A method for handling fault mitigation in a vapour compression system
A technology of vapor compression and compressor, which is applied in the direction of climate sustainability, lighting and heating equipment, fluid circulation arrangement, etc., and can solve the problem of non-optimal operation of the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
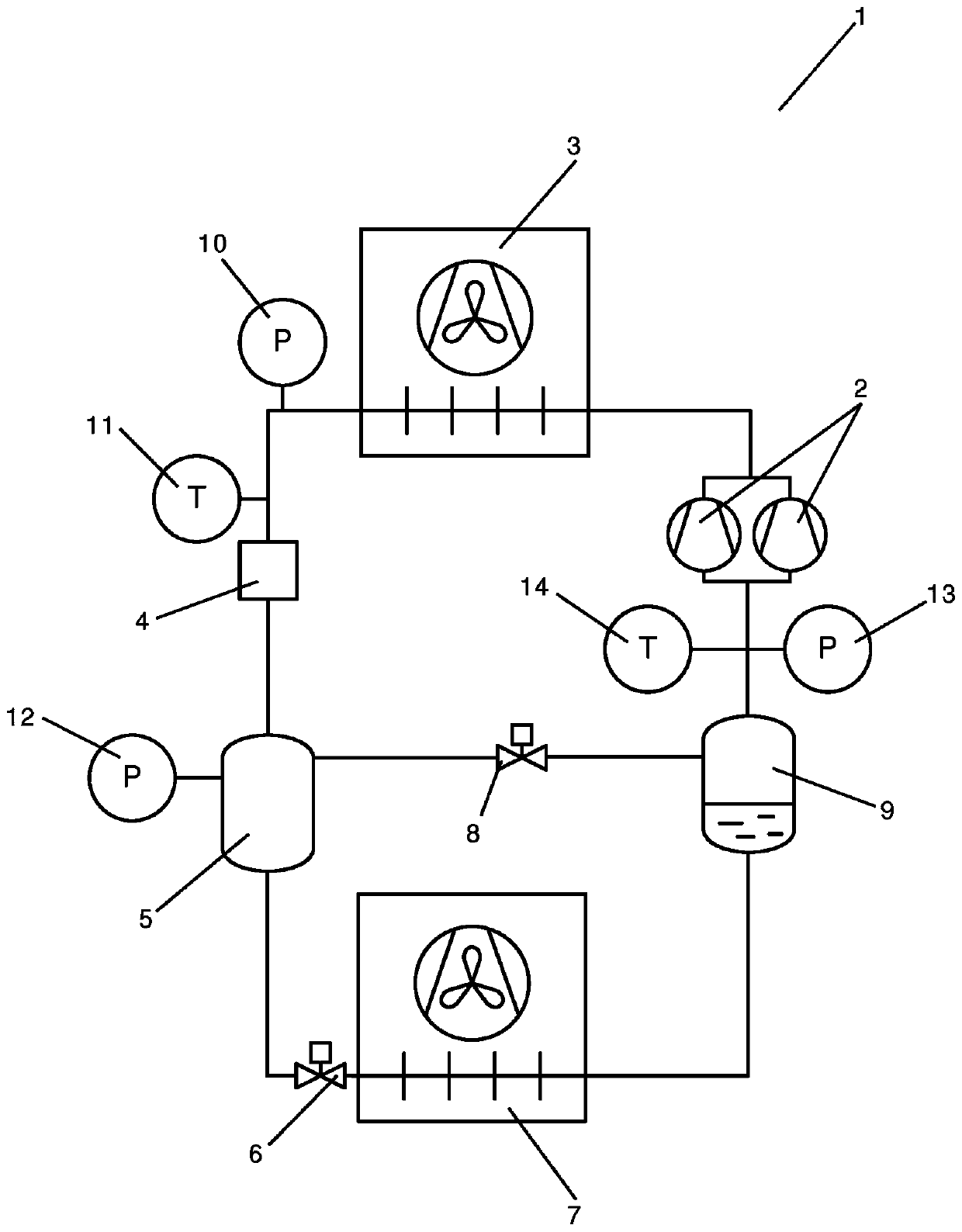
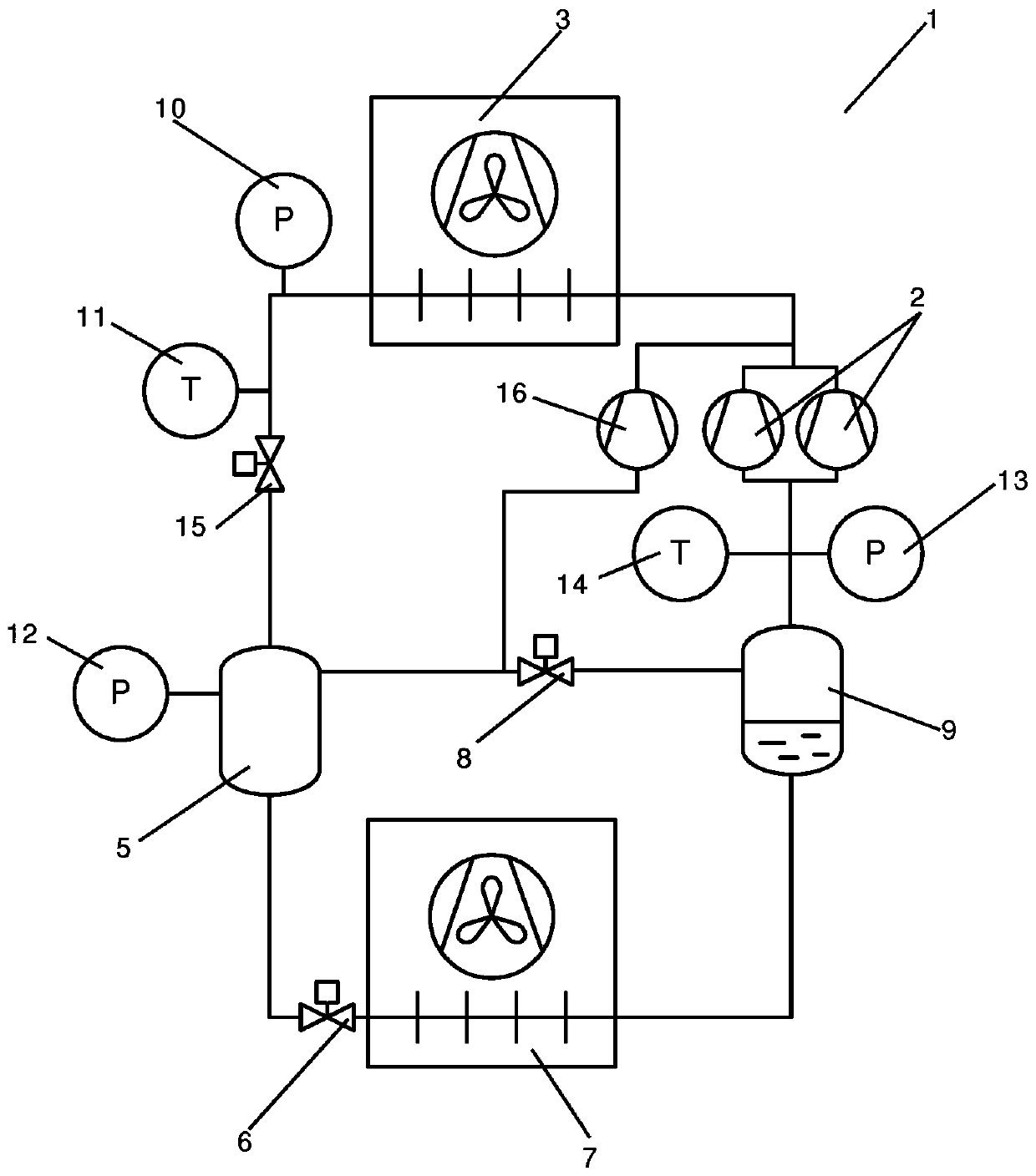
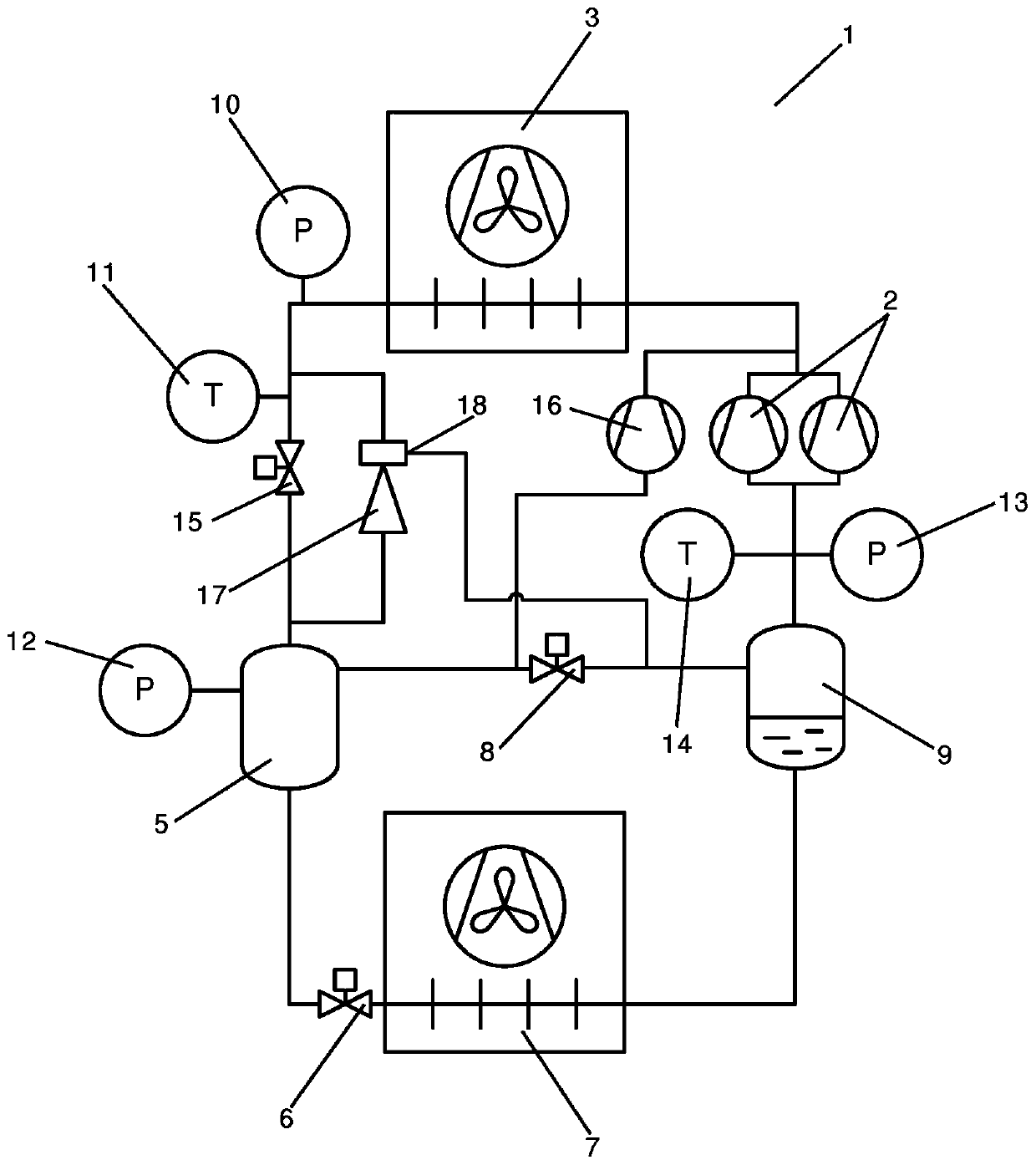
[0048] figure 1 is a simplified diagram of a vapor compression system 1 controlled using a method according to a first embodiment of the invention. A vapor compression system 1 comprises a compressor unit comprising a plurality of compressors 2 (two of which are shown) arranged in a refrigerant path, a heat rejection heat exchanger 3, a high pressure expansion device 4, a receiving 5, an evaporator expansion device 6 in the form of an expansion valve, an evaporator 7, a gas bypass valve 8, and a suction line receiver 9.
[0049] The refrigerant flowing in the refrigerant path is compressed by the compressor 2 before being supplied to the heat rejection heat exchanger 3 . In the heat rejection heat exchanger 3, heat exchange takes place with the auxiliary fluid flow flowing through the heat rejection heat exchanger 3 by removing heat from the refrigerant. In case the heat rejection heat exchanger 3 is in the form of a condenser, the refrigerant passing through the heat reject...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com