Visual servo trajectory tracking and concurrent depth identification on the wheeled mobile robot
A mobile robot and trajectory tracking technology, applied in the direction of instruments, image data processing, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the lack of depth information, the inability to obtain the scene model, and the difficulty of recovering external three-dimensional scene information and mobile robot motion information And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
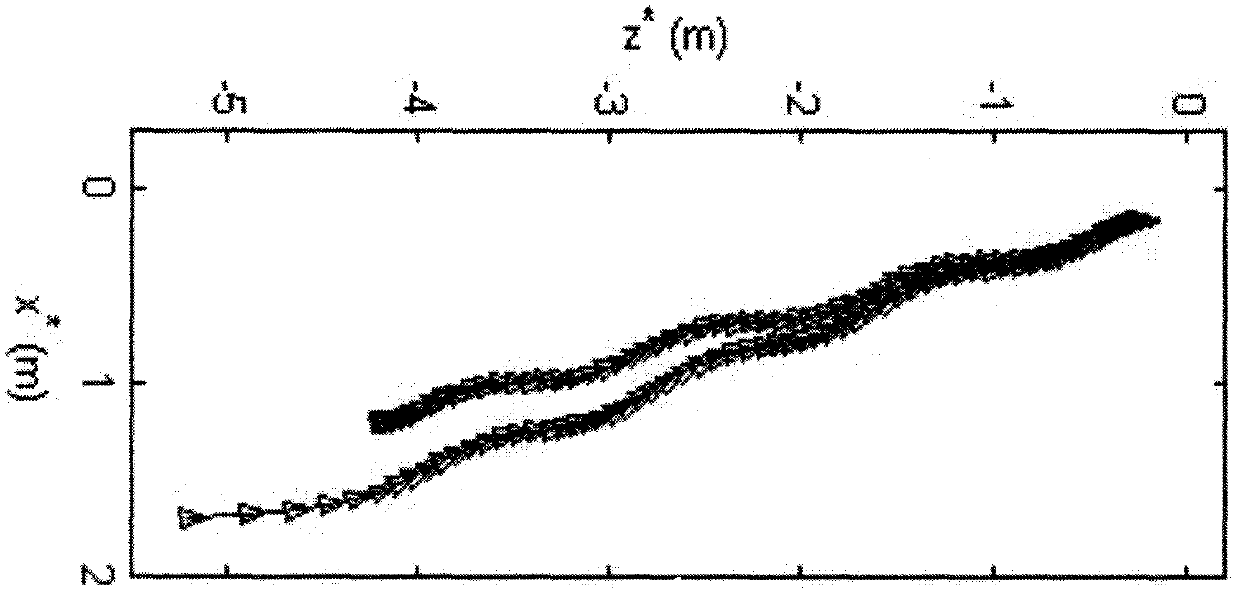
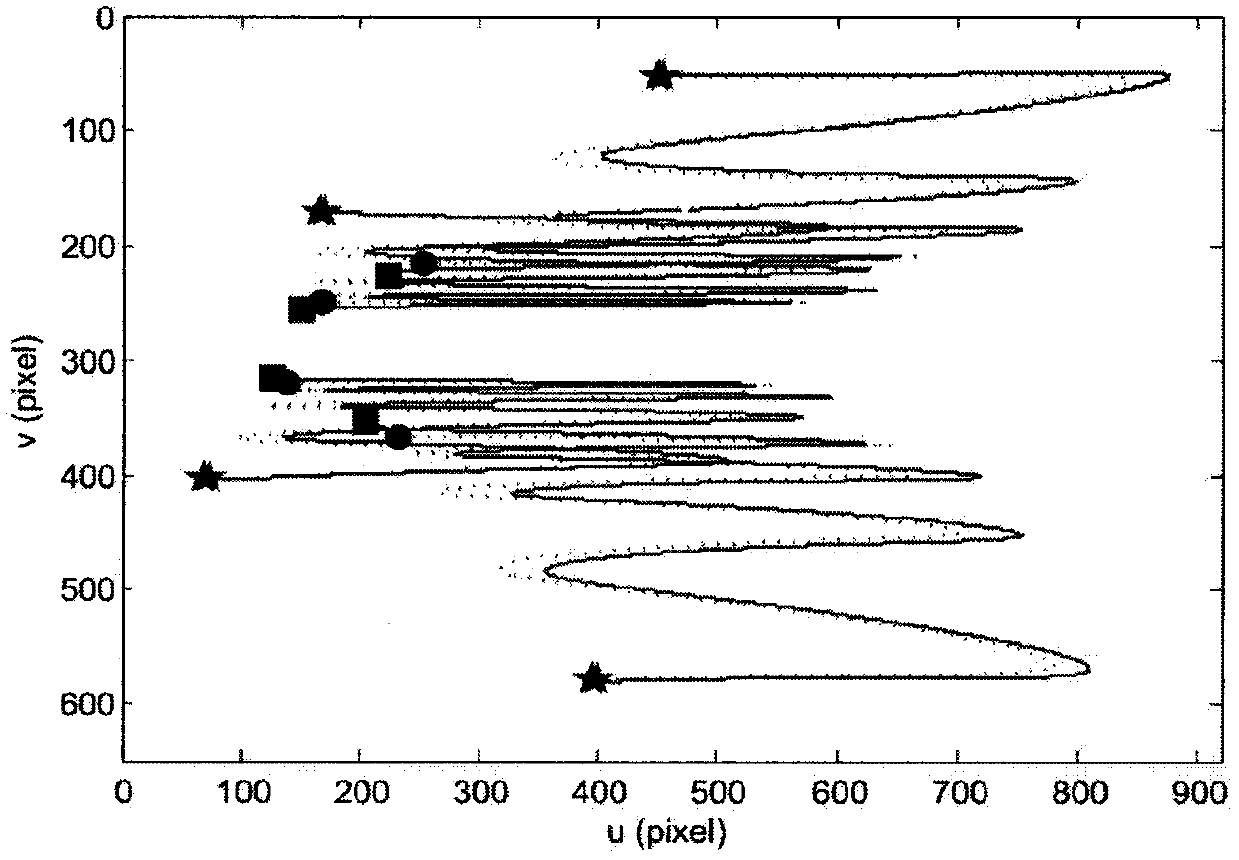
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
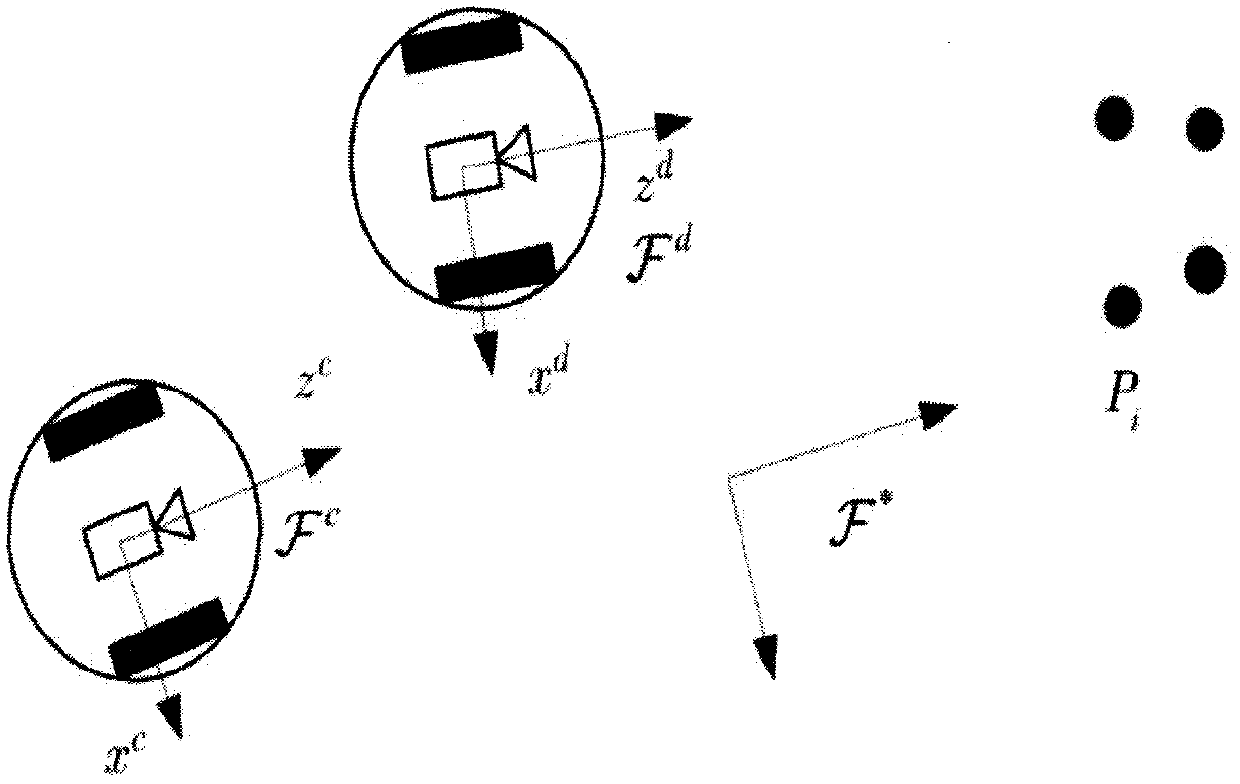
[0063] 1. A wheeled mobile robot simultaneous visual trajectory tracking concurrent adaptive depth identification method, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0064] First, define the system coordinate system, including:
[0065] Define the coordinate system of the wheeled mobile robot as follows: Represents the reference coordinate system of the camera relative to the stationary feature point, with Indicates the current pose coordinate system of the wheeled mobile robot, with Represents the Cartesian coordinate system corresponding to the expected pose of the wheeled mobile robot, with the coplanar feature point P i The determined plane is the reference plane π, and the unit normal vector defining the plane π is n * , 3-D Euclidean coordinates P i exist Next use respectively To represent:
[0066]
[0067] Assuming that the distance from the origin of each coordinate system to the feature point along the optical axis is always positive, fro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com