Star sensor installation layout method based on staring attitude of remote sensing satellite
A technology for star sensors and remote sensing satellites, applied in the field of remote sensing satellites, can solve problems such as the complexity of star sensor layout methods, and achieve the effect of simple layout methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
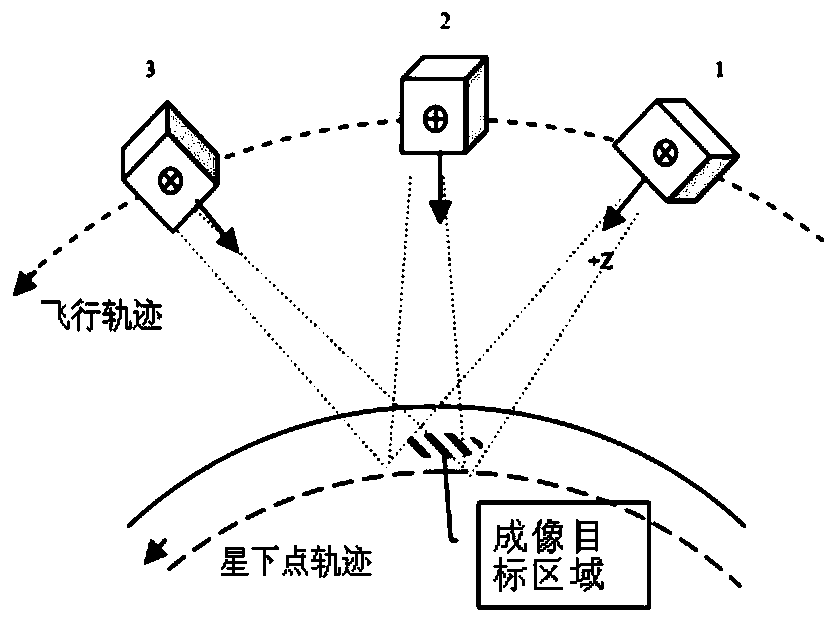
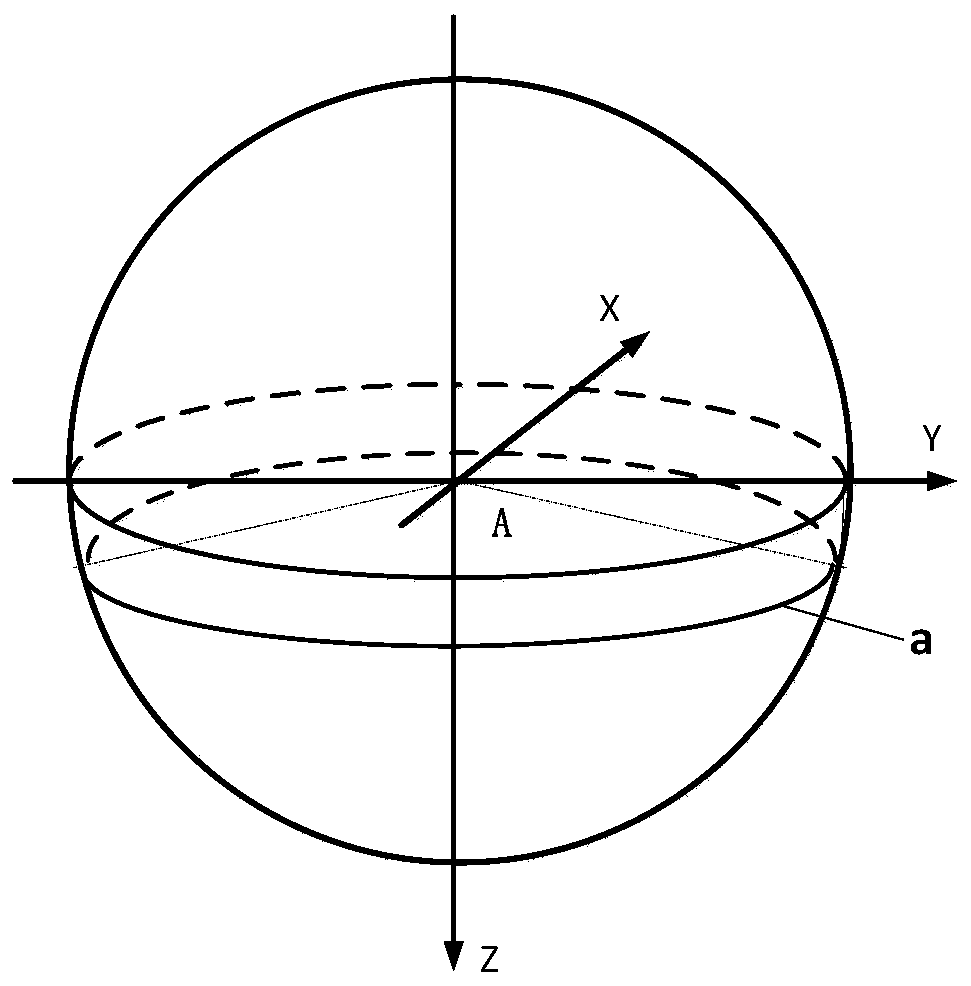
[0033] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figure 2 to Figure 7 Describe this embodiment, the star sensor installation layout method based on remote sensing satellite staring attitude, this method is realized by the following steps:
[0034] First, define two coordinate systems: the satellite orbit coordinate system and the satellite body coordinate system:
[0035] Satellite body coordinate system: the satellite body coordinate system refers to the rectangular coordinate system fixed to the satellite, the coordinate origin is at the center of mass of the satellite, and the +Z axis is perpendicular to the docking surface of the satellite docking ring and the transition section of the vehicle, pointing to the optical camera; +X The axis is in the docking plane between the satellite docking ring and the transition section of the vehicle, and is in the same direction as the satellite flight direction; the +Y axis is determined according to the right-hand rule.
[0036] ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0053] Specific embodiment two, combine Figure 8 and Figure 9 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment is the embodiment of the star sensor installation layout method based on remote sensing satellite staring attitude described in specific embodiment one:
[0054] In this embodiment, the altitude of the satellite orbit is set: 500.0km; the local time of the descending node: 11:30am; the sun avoidance angle of the star sensor: 25°; the earth avoidance angle of the star sensor: 25°; the staring angle of the satellite: 30°.
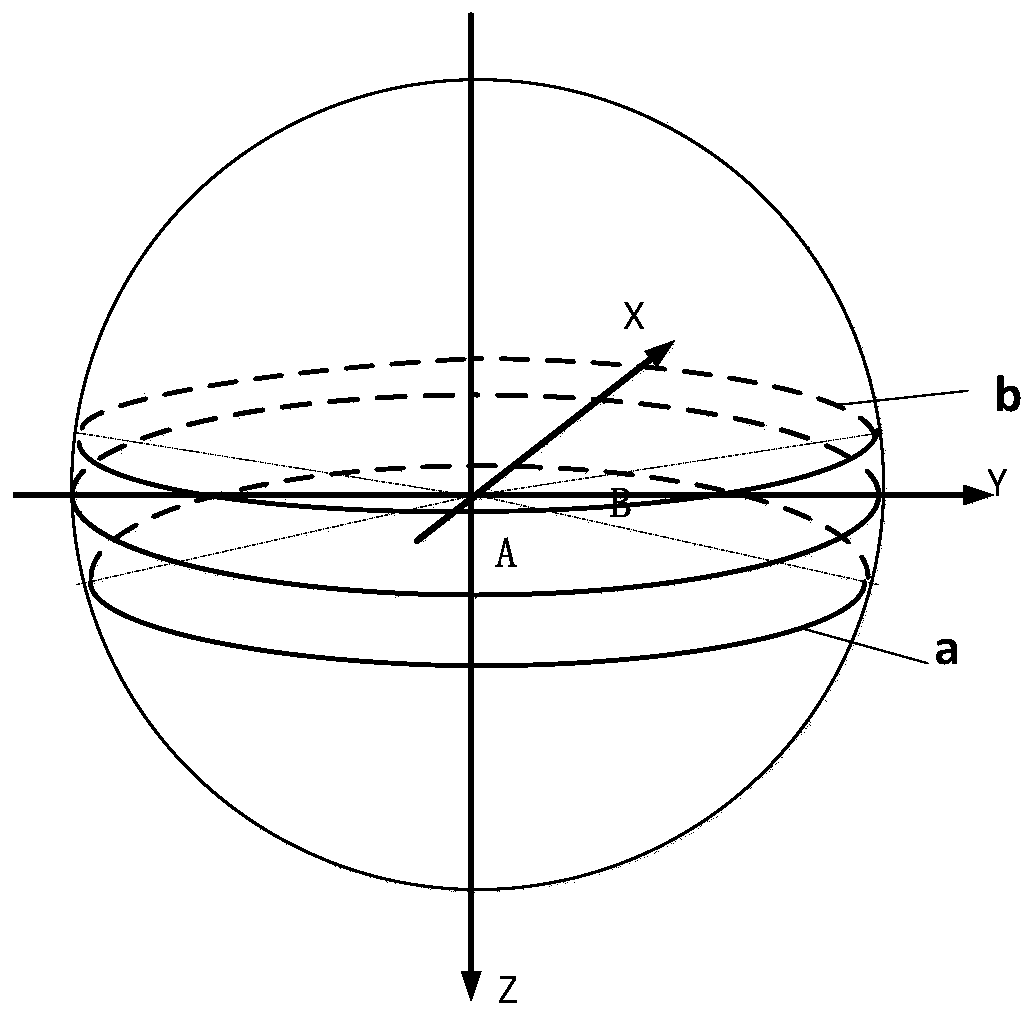
[0055] The included angle ∠A=70.3635° is calculated by the formula, and the range of the included angle between the sun vector and the orbital surface within a year is 3.5°~12.6° through orbital analysis software simulation analysis.
[0056] Using the method described in Embodiment 1, the calculated results are as follows Figure 9 shown. The area shown in the figure is the area that satisfies the Earth avoidance angle of the star sensor, and the dark...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0060] Specific implementation mode three, combination Figure 10 and Figure 11 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment is the embodiment of the star sensor installation layout method based on remote sensing satellite staring attitude described in specific embodiment one:
[0061] Satellite orbit altitude: 636.0km; descending node local time: 10:00am; star sensor sun avoidance angle: 30°; star sensor earth avoidance angle: 30°; satellite gaze angle: 35°.
[0062] The included angle ∠A=67.4554° is calculated by the formula, and the range of the included angle between the sun vector and the orbital surface within a year is 23.5°~34.5° through orbital analysis software simulation analysis.
[0063] According to the method described in specific embodiment one, the calculated result is as follows Figure 11 shown. The area shown in the figure is the area that satisfies the Earth avoidance angle of the star sensor, and the dark area in the figure is the effective area where th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com