Control system and method capable of realizing autonomous navigation and precise positioning of mobile robot
A mobile robot and precise positioning technology, applied in control/adjustment system, non-electric variable control, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of low control frequency, low control accuracy, and poor real-time performance. To achieve the effect of improving real-time performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This embodiment provides a control system capable of realizing autonomous navigation and precise positioning of a mobile robot, capable of performing real-time trajectory following control, and realizing autonomous navigation and precise positioning of a mobile robot.
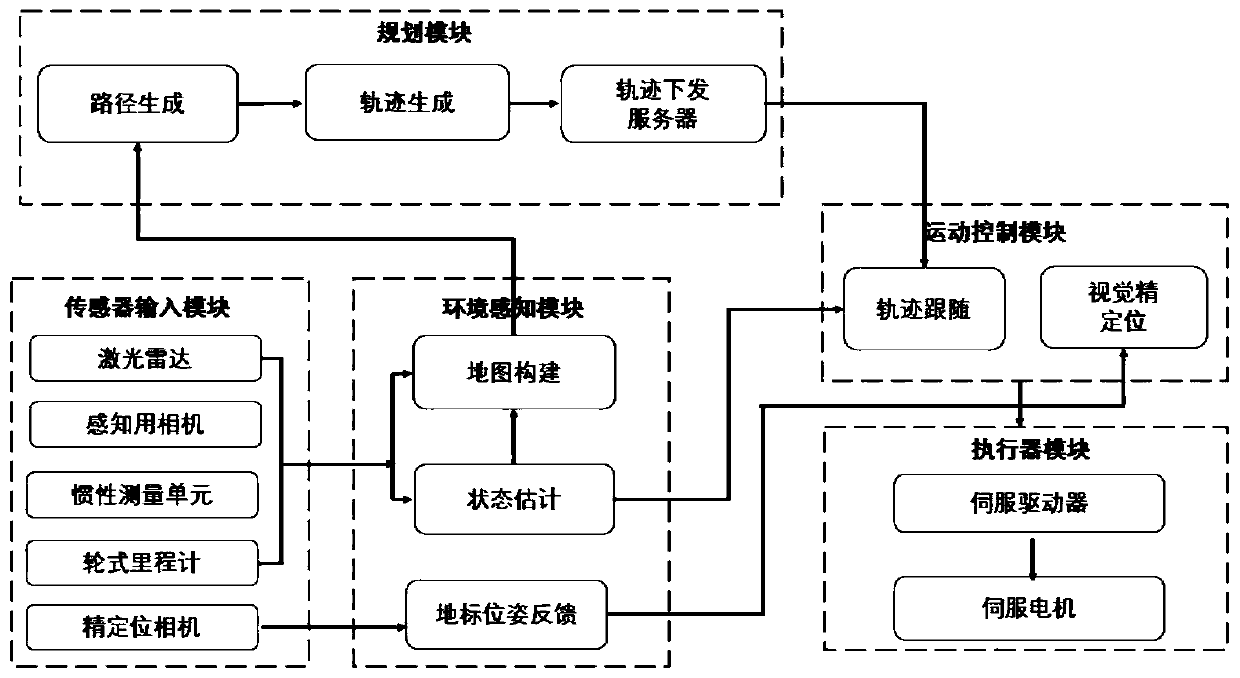
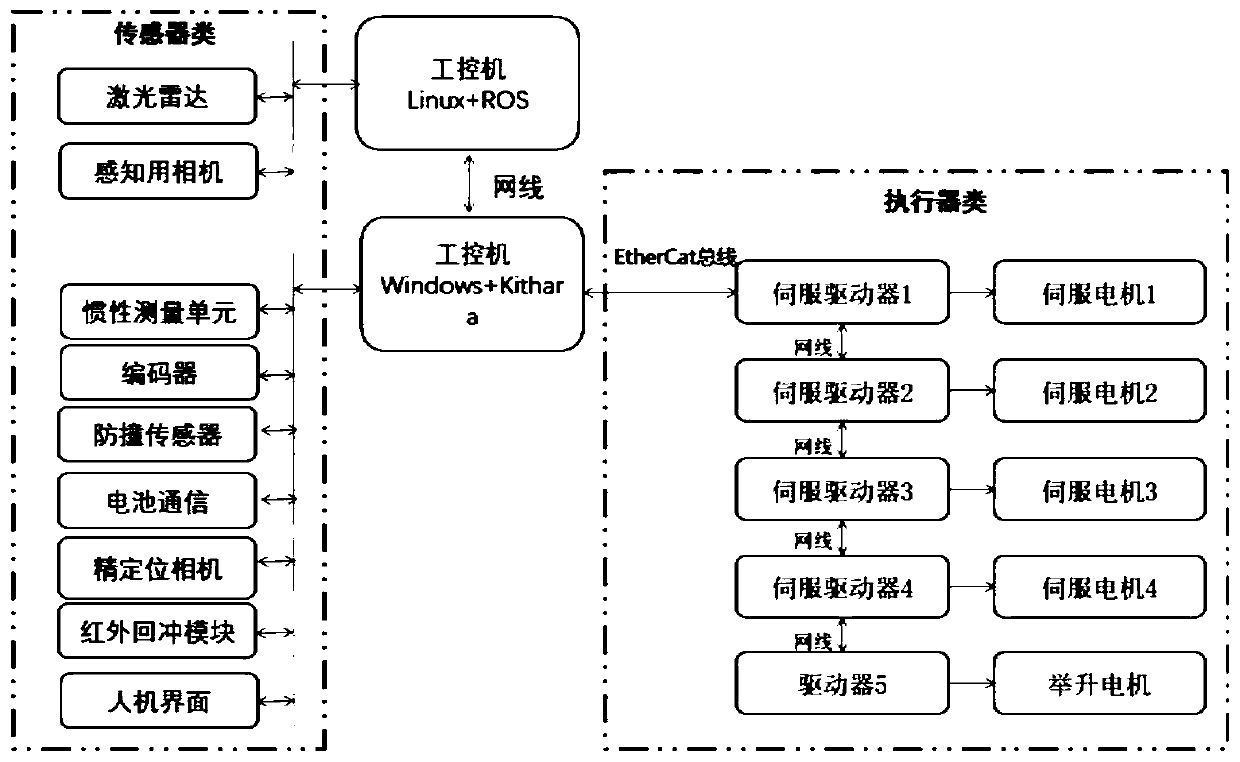
[0034] Please refer to the attached figure 1 , the control system includes a sensor module, a main control module and an execution module arranged on the mobile robot.
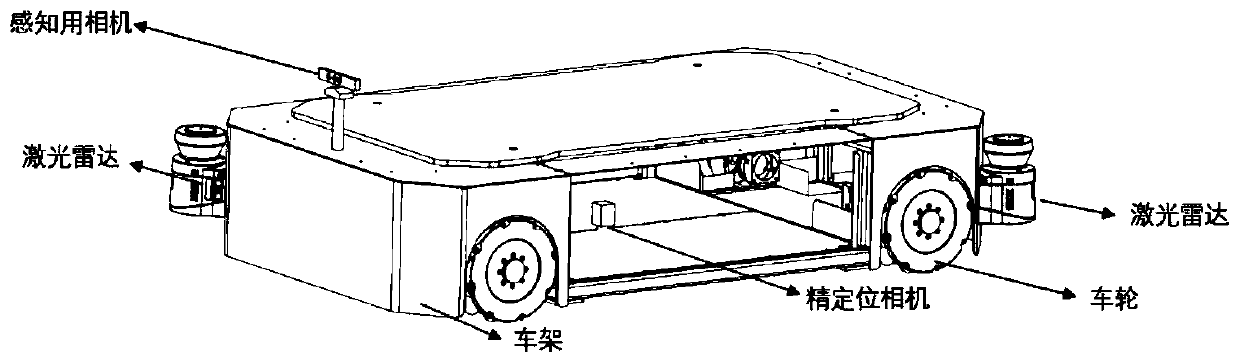
[0035] Please refer to the attached figure 2 , the sensor module includes a laser radar, an inertial measurement unit, an encoder, an anti-collision sensor, an infrared backlash unit, a sensing camera and a precise positioning camera.
[0036] The number of the laser radar is 2, which are installed on the front side and the rear side of the mobile robot respectively, and are located on the same diagonal line, and are used to scan the environment area where the mobile robot is located, extract the environmental contour information, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0114] This embodiment provides a control method for realizing autonomous navigation and precise positioning of a mobile robot. The method is implemented based on the control system for realizing autonomous navigation and precise positioning of a mobile robot described in Embodiment 1. The method includes the following steps:
[0115] S101, the industrial computer I acquires sensor data, calculates the wheel odometer data, constructs static and dynamic maps of the environment, estimates the pose of the mobile robot, plans the trajectory of the mobile robot, and feeds back to the industrial computer II.
[0116] Specifically, the industrial computer I scans the environmental contour information of the mobile robot through two laser radars, collects the image data in front of the robot through the sensing camera, and receives the inertial measurement unit uploaded by the industrial computer II to measure the forward, lateral, and horizontal directions of the mobile robot. Velocit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com