A spatio-temporal clustering method for irregular shapes based on maximum correlation and risk deviation
A space-time scanning and clustering method technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, epidemic warning systems, etc., can solve problems such as disease early warning loss, panic, and aggregation risk assessment, so as to avoid early warning loss and increase reliability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
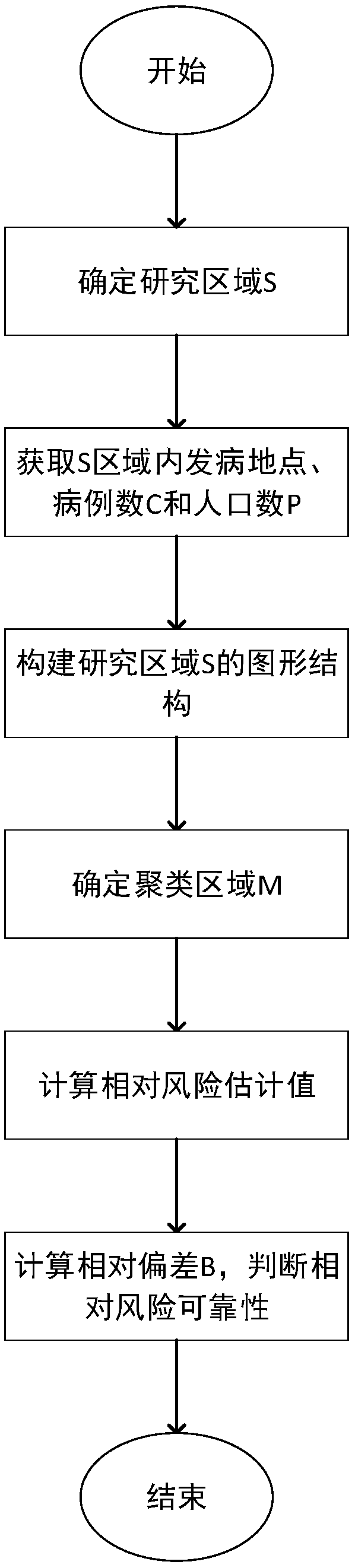
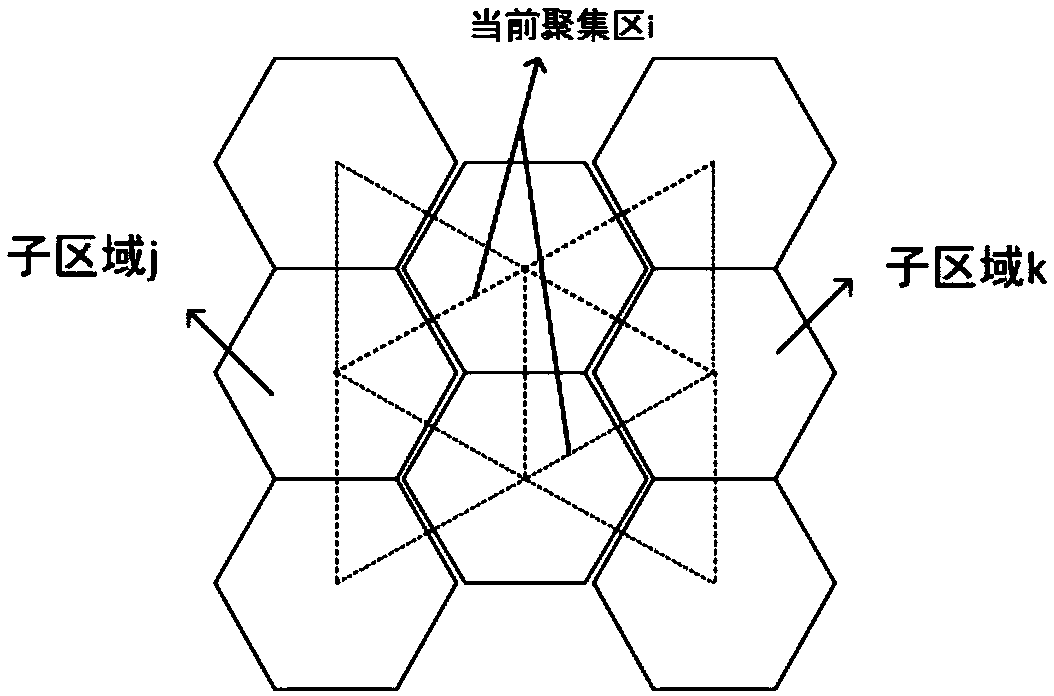
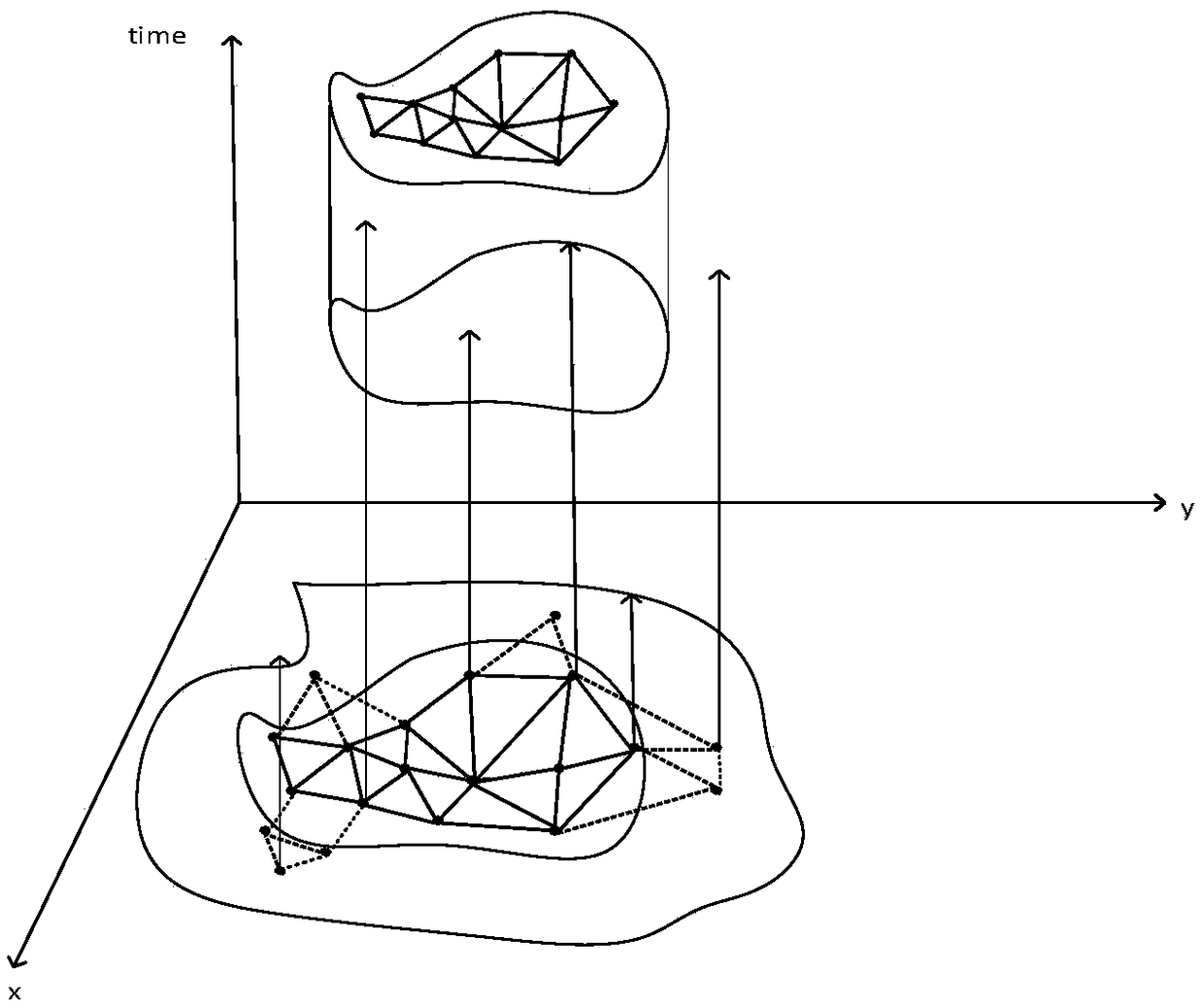
[0047] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, an irregular-shaped spatio-temporal scanning clustering method based on maximum association and risk deviation, introducing graph structure and maximum association (mlink) algorithm, finds that there is an unconventional shape aggregation area in this area; and then by calculating the relative Risk and risk deviation, to judge whether the relative risk of this gathering is accurate.
[0048] The specific steps are:
[0049] Step1. Determine the research area S;
[0050] Step2. Obtain the number of cases C in the monitoring area S and the onset location and population P of each case;
[0051] Step3, according to the location coordinates and the traffic route map of each sub-area in the area S, construct the graphic structure of the area S;
[0052] Step4. According to the maximum association algorithm, detect and determine the shape of the scanning window from the area S and search for the potential aggregation area M;
[0053] Ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com