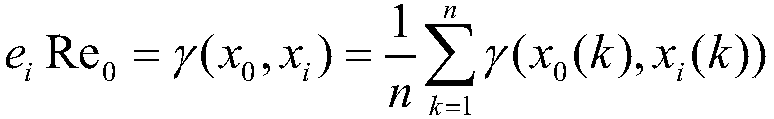Systematic method for determining hierarchical structure of accident factors by using gray correlation
A technology of gray correlation degree and construction method, which is applied in the field of systematic analysis of the relationship between multiple levels of accident factors, can solve the problems of incomplete and non-specific analysis of accident factor levels, and achieve the effect of reducing impact and reducing safety accidents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
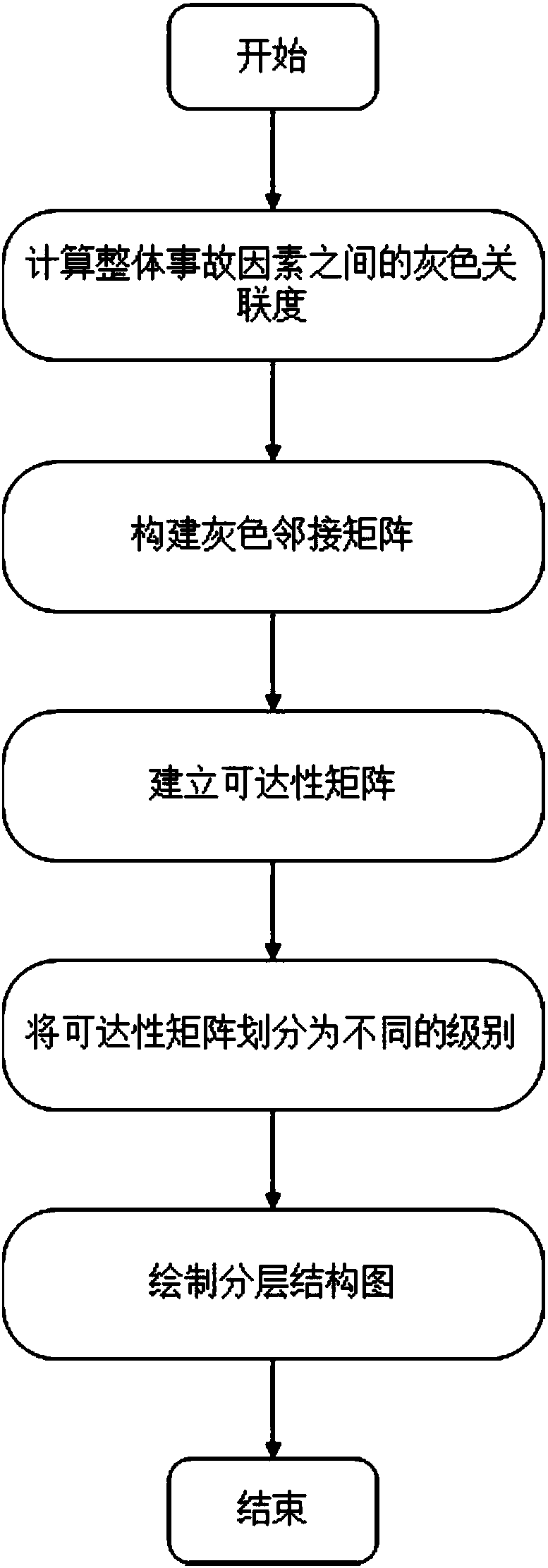
[0027] This example realizes that the technology for determining the level of accident factors includes four parts:
[0028] (1) Calculate the correlation degree among the accident factors. Suppose there are n elements in the accident system, the set is S={e 1 ,e 2 ,...,e n}, by corresponding to the items checked in the observation enforcement checklist, the behavior sequence of all elements can be obtained, here is the time series. X is the set of these time series: X={x i |i=0,1,2,...,n}. x i ,y i ∈X, symbol γ(x i ,y i ) means x i and y i The degree of adjacency between them is the so-called gray correlation coefficient. The theorem of gray relation is:
[0029] 1) Comparable. That is, each sequence in X is dimensionless, equal in size, uniform in polarity, and the number is greater than three.
[0030] 2) Norm interval. 00 ,y i )≤1. (i) if x i =x j , γ(x i ,y i )=1. (ii) if x i ,y j ∈φ, γ(x i ,y i ) = 0.
[0031] 3) Integrity. If n≥3 and i≠j, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com