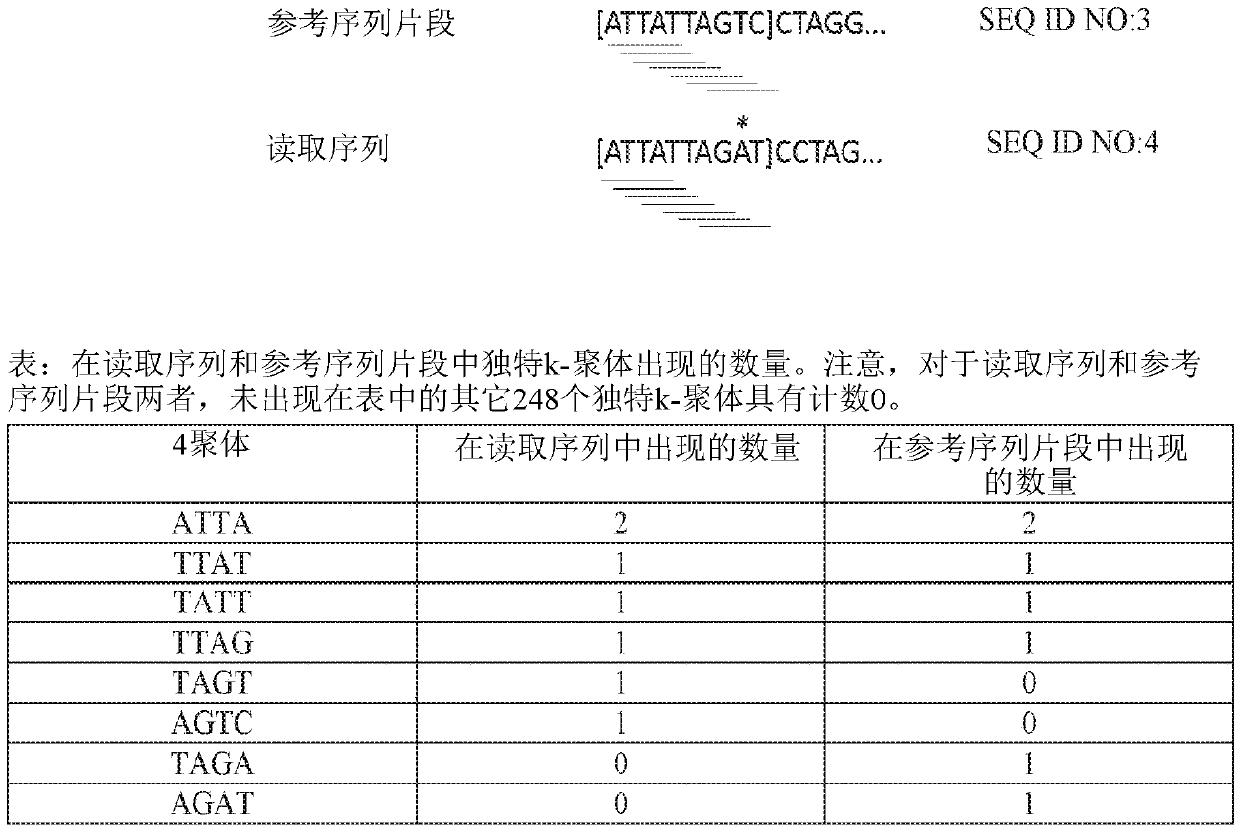
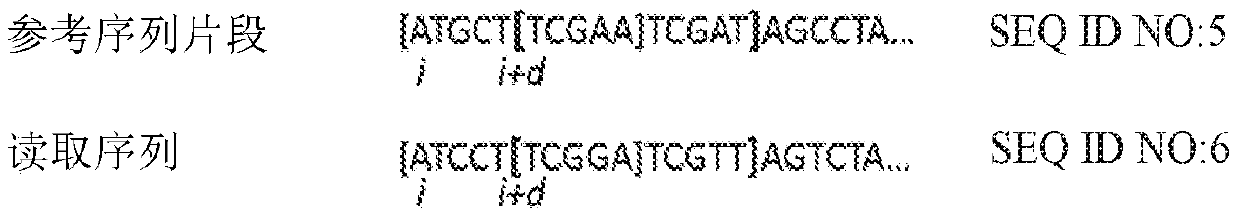Third generation sequencing alignment algorithm
A sequence and iterative technology, applied in the field of third-generation sequencing alignment algorithms, which can solve problems such as high error rate and confusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0124] The following are examples of specific embodiments for carrying out the invention. Examples are provided for illustrative purposes only and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
[0125] Efforts have been made to ensure accuracy with respect to numbers used (eg amounts, temperature, etc.), but some experimental errors and deviations should be granted.
example 1
[0127] Demonstration of the effect of the cosine similarity measure using the E. coli genome.
[0128] Cosine similarity is a measure used to determine the similarity between two vectors by measuring the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. To demonstrate the effect of this metric, 1000 sequences of 5000 bases in length were each selected at random positions in the E. coli genome. For each sequence, between non-overlapping windows of different lengths w = 50, 100, 500, 1000 and 5000 bases, and 10 of them within each window of sequences and average substitution rates of 15% and 35% The distance cosine (1-cosine similarity) is calculated between random mutation patterns. Figure 7-8 and 9-10 exhibit a distance cosine distribution for k=3 and k=4, respectively. Figure 7-8 and 9-10 illustrate how the distribution of the distance cosines between short k-mer count vectors at random positions is distinguishable from their mutation patterns. Furthermore, as expected, the d...
example 2
[0134] Accuracy and performance analysis using the E. coli genome
[0135] The accuracy and performance of this method was evaluated using a dataset of 20x simulated reads from the E. coli genome with average lengths of 5 kbps and 10 kbps and different sequence accuracies of 85%, 75%, 65% and 55%. read-seq using with-options (--data-typeclr --depth20 --model_qc model_qc_clr --accuracy-min 0.5 --length-average[5000|10000] --length-sd 2000 --accuracy-average [.85|.75|.65|.55] - Accuracy - sd 0.02) simulation of PBSIM (Ono et al., 2013).
[0136] In the default setting (w=500, L t = 7500, f = 2, g = 1, max-num-top-peak = 10, max-fft-block-size = 32768 are reported in Tables 1 and 2 for data sets with average sequence lengths of 5 kbps and 10 kbps, respectively Performance of k=3,4. Even with ~45% error rate, k=4 has almost perfect accuracy. As expected from Table 2, longer reads resulted in a higher overall alignment rate, particularly when mapping reads covering long repeat ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com