Mobile robot obstacle avoidance method based on DoubleDQN network and deep reinforcement learning
A mobile robot and reinforcement learning technology, applied in biological neural network models, instruments, non-electric variable control and other directions, can solve the problems of long training time, low obstacle avoidance success rate, and high response delay, shortening training time and improving training. Efficiency, overcoming the effect of high response delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
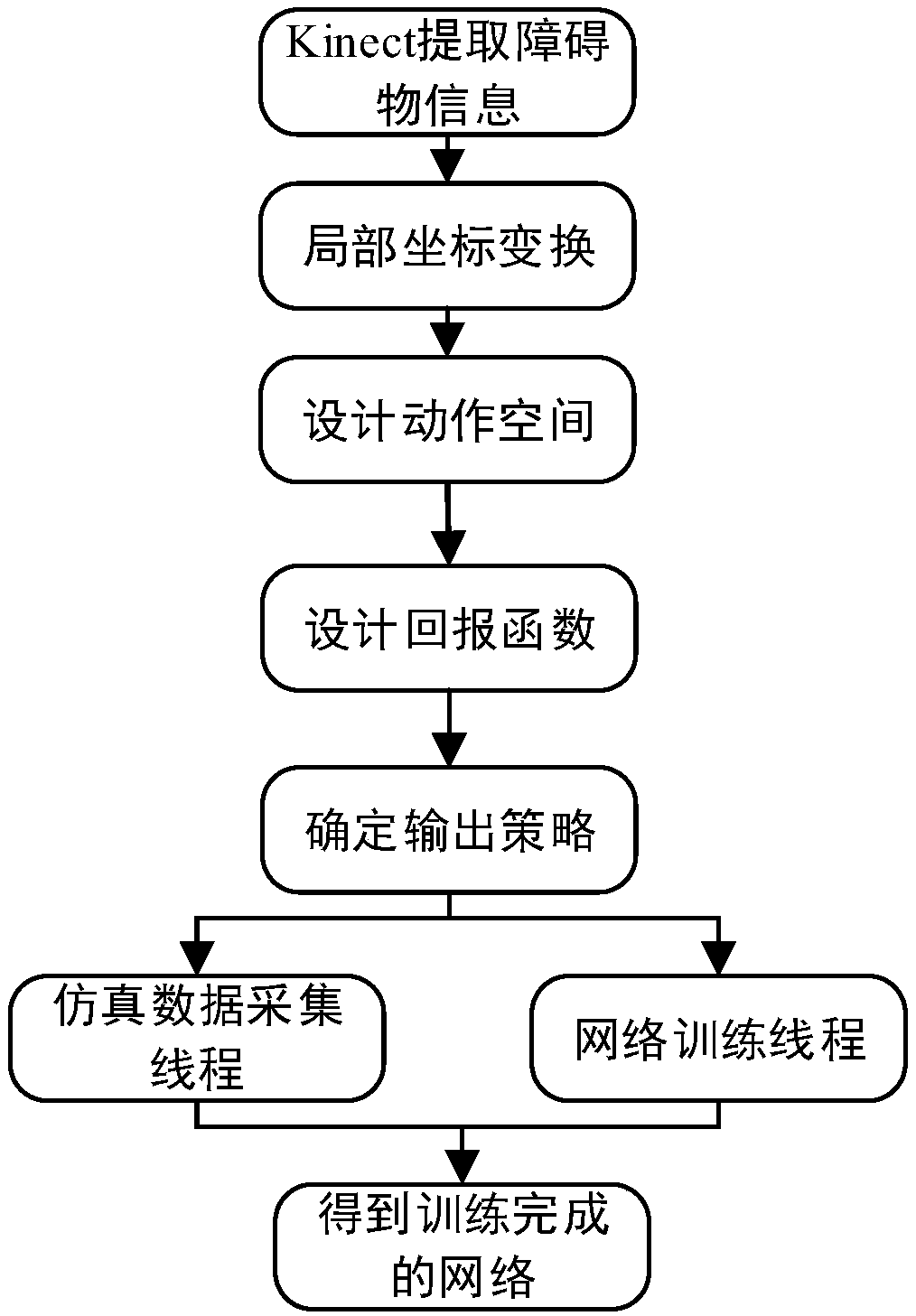
[0024] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 1 As shown, the mobile robot obstacle avoidance method based on DoubleDQN network and deep reinforcement learning described in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0025] Step 1: use Kinect on the mobile robot to map the current environment where the mobile robot is located, and extract all obstacle information in the current environment where the mobile robot is located;
[0026] Step 2: Transform the mobile robot itself, target position and all obstacle information extracted in step 1 in the global coordinate system to the local coordinate system, and transform the mobile robot itself, target position and all obstacles extracted in step 1 in the local coordinate system The object information is used as the state input of the Double DQN network;
[0027] Step 3: Design the decision-making action space output by the Double DQN network;
[0028] Step 4: Design the reward function of the Double DQN network. The rew...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: the specific process of said step two is:
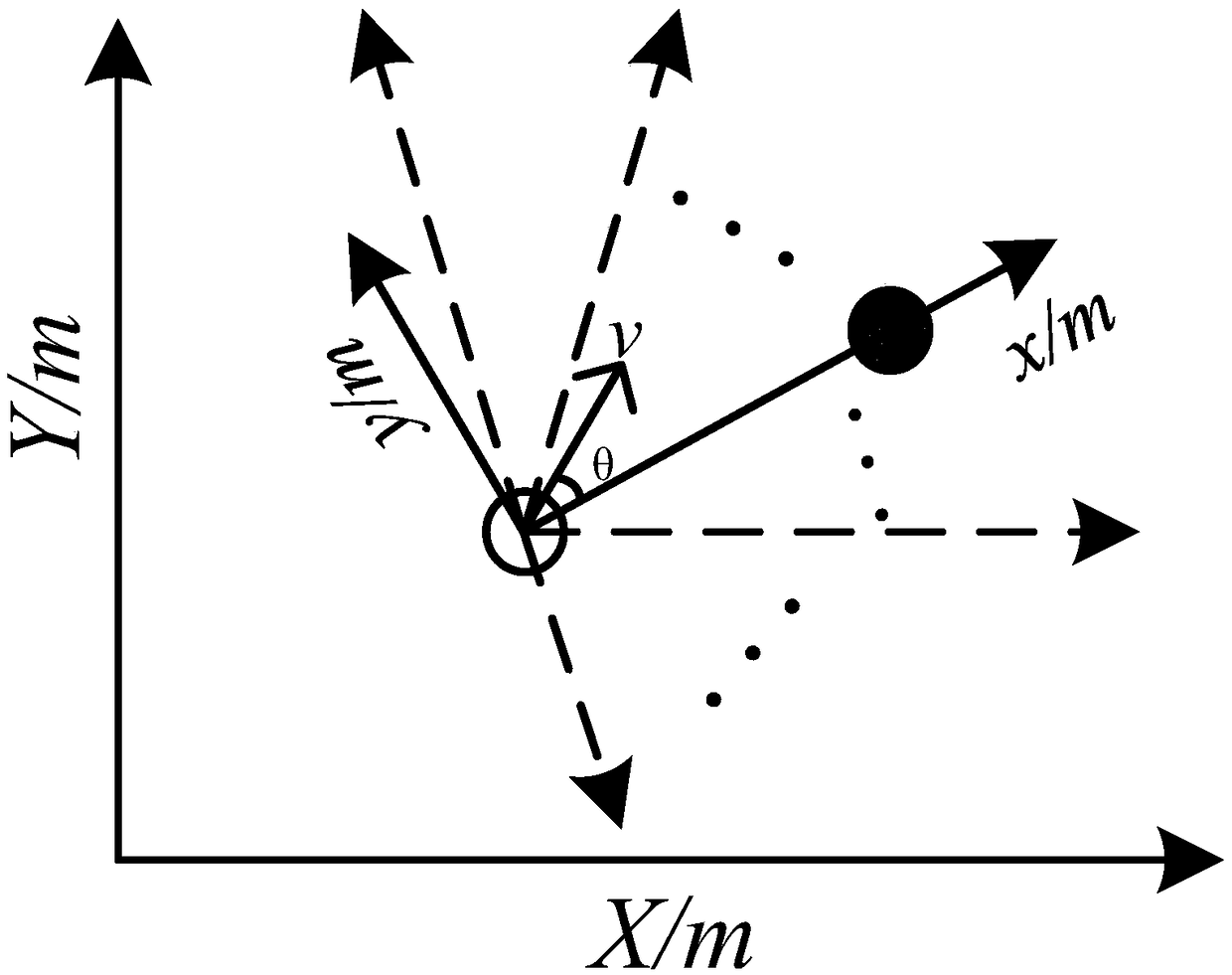
[0034] Transform the mobile robot itself, the target position and all obstacle information extracted in step 1 in the global coordinate system to the local coordinate system. The coordinate transformation is as follows: figure 2 As shown, v in the figure represents the expression form of the mobile robot speed (including direction and size) in the local coordinate system; the mobile robot itself, the target position and all obstacle information extracted in step 1 in the local coordinate system are used as the DoubleDQN network State input; the local coordinate system is based on the mobile robot itself as the coordinate origin, the direction of the mobile robot pointing to the target position is the positive direction of the x-axis, and the direction of the y-axis satisfies the right-hand rule and is perp...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: the specific process of the step three is:
[0041] In the local coordinate system, the set of decision-making action space a output by the DoubleDQN network is designed as A, where: set A refers to the x-axis direction of the local coordinate system as the center direction, and the angle difference from the center direction is -90°, -85° °, -80°, ... 0°, 5°, ... 85°, 90°, a set of candidate speed directions, then set A contains 37 candidate actions. The schematic diagram of the action space is as image 3 As shown in , the candidate actions are indicated by dashed arrows.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com