Automated guided vehicle AGV path optimization method and system in automated container terminal quay crane transpoint QCTP operation
An automated dock and route optimization technology, applied in the field of automated docks, can solve problems such as affecting the efficiency of AGV operations, less workload, and waste of resources, and achieve the effect of improving the efficiency of AGV operations and reducing the running distance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The specific implementation manners of the present application will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
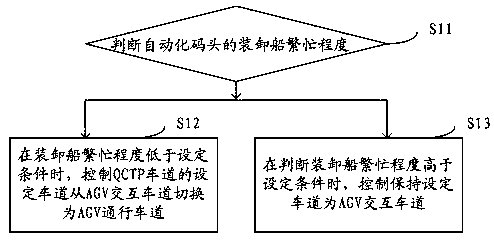
[0023] The AGV path optimization method in the automatic terminal QCTP operation proposed by this application, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
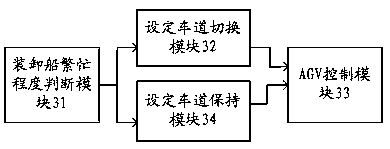
[0024] Step S11: Determine the busyness of the loading and unloading ships at the automated terminal.
[0025] The busyness of loading and unloading ships represents the current workload of the automated terminal, and is defined to a set condition, such as the container loading and unloading volume per hour, or the utilization rate of bridge cranes or field cranes within a set time period, etc., in this application In the embodiment, for the QCTP lane, it is possible to determine the frequency of the AGV entering and leaving the QCTP lane.
[0026] Step S12: When the busyness of the loading and unloading ship is lower than the set condition, control t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com