A method for recognizing and evaluating a pedal motion in a virtual assembly operation
A technology of motion recognition and virtual assembly, applied in the field of somatosensory interaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] A method for recognizing and evaluating pedal movements in virtual assembly operations, the specific process is as follows:
[0053] Step 1: Build the pedal scene
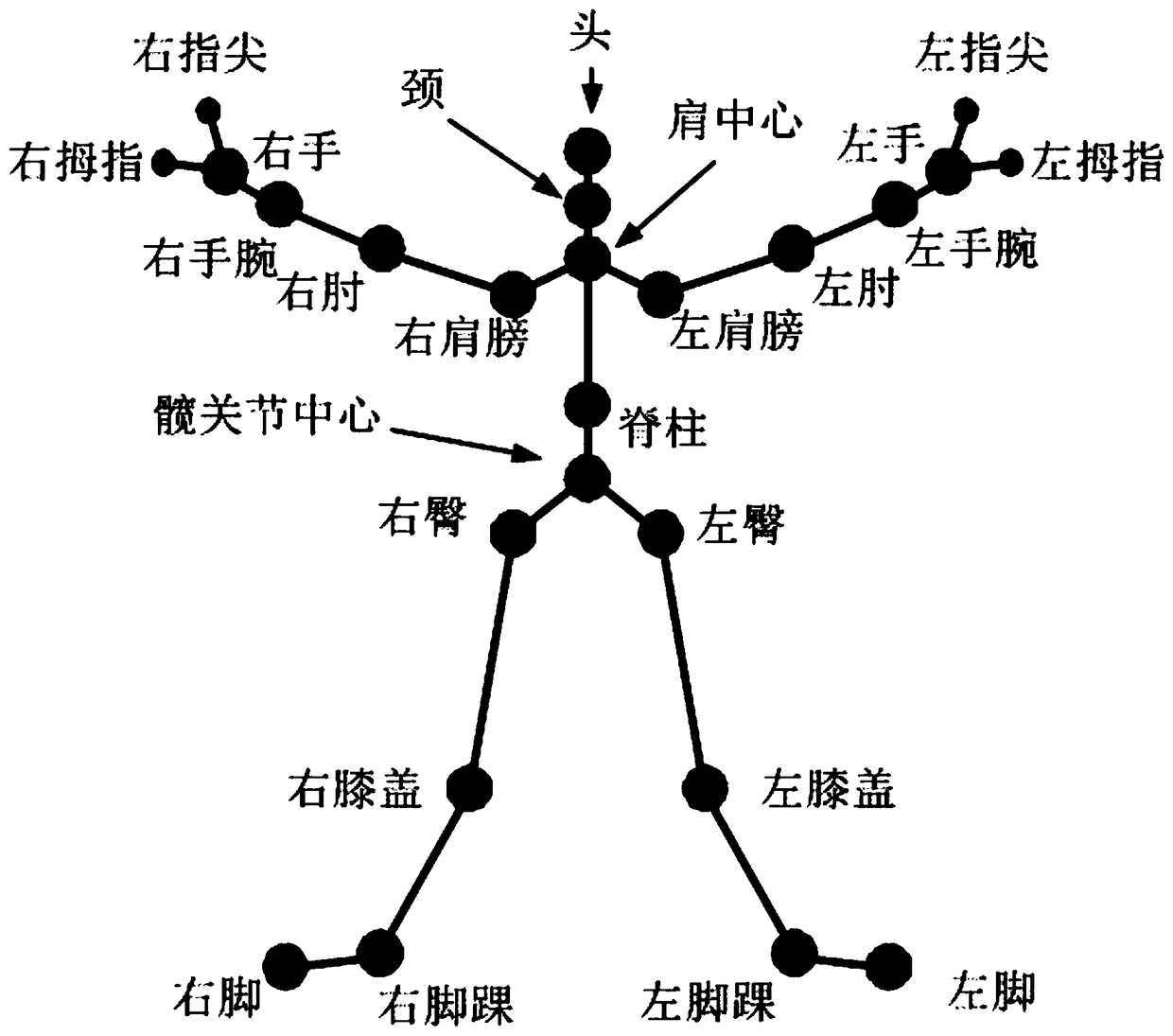
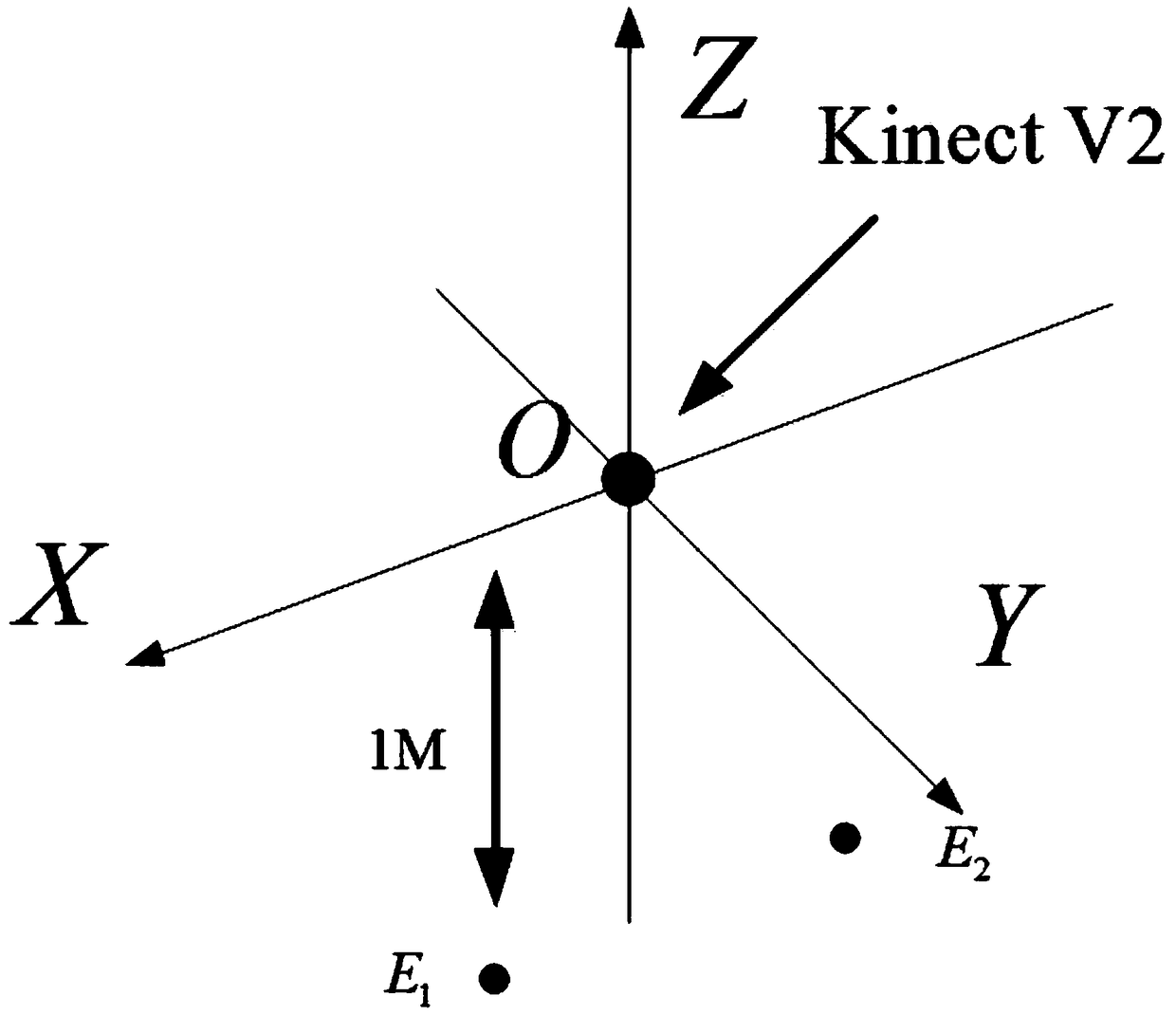
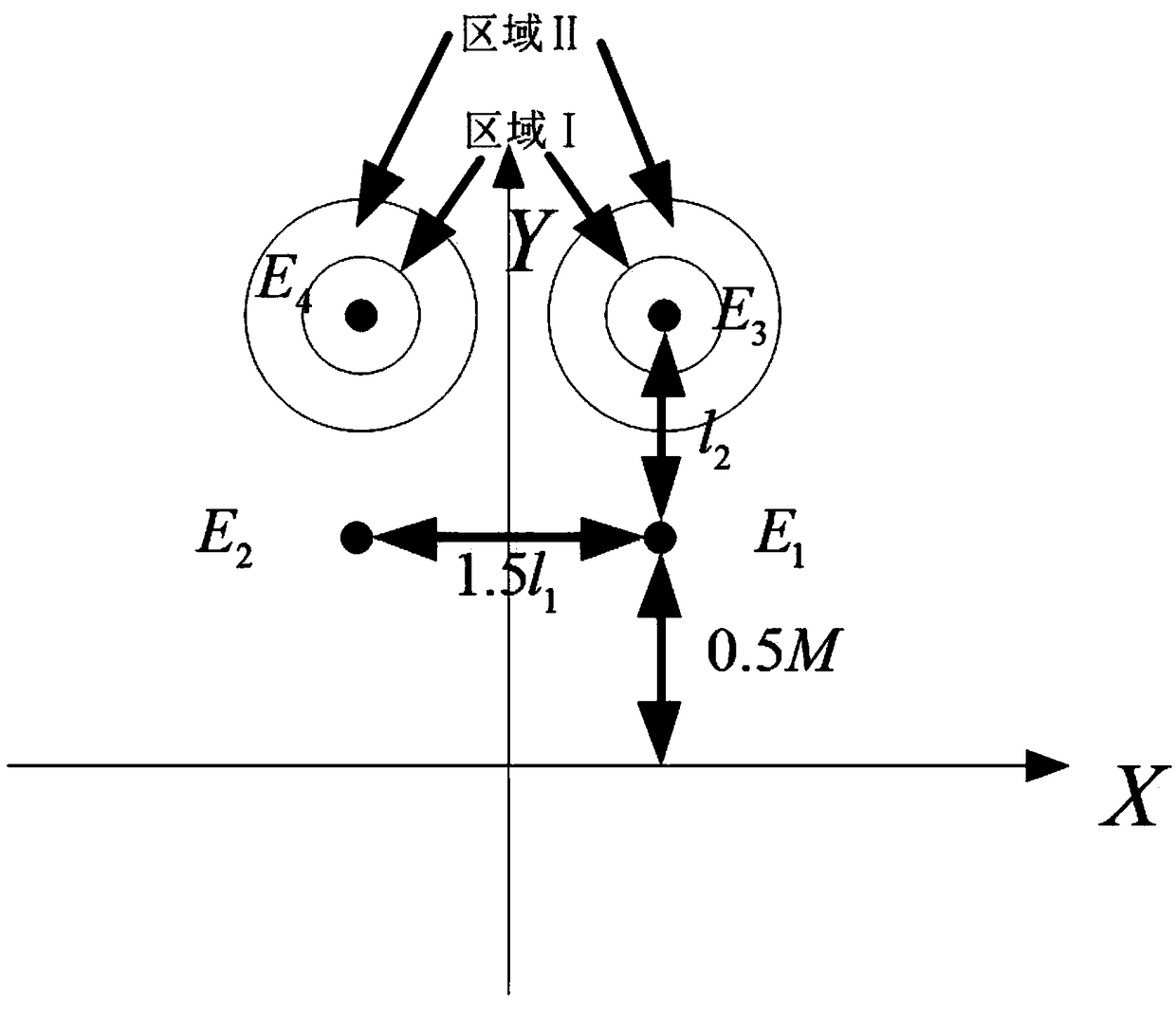
[0054] refer to figure 1 , put the Kinect V2 device horizontally, and keep a distance of 1m from the ground in the virtual scene; use Kinect V2 to collect 25 human skeleton points including head, neck, shoulder center, left thumb, right thumb, left fingertip, right fingertip , left hand, right hand, left wrist, right wrist, left elbow, right elbow, left shoulder, right shoulder, spine, hip center, left hip, left knee, left ankle, left foot, right hip, right knee, right ankle, Right foot; where, A 1 (x 1,i ,y 1,i ,z 1,i ) represents the coordinate point of the left buttock of the i-th frame, 25 frames per second, and 0.04 seconds per frame; A 2 (x 2,i ,y 2,i ,z 2,i ) represents the coordinate point of the left knee of the i-th frame, 25 frames per second, 0.04 seconds per frame; A 3 (x 3,i ,y 3,i ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com