Method for evaluating activity of bacteria after transplanting bacteria into digestive tract
A method for evaluating the activity of bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] With reference to the following detailed description and exemplary embodiments, it should be understood that the application is not limited to the details or methodology set forth in the specification or shown in the drawings.
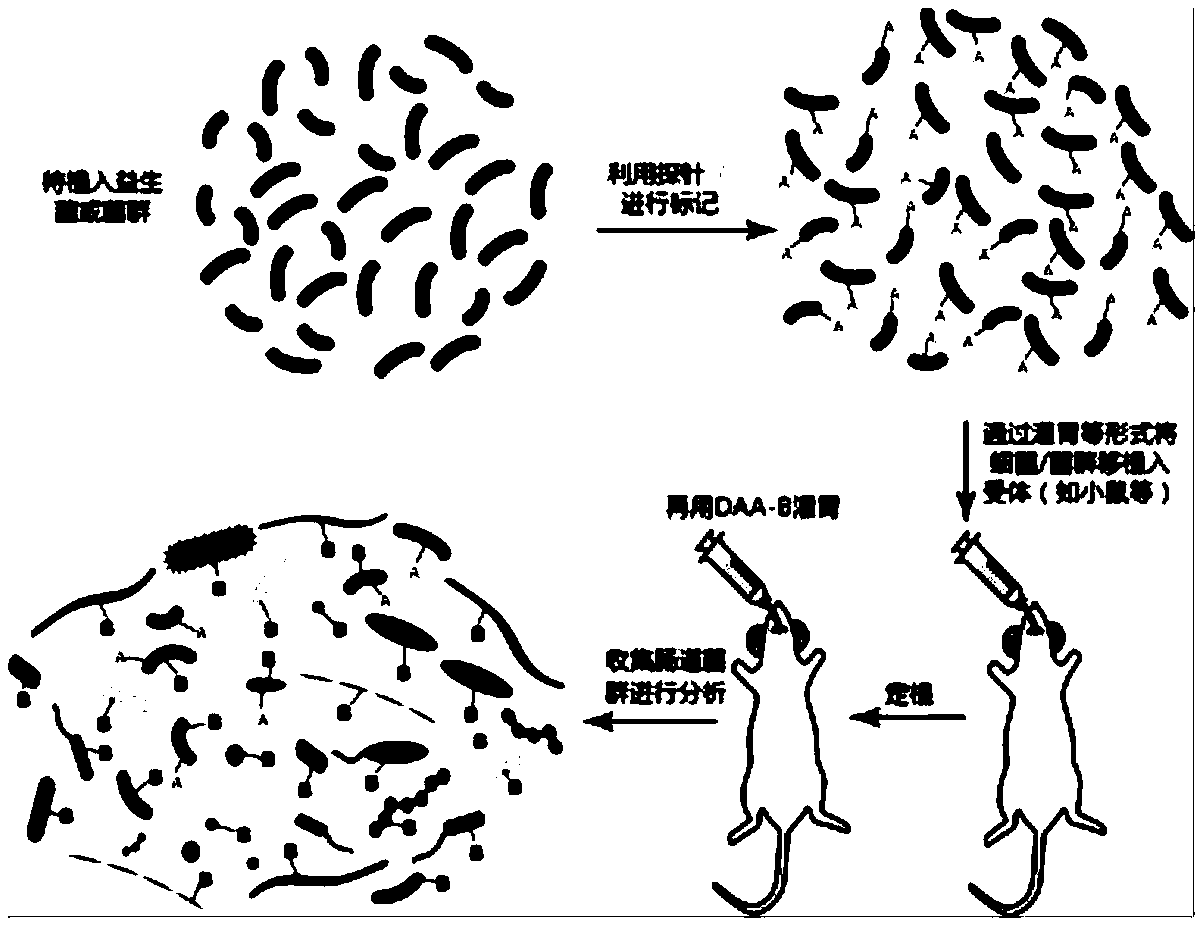
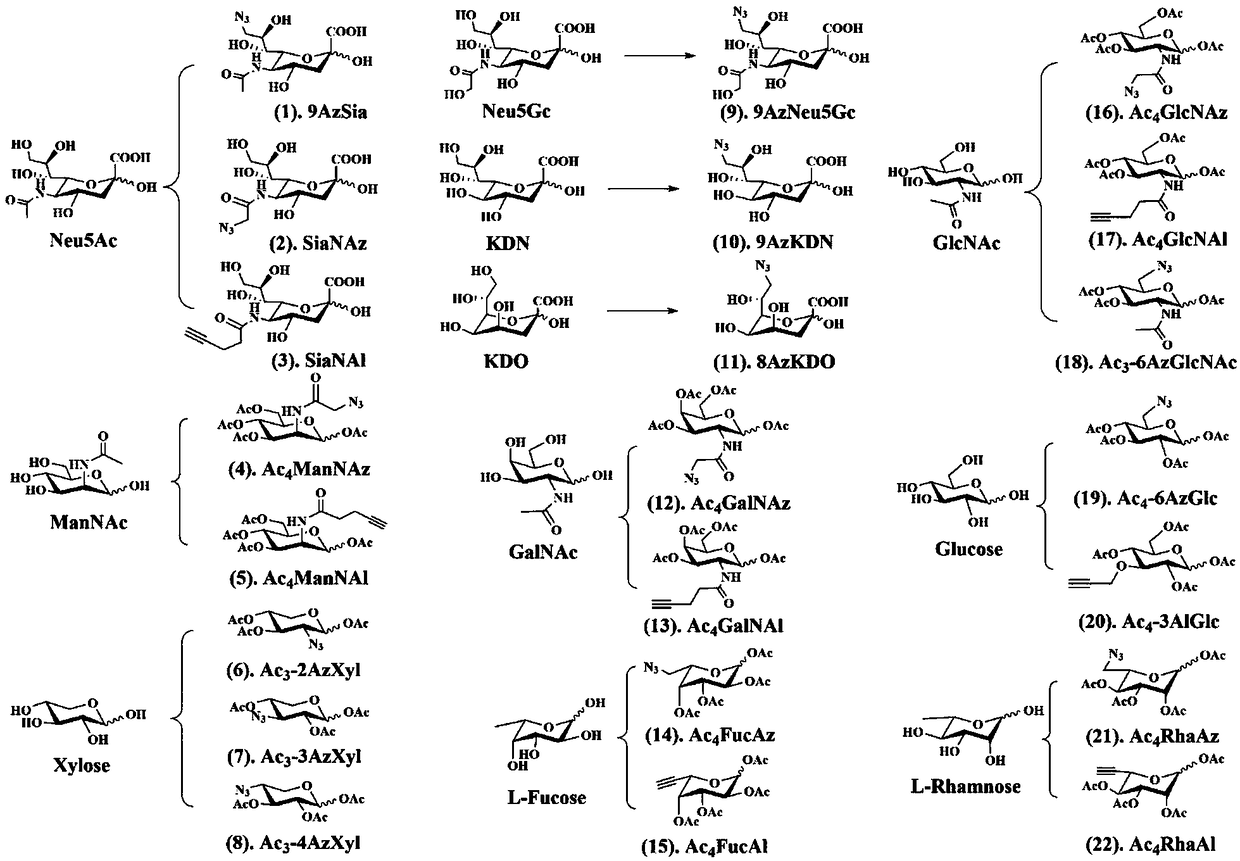
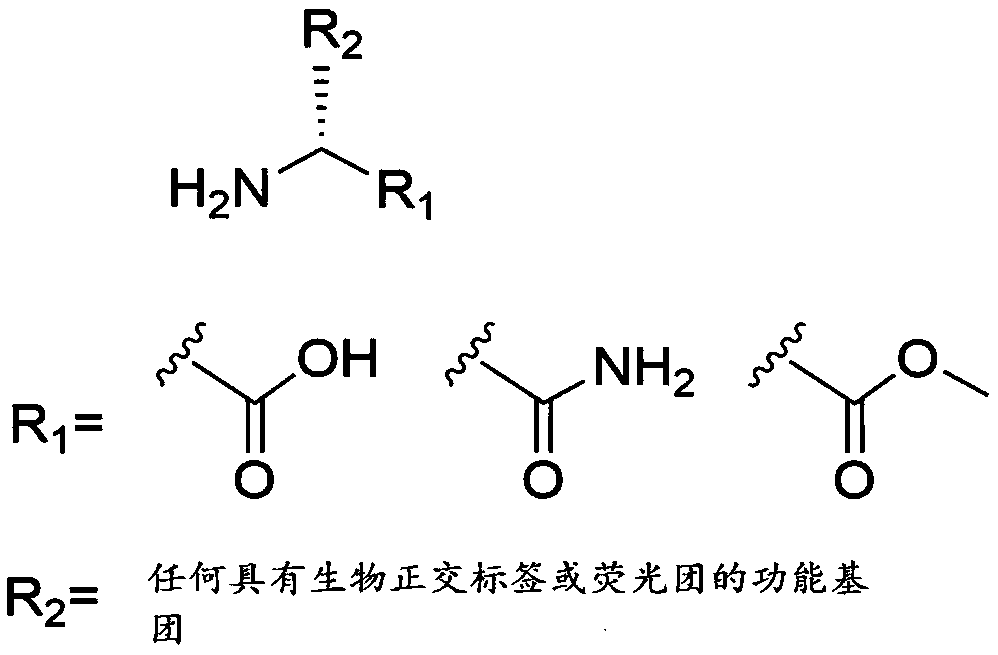
[0018] refer to figure 1 Shown, in the activity evaluation method of the bacterium that the present invention relates to transplanting into the alimentary canal, in the cultivation process (such as in vivo or in vitro cultivation) before implantation bacterium implantation, add A group marker (or be referred to as the first group marker) so that the cultured and active implanted bacteria are marked with the A group; then the implanted bacteria are transplanted into the digestive tract of the host (such as by gavage), and after a period of colonization (such as 6-12h) , using a marker with a B group (or called a second group marker) to treat the intestinal flora of the recipient after receiving the implanted bacteria, for example, by gavage the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com