A method for unloading content at the edge of the Internet of Vehicles, and a mobile resource allocation system
A vehicle networking and content technology, applied in vehicle components, vehicle-to-vehicle communication, and vehicle wireless communication services, etc., can solve the problems of consuming network resources, wasting resources, and not taking into account the computing power of vehicles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
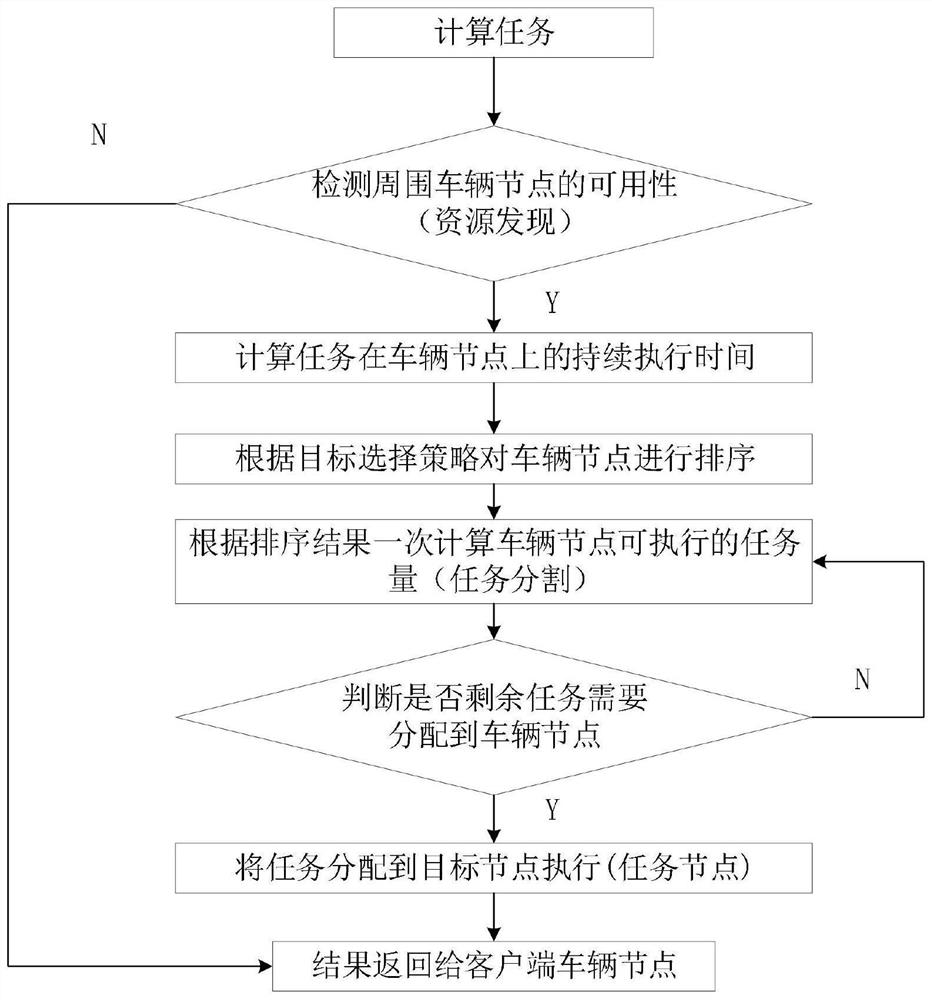
[0053] Such as figure 2 As shown, the Internet of Vehicles content edge offloading method provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps: including the following steps:
[0054] Step 1. In the vehicular ad hoc network, due to the high-speed mobility of vehicle nodes, the number and location of resources may change at any time. Therefore, before task offloading, it is necessary to detect resources and filter out available resource information that meets the conditions. ;
[0055] When the client vehicle has a computing task that needs to use the resources of the surrounding vehicles, the resource discovery module first detects the availability of the surrounding vehicles, that is, detects those vehicles that can provide computing resources (resource discovery), and queries the available vehicle node information (vehicle relative position, speed of movement, direction of movement, computing power, etc.).
[0056] Step 2, based on the collecte...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The method for unloading the Internet of Vehicles content edge provided by the embodiment of the present invention is the same as that in Embodiment 1;
[0062] The detection of those vehicles in step 1 that can provide computing resources includes the following:
[0063] The resource discovery module is used to discover available vehicle node computing resources, that is, vehicle node reachability monitoring and resource availability detection, and record the parameters of these nodes, usually recording the computing power, moving speed, moving direction, relative Location.
[0064] Define parameters:
[0065] Computing capability of the vehicle: the computing capability C of the vehicle i ,i=1,2,3..., indicating the number of subtasks that the vehicle can execute per second.
[0066] The moving speed of the vehicle: v i ,i=1,2,3..., the speed of the vehicle.
[0067] The maximum time that vehicles can communicate with each other: T ij , i, j = 1, 2, 3..., that i...
Embodiment 3
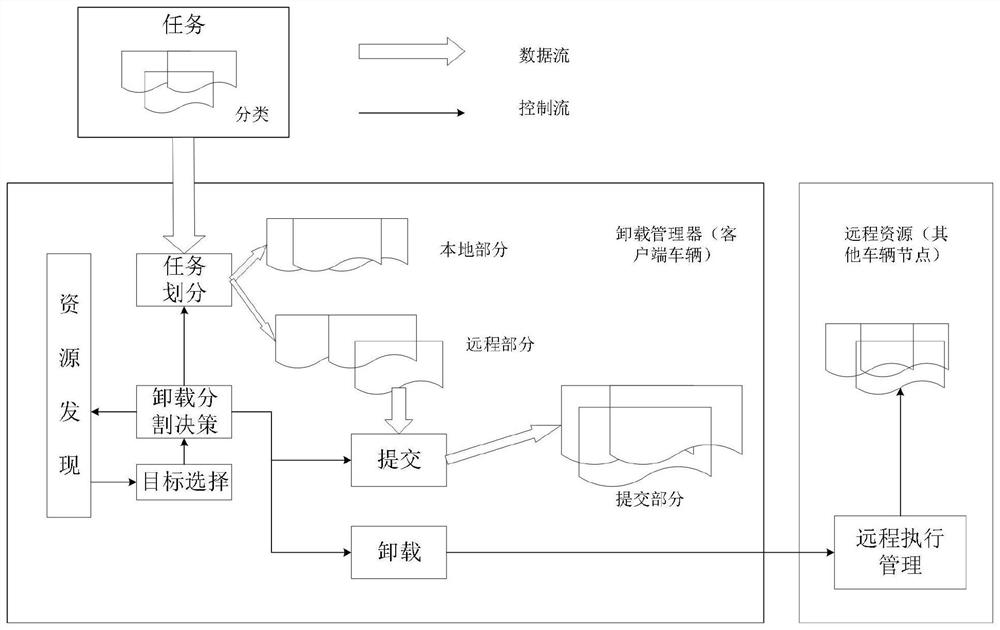
[0073] The edge offloading method of Internet of Vehicles content provided by the embodiment of the present invention is the same as Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, such as Figure 5 As shown, the task division in step 2 includes the following:
[0074] The task division module divides the task into small subtasks according to the information of available resources, and makes the connection between the subtasks as few as possible, strong independence, low coupling and high aggregation. Computational tasks are composed of several subtasks, namely The subtasks are relatively independent, and the size of each subtask is the same, that is, then J 1 =J 2 =…=J i =…=J n , each vehicle node can perform several subtasks according to the amount of computing resources.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com