Chronic disease follow-up surveying method and electronic device
An electronic device, chronic disease technology, applied in speech analysis, promoting communication between doctors or patients, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency, cost, and lack of flexibility in the follow-up of chronic diseases, so as to reduce the cost of follow-up, enhance communication, improve effect of completion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
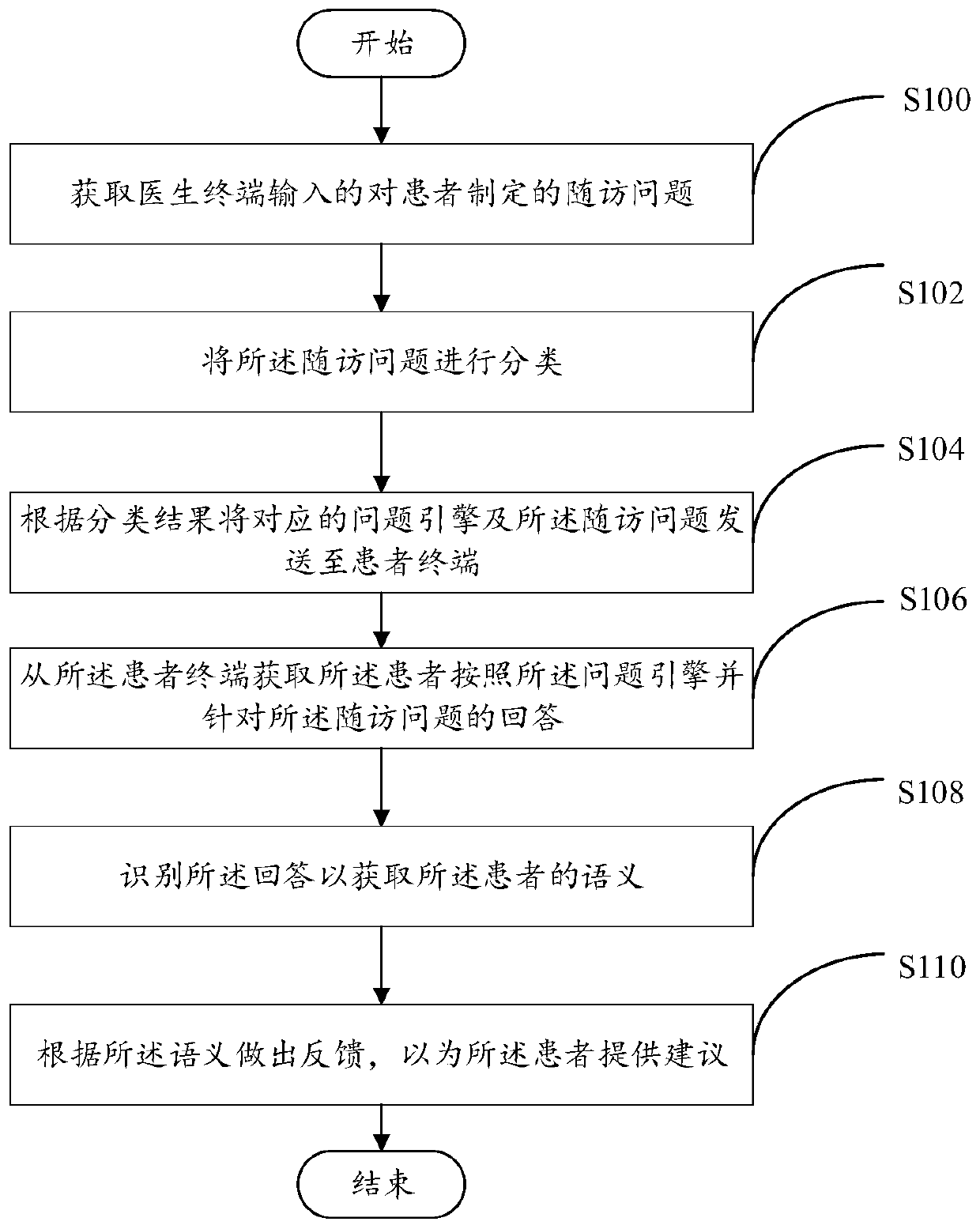
[0076] refer to figure 1 , shows a flow chart of the steps of the chronic disease follow-up method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. It can be understood that the flowchart in this method embodiment is not used to limit the sequence of execution steps. It should be noted that this embodiment uses the electronic device 2 as an execution subject for an exemplary description. details as follows:
[0077] Step S100, acquiring the follow-up question formulated for the patient input by the doctor terminal.
[0078] Specifically, the doctor formulates corresponding follow-up questions for the patient by acquiring relevant information of the patient. Wherein the relevant information at least includes: the current physical health status of the patient, the effect on the medicine and therapy, and the medical history information.
[0079] In a preferred embodiment, when the patient has set the physical health index of concern on the patient terminal, the electronic device 2 a...
Embodiment 2
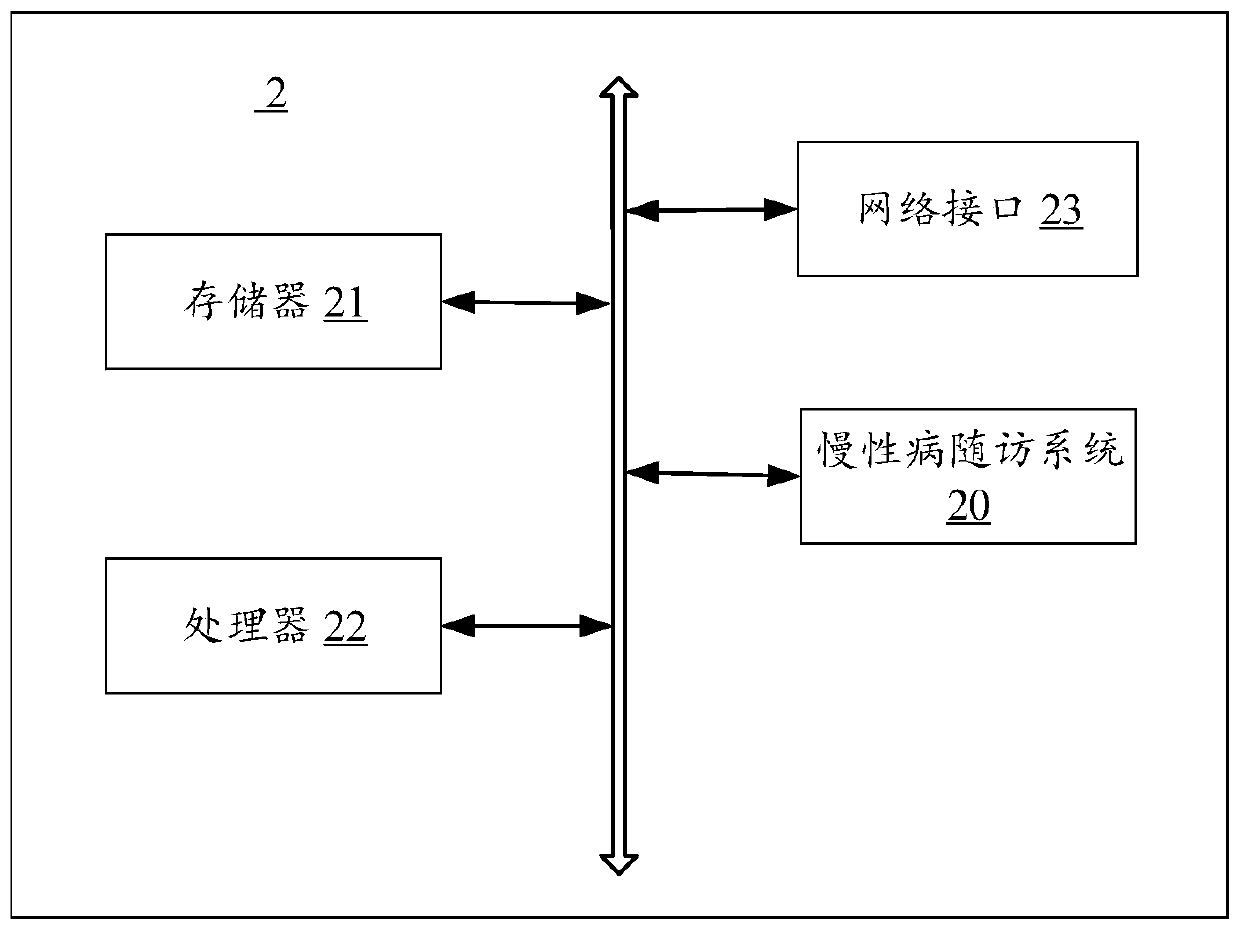
[0096] see figure 2 , shows a schematic diagram of the hardware architecture of the electronic device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The electronic device 2 includes, but is not limited to, a memory 21, a processing 22, and a network interface 23 that can communicate with each other through a system bus, figure 2 Only the electronic device 2 is shown with components 21-23, but it should be understood that implementation of all of the illustrated components is not required and that more or fewer components may instead be implemented.
[0097] The memory 21 includes at least one type of readable storage medium, and the readable storage medium includes a flash memory, a hard disk, a multimedia card, a card-type memory (for example, SD or DX memory, etc.), random access memory (RAM), static Random Access Memory (SRAM), Read Only Memory (ROM), Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM), Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM), Magnetic Memory,...
Embodiment 3
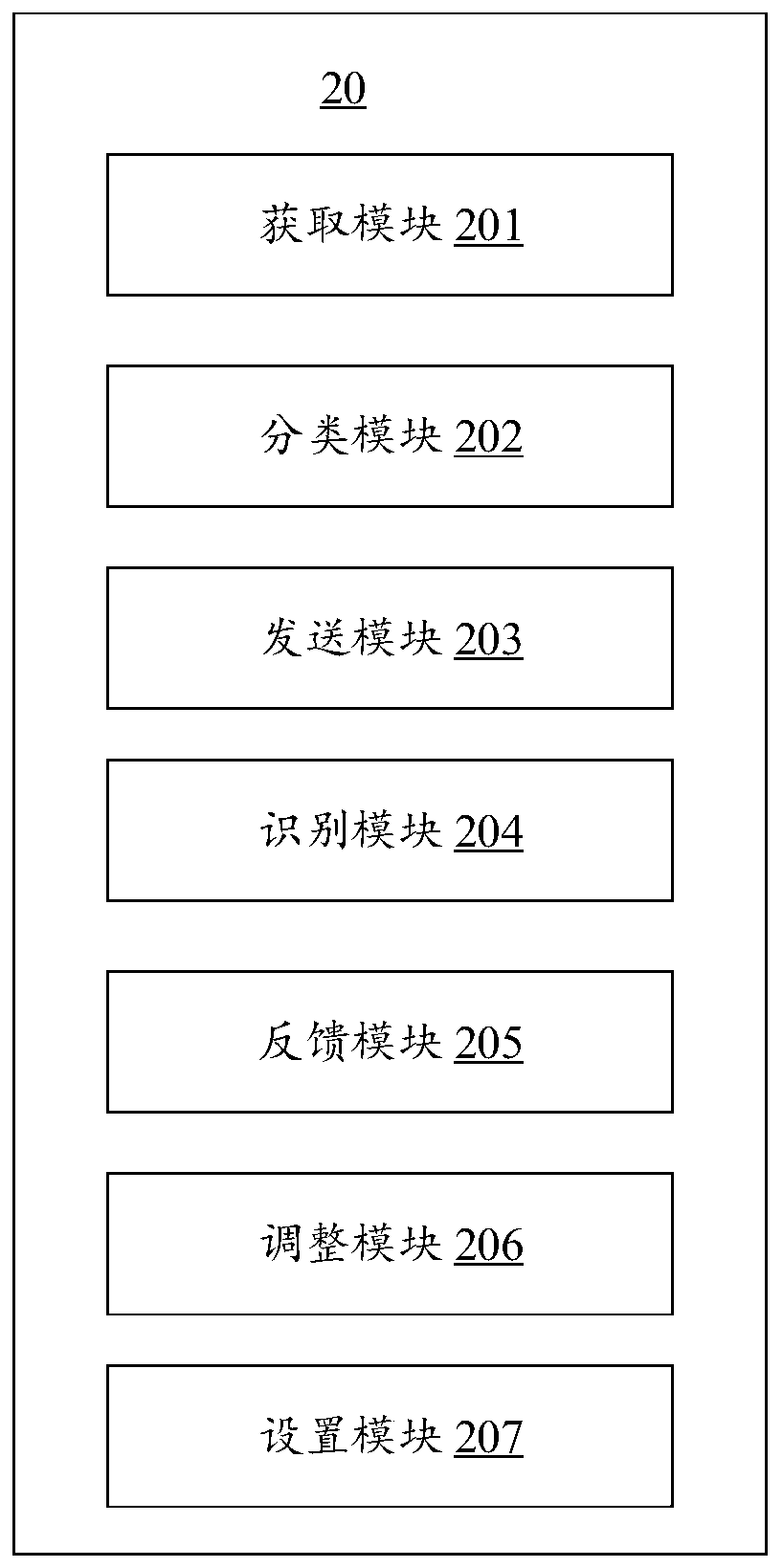
[0101] see image 3 , shows a schematic diagram of the program modules of the chronic disease follow-up system according to the third embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the chronic disease follow-up system 20 may include or be divided into one or more program modules, and one or more program modules are stored in a storage medium and executed by one or more processors to complete this Invention, and can realize the above chronic disease follow-up method. The program module referred to in the embodiment of the present invention refers to a series of computer program instruction segments capable of completing specific functions, which is more suitable for describing the execution process of the chronic disease follow-up system 20 in the storage medium than the program itself. The following description will specifically introduce the functions of each program module of the present embodiment:
[0102] The acquiring module 201 is configured to acquire follo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com