Method for detecting design reasonability of N/P ratio of lithium ion three-electrode battery
A lithium-ion battery, three-electrode technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems of battery danger, waste of battery synthesis and feeding, battery lithium analysis, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation and good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
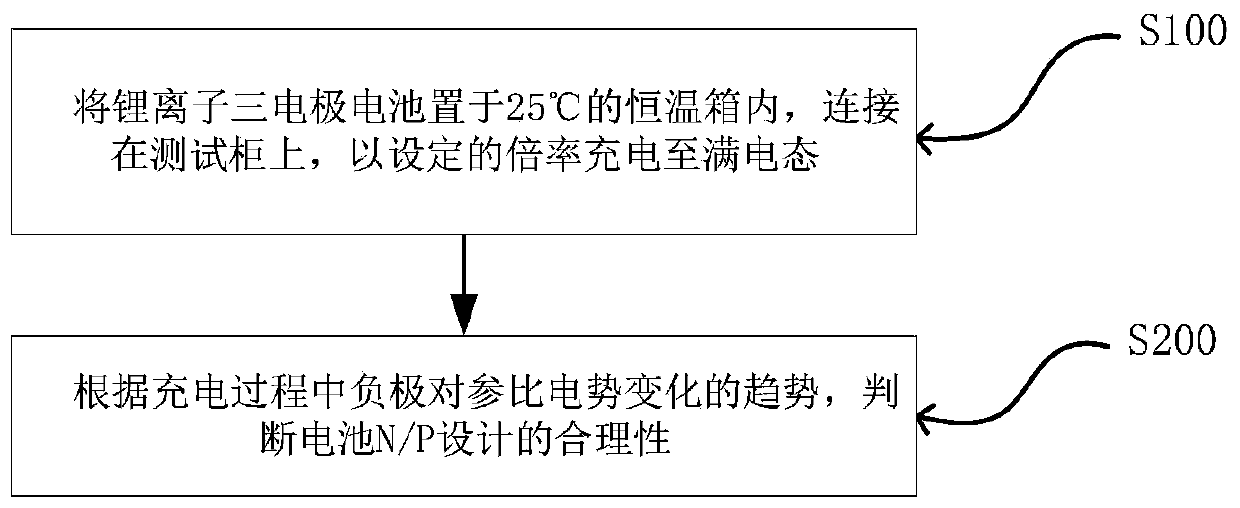
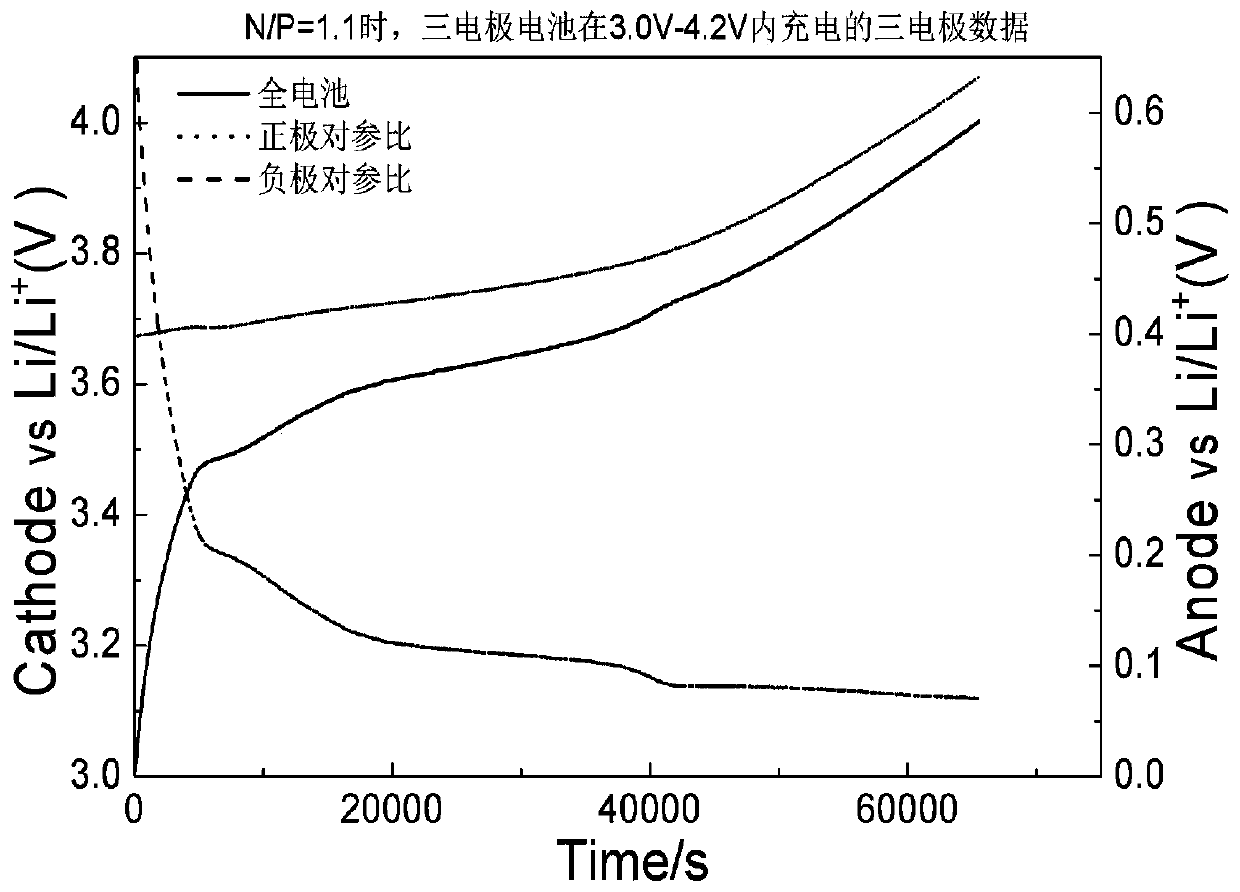
[0028] When N / P = 1.1, the judgment of the design rationality of the N / P ratio of the three-electrode battery:
[0029] (1) Put the three-electrode battery with N / P = 1.1, lithium foil as the reference and graphite as the negative electrode in a thermostat at 25°C, connect to the test cabinet, and charge to full charge at 0.05c.
[0030] (2) Analyze the change trend of the potential of the negative electrode to the reference during the charging process;
[0031] (3) by figure 2 It can be seen from the middle curve that during the process of charging to 4.2V, three complete lithium-intercalation platforms appear on the curve of the negative electrode to the reference potential of the battery. This phenomenon indicates that the positive electrode of the battery is charged from 0.05c to 4.2V. The extracted reversible lithium happens to be embedded in the negative electrode graphite, so it is judged that the N / P ratio of the battery is designed to be reasonable.
example 2
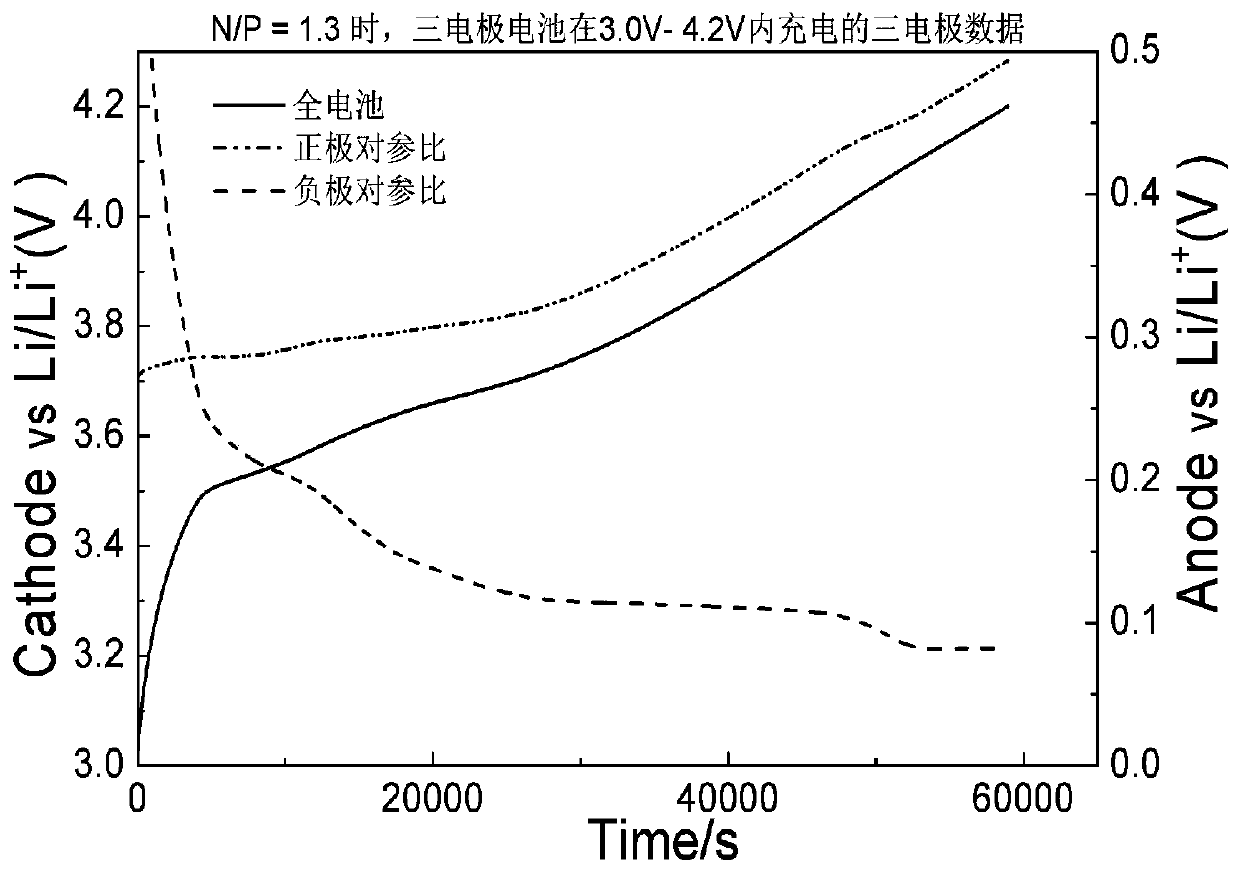
[0033] When N / P = 1.3, the judgment of the design rationality of the N / P ratio of the three-electrode battery:
[0034] (1) A three-electrode battery with N / P = 1.3, lithium foil as the reference and graphite as the negative electrode is placed in a thermostat at 25°C, connected to the test cabinet, and charged to full charge at 0.05c.
[0035] (2) Analyze the change trend of the potential of the negative electrode to the reference during the charging process;
[0036] (3) by image 3 It can be seen from the middle curve that during the process of charging to 4.2V, the third lithium-intercalation platform on the curve of the negative electrode to the reference potential of the battery did not fully appear. This phenomenon indicates that the battery is charged from 0.05c to 4.2V. The active lithium extracted from the positive electrode cannot be embedded in the graphite of the negative electrode. Therefore, it is judged that the N / P ratio of the battery is too large and unreasonable. ...
example 3
[0038] When N / P = 0.8, the judgment of the design rationality of the N / P ratio of the three-electrode battery:
[0039] (1) Put a three-electrode battery with N / P = 0.8, lithium foil as a reference, and graphite as the negative electrode in a thermostat at 25°C, connect to the test cabinet, and charge to full charge at 0.05c.
[0040] (2) Analyze the change trend of the potential of the negative electrode to the reference during the charging process;
[0041] (3) by Figure 4 It can be seen from the middle curve that in the process of charging to 4.2V, in addition to three complete lithium insertion platforms appearing on the curve of the battery’s negative electrode versus reference potential, there is also a fourth lithium evolution platform around 0V. This phenomenon indicates When the battery is charged from 0.05c to 4.2V, the amount of active lithium released from the positive electrode is greater than the amount of lithium that can be accommodated when the surface of the negat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com