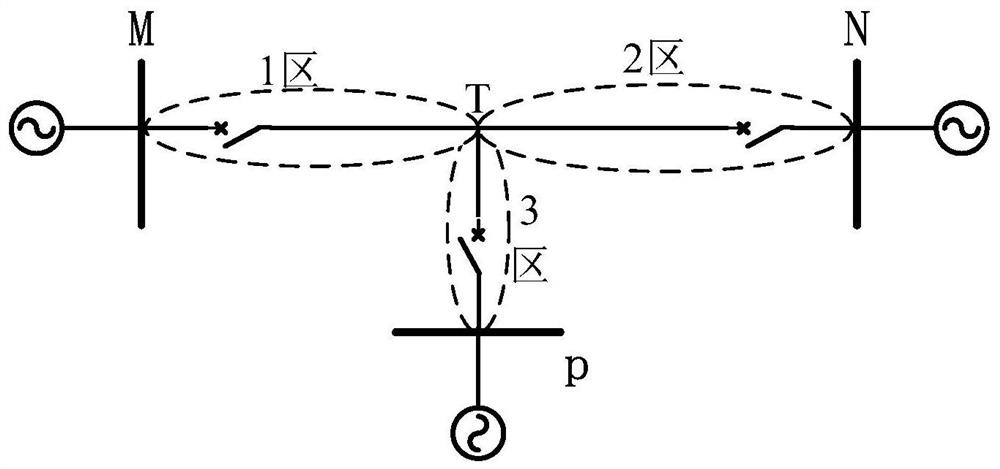
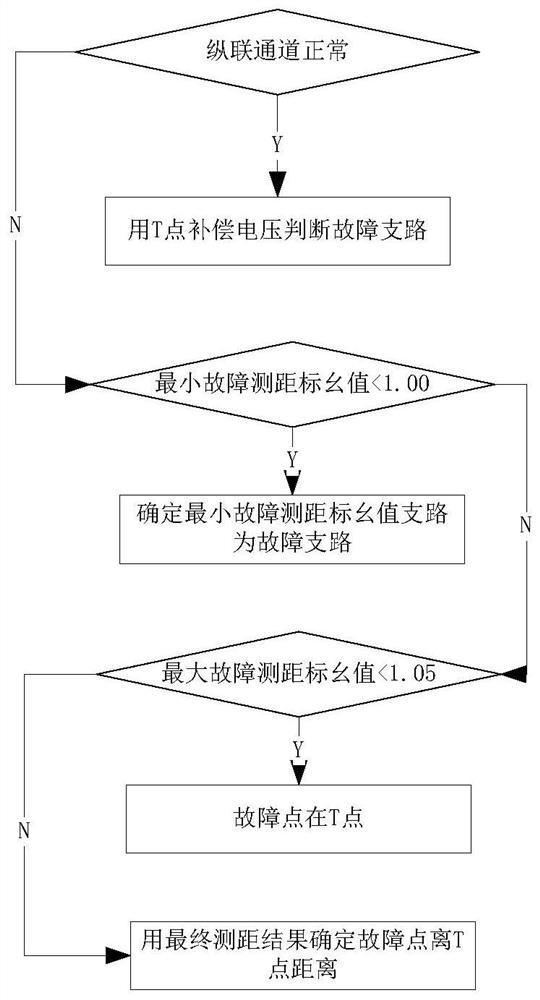
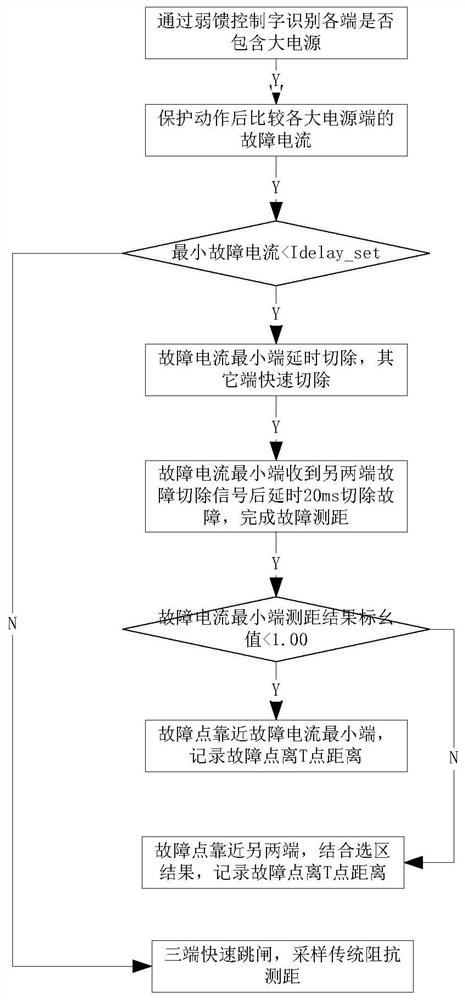
A method for fault distance measurement of T-connection line
A technology of fault distance measurement and line connection, which is applied to the fault location, fault detection according to the conductor type, and electrical measurement. It can solve problems such as complex principles, difficult engineering, and small amount of calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0071] established as Figure 4 The RTDS simulation model shown, the model parameters are shown in Table 1:
[0072] Table 1 Model parameters
[0073] project parameter unit Positive sequence resistance 0.147 Ω / km Positive sequence reactance 0.430 Ω / km Positive sequence parallel capacitive reactance 0.530 MΩ*km Zero sequence resistance 0.500 Ω / km Zero sequence inductive reactance 1.200 Ω / km Zero sequence parallel capacitive reactance 0.786 MΩ*km Line length MT (zone 1) 20 km Line length NT (Zone 2) 30 km Line length PT (Zone 3) 40 km
[0074] If the simulated fault point K1 is 50% away from the M side, the theoretical T point distance measurement result is 20*0.5=10kM; the simulated fault point K2 is 50% away from the N side fault, and the theoretical T point distance measurement result is 30*0.5=15kM; simulated fault The point K3 is 30% away from the fault on the P side, and the theoret...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap