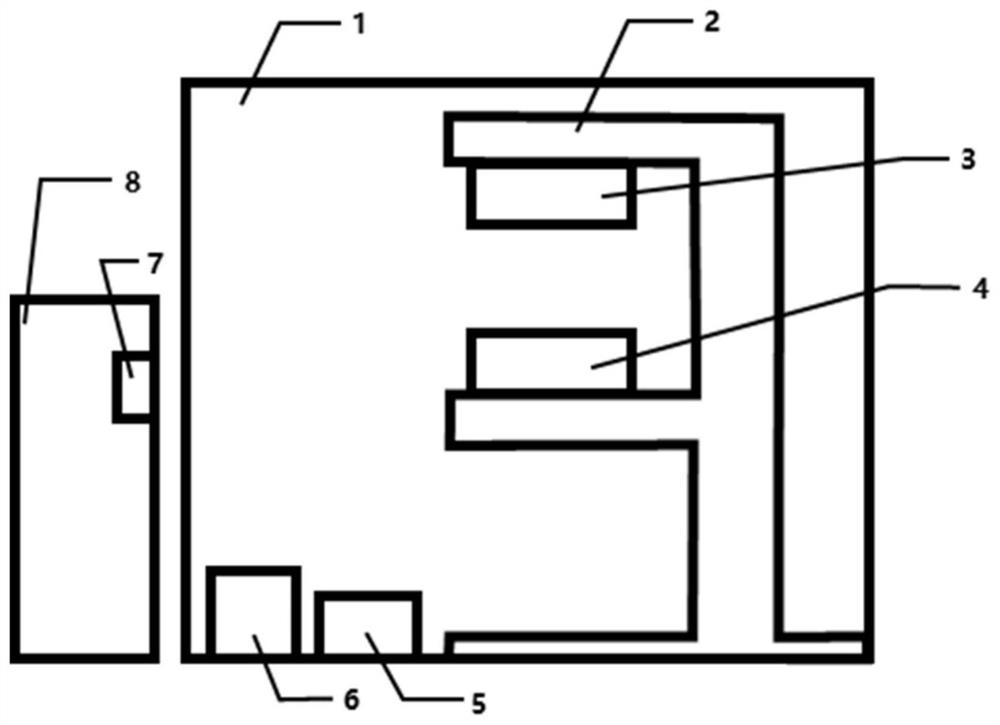
[0042] figure 1 is the measuring device of the present invention. Including Faraday shielding box 1, loading platform 2, semiconductor laser 3, LAPS sensor 4, constant voltage device 5, lock-in amplifier 6, acquisition card 7 and computer 8; wherein, loading platform 2 is placed in Faraday shielding box 1, semiconductor laser 3 and the LAPS sensor 4 are installed on the loading platform 2, the potentiostat 5 is connected with the electrodes on the lock-in amplifier 6 and the LAPS sensor 4, the lock-in amplifier 6 is connected with the acquisition card 7, and the acquisition card 7 is installed on the computer 8 for The photocurrent of LAPS sensor 4 is collected.
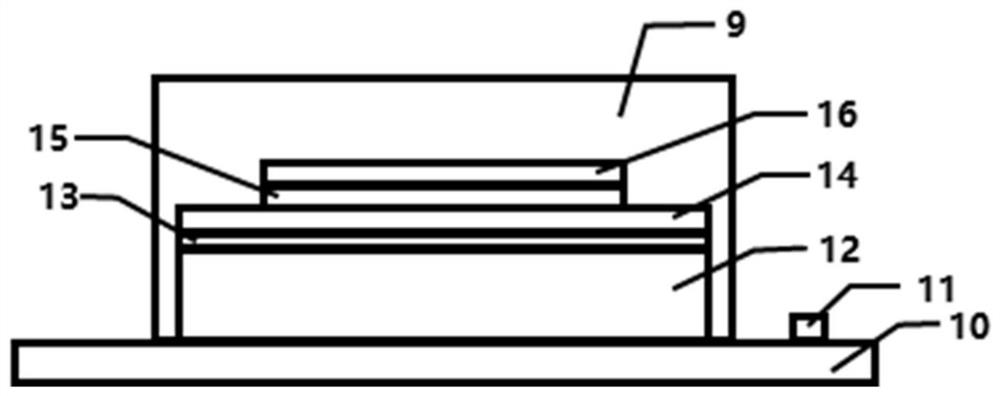
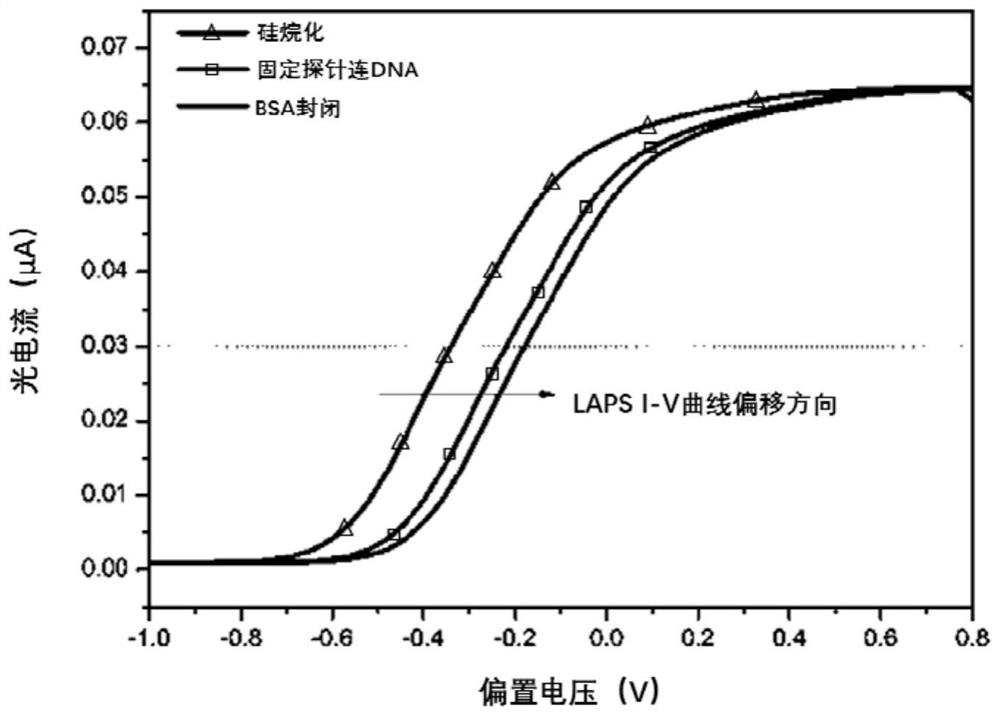
[0043] see figure 2 , LAPS sensor 4 comprises alloy plate 10, and the middle position of alloy plate 10 is successively provided with Si layer 12, SiO 2layer 13 and Al layer 14, the middle position of Al lay...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com