Robot control method, robot control system and robot
A control method and robot technology, applied in the direction of program control of manipulators, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as mechanical impact, damage to the reducer, and speed up robot loss, so as to reduce loss and avoid mechanical impact.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
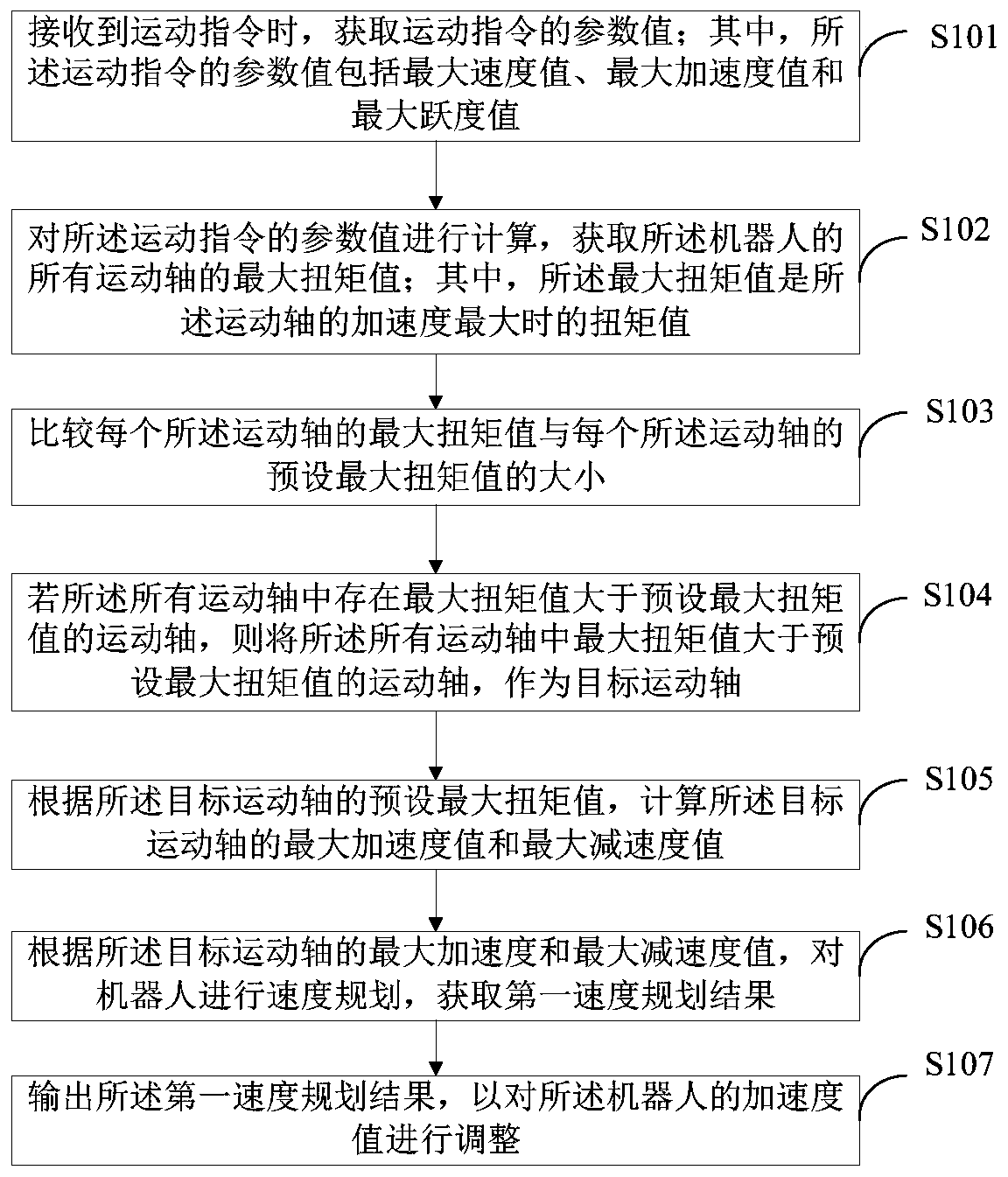
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a robot control method, which can be applied to terminal devices such as mobile phones, PCs, tablet computers, and robots. The robot control method provided in this embodiment includes:
[0054]S101. When a motion command is received, obtain a parameter value of the motion command; wherein, the parameter value of the motion command includes a maximum velocity value, a maximum acceleration value, and a maximum jerk value.
[0055] In a specific application, if a motion command for controlling the motion of the robot is received, the parameter value of the motion command is obtained according to a first preset algorithm, so as to obtain the motion state of the robot according to the parameter value of the motion command. Wherein, the parameter value of the movement instruction includes but not limited to the maximum speed value, the maximum acceleration value and the maximum jerk value; in this embodiment, the first pre...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is a further description of the method steps in the first embodiment. In this embodiment, after step S103, it also includes:
[0071] S201. If there is no motion axis whose maximum torque value is greater than a preset maximum torque value among all the motion axes, perform speed planning on the robot according to the parameter value of the motion command, and obtain a second speed planning result;
[0072] In a specific application, if there is no motion axis whose maximum torque value is greater than the preset maximum torque value among all the motion axes, then the parameter value of the motion command is less than or equal to the preset motion parameter value, and the speed of the robot is adjusted according to the parameter value of the motion command. Planning, to obtain the second velocity planning results.
[0073] S202. Output the second speed planning result to adjust the acceleration value of the robot.
[0074]...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment is a further description of the method steps in the first embodiment. In this embodiment, step S101 includes:
[0081] S1011. When the motion command is received, obtain a parameter value of the motion command according to a parameterized equation.
[0082] In a specific application, if a motion command is received, the parameter value of the motion command is obtained according to a parameterized equation; wherein, the parameter value of the motion command includes but is not limited to a maximum velocity value, a maximum acceleration value, and a maximum jerk value. Through the parametric equation, the constraint problem of the n-dimensional motion command is transformed into a single-dimensional constraint problem, which simplifies the amount of calculation.
[0083] In one embodiment, the parametric equation is:
[0084] q i = f i (s), i=1,2,...,dof;
[0085] Wherein, the s∈[0,1] is a normalization parameter, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com