Method for evaluating stability of multi-inverter grid-connected system in two dimensions
A system stability, multi-inverter technology, applied in the direction of AC network circuit, single-net parallel feeding arrangement, wind power generation, etc., can solve the problems of grid-connected current distortion and divergence, difficulty in analyzing interaction phenomena, and resonance, etc., to achieve The effect of clear coupling relationship, good feasibility and practical value, and clear damping characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
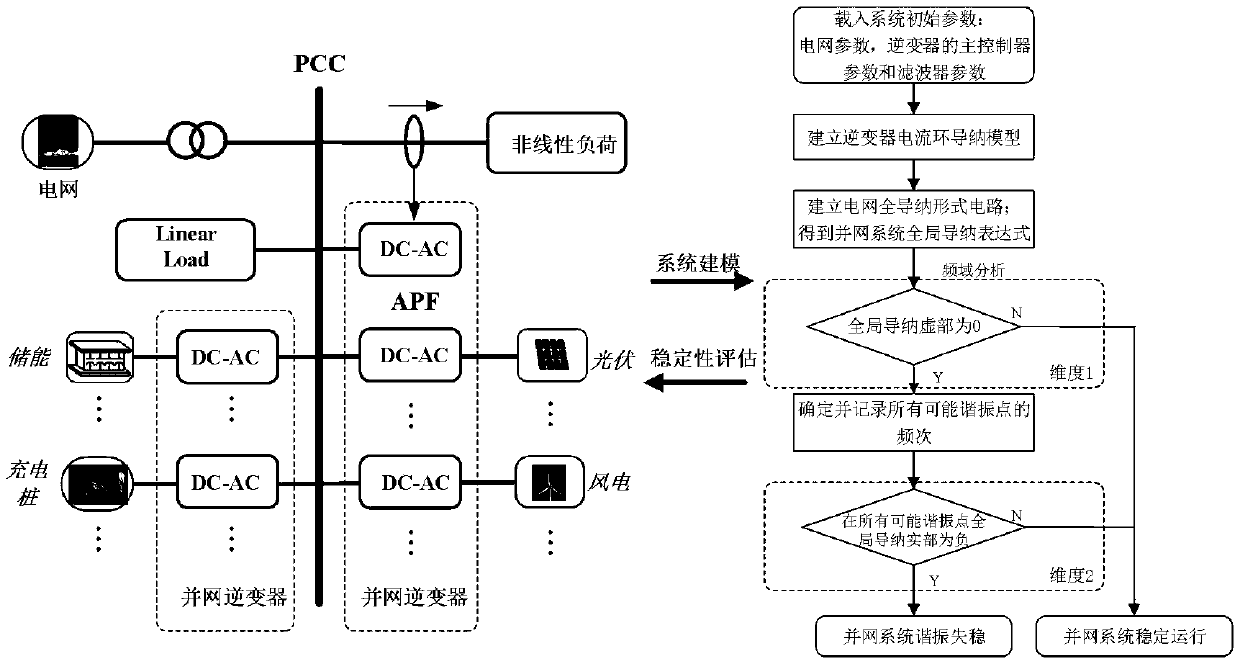
[0035] figure 1 It is a flow chart of a typical distributed power generation system topology and the stability assessment method proposed by the present invention; it specifically includes the following steps:
[0036] Step 1: Load grid parameters and inverter-related parameters for system modeling. Grid parameters include grid admittance, equivalent admittance of passive devices at the grid-connected end, etc. Inverter-related parameters include inverter filters parameters and its controller parameters, etc.
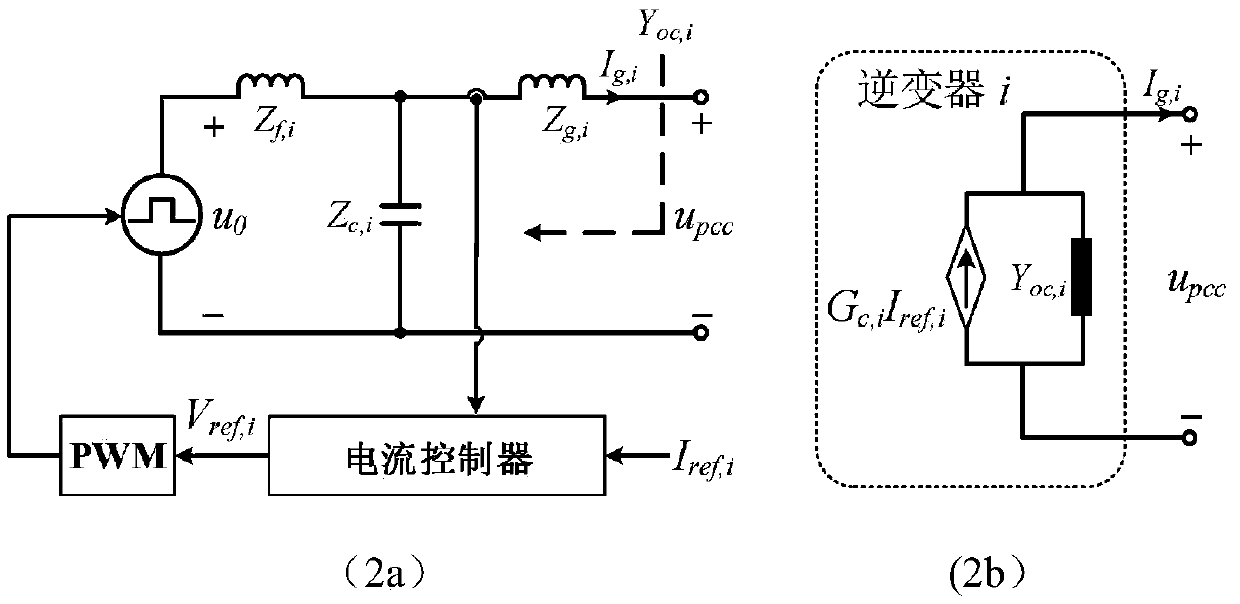
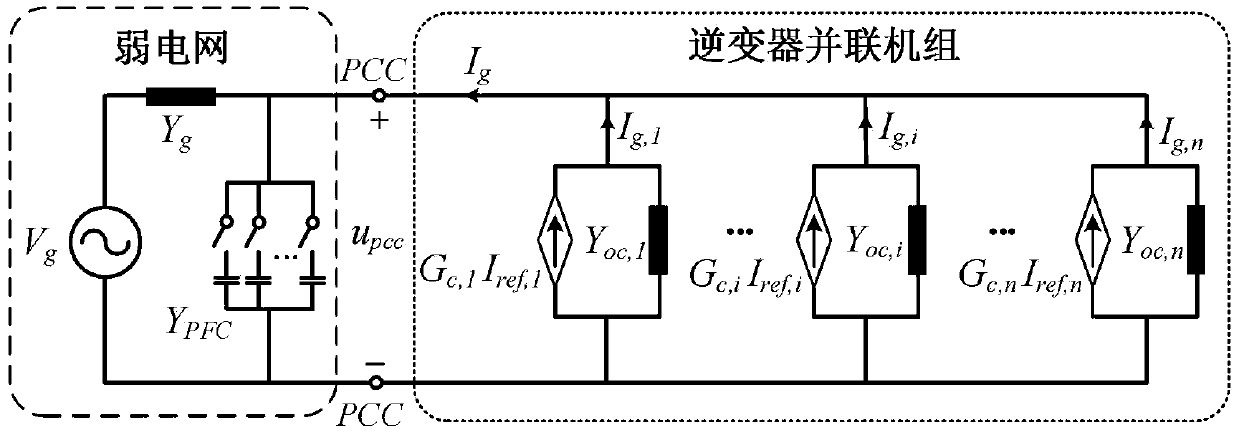
[0037] Step 2: figure 2 (a) A schematic diagram of the inverter current control loop is given. The difference between the grid-connected current of the inverter and the command current is passed through the current controller to generate a PWM signal to control the on-off of the switch tube. According to the inverter parameters can be established figure 2 (b) shows the current loop admittance model of the inverter, that is, a single inverter is equivalent to a cont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com