A blockchain fast consensus method and device
A blockchain and consensus technology, applied in the blockchain field, can solve problems such as slow consensus, low efficiency, and long time consumption, and achieve the effect of avoiding slow speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
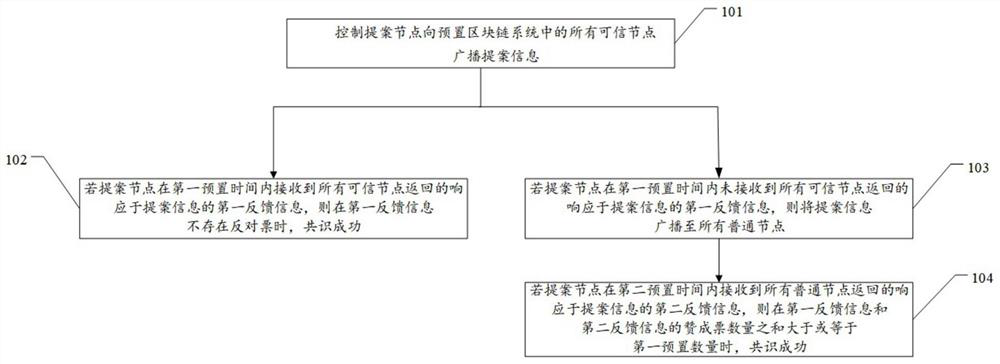
[0050] For ease of understanding, see figure 1 , Embodiment 1 of a blockchain fast consensus method provided by this application, including:
[0051] Step 101, the control proposal node broadcasts proposal information to all trusted nodes in the preset blockchain system.
[0052] Among them, the proposal information corresponds to the proposal data request sent by the preset blockchain system to the proposal node.
[0053] Step 102: If the proposing node receives the first feedback information in response to the proposal information returned by all trusted nodes within the first preset time, then the consensus is successful if there is no negative vote in the first feedback information.
[0054] Step 103: If the proposing node does not receive the first feedback information in response to the proposal information returned by all trusted nodes within the first preset time, broadcast the proposal information to all common nodes.
[0055] Step 104: If the proposing node receives ...
Embodiment 2
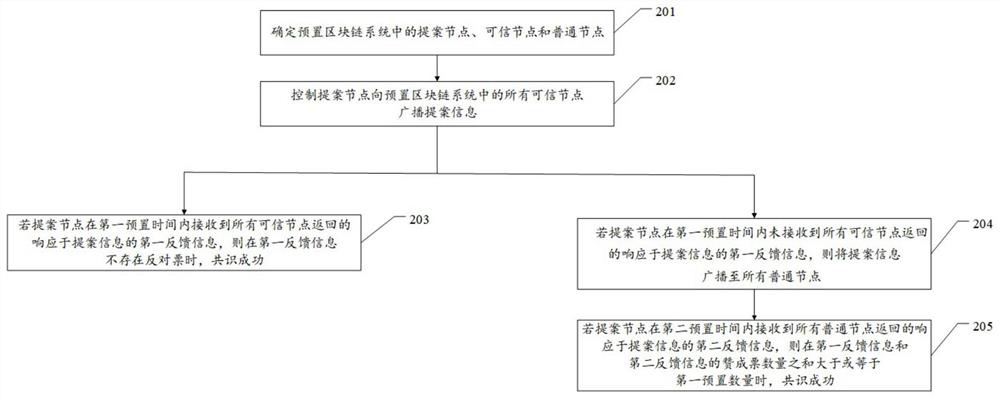
[0060] For ease of understanding, see figure 2 , the embodiment of this application provides a second embodiment of a block chain fast consensus method, including:
[0061] Step 201. Determine the proposal nodes, trusted nodes and common nodes in the preset blockchain system.
[0062] It should be noted that the determination of the proposal nodes, trusted nodes, and common nodes in the pre-set blockchain system specifically includes the following steps: first, determine the target node that the pre-set blockchain system sends the proposal data request as the proposal node; then count The historical information of all nodes in all blockchain systems, and calculate the credibility points of each node based on these historical information; secondly, sort the credibility points of all nodes in descending order; finally, sort the top 2 / 3 nodes are trusted nodes, and the last 1 / 3 nodes are ordinary nodes.
[0063] It should be noted that any node in the preset blockchain system...
Embodiment 3
[0078] For ease of understanding, please participate in Figure 5 , this application also provides a third embodiment of a block chain fast consensus method, including:
[0079] Step 301. Determine the proposal nodes, trusted nodes and common nodes in the preset blockchain system.
[0080] It should be noted that the determination of the proposal nodes, trusted nodes, and common nodes in the pre-set blockchain system specifically includes the following steps: first, determine the target node that the pre-set blockchain system sends the proposal data request as the proposal node; then count The historical information of all nodes in all blockchain systems, and calculate the credibility points of each node based on these historical information; secondly, sort the credibility points of all nodes in descending order; finally, sort the top 2 / 3 nodes are trusted nodes, and the last 1 / 3 nodes are ordinary nodes.
[0081] It should be noted that any node in the preset blockchain syst...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com