Block chain consensus method
A blockchain and consensus technology, applied in the blockchain field, can solve problems such as low efficiency, Validator is easy to do evil, illegal, etc., and achieve high efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: This embodiment specifically illustrates the steps of the blockchain consensus method, as follows:
[0028] The roles of the consensus method include: Validator, Validator Set, Vg, fund account and mortgage account;
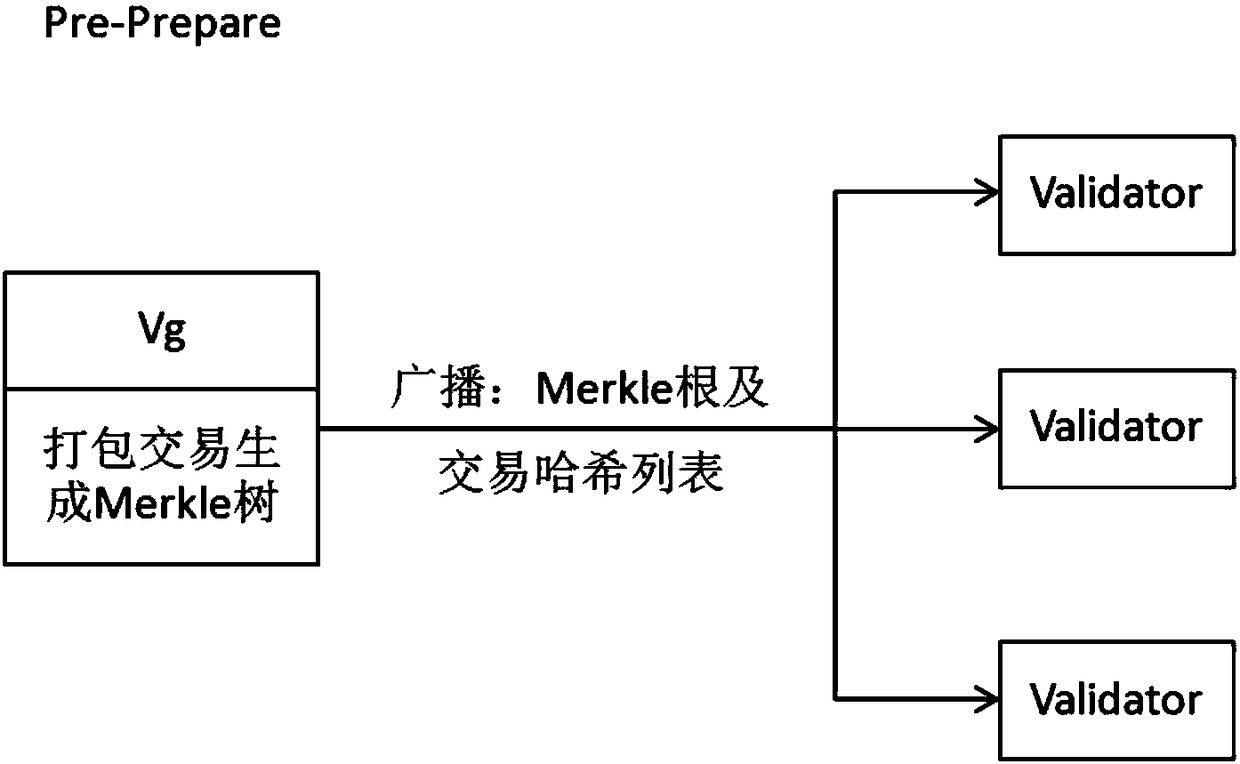
[0029]Validator is a node that votes on the block. Each Validator holds a certain stake. Validators include honest Validators and dishonest Validators. The number of Validators is 3f+1, where f is a positive integer, and non-honest Validators The number of validators is not greater than f; Validator Set is a collection of all validators participating in voting, and the validator set needs to be determined before each round of consensus; during each round of consensus, a validator is randomly selected from the validator set to generate a block, and the selected validator is Vg , Vg is also used to package transactions, generate Merkle trees, and broadcast lists of Merkle roots and transaction hashes; the fund account is used to store the secur...
Embodiment 2
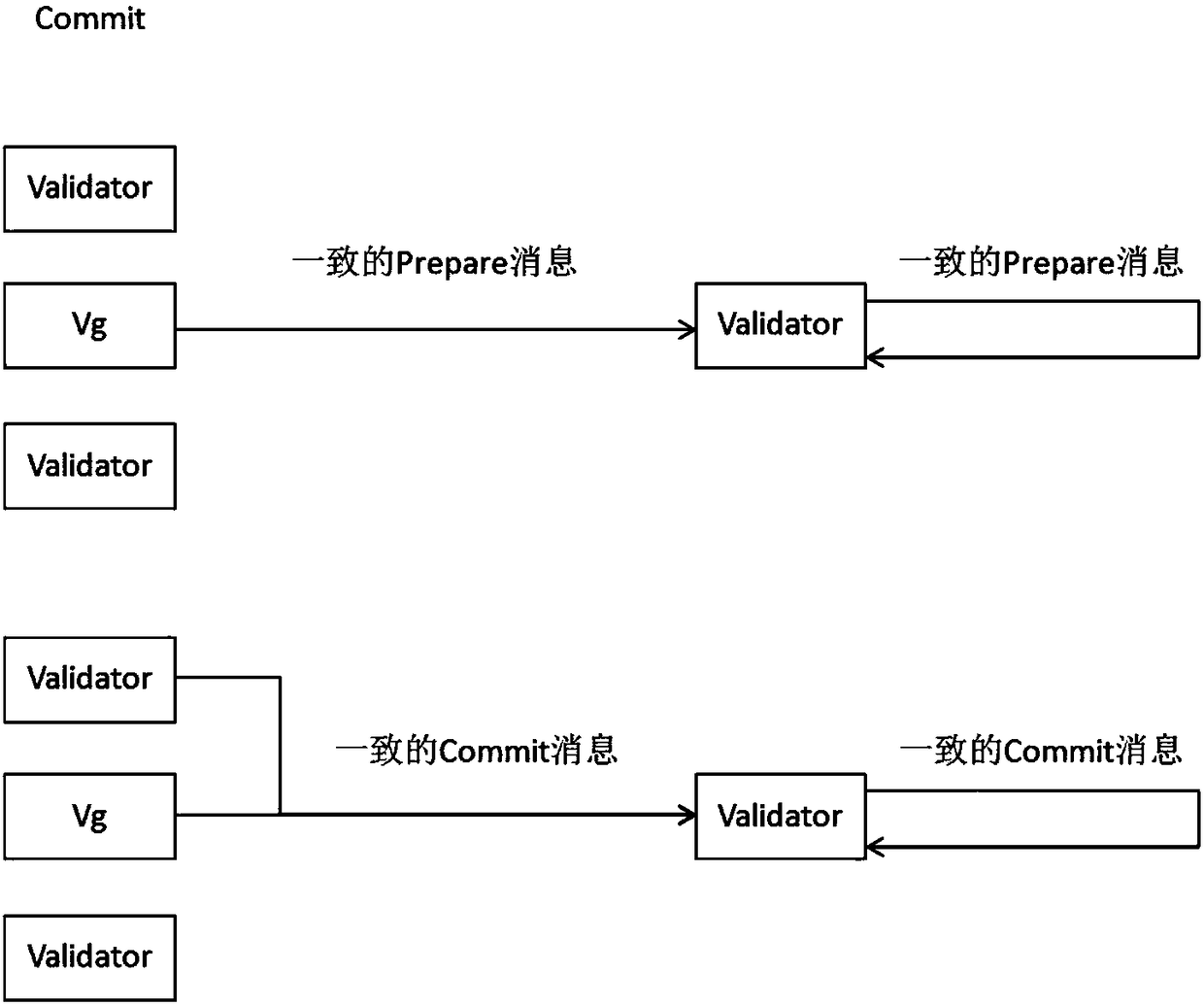
[0042] Embodiment 2: This embodiment exemplifies the process of generating blocks by the consensus method of the block chain, such as figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 :
[0043] After the previous block is packaged and written into the blockchain, a new round of consensus is started to generate a new block. The steps for generating a block by the consensus method are as follows:
[0044] Step S1: Determine the Validator Set, assuming f=1, there are at least 4 Validators in the system (3f+1=4); among them, 1 Validator is selected as Vg, in fact, there are 1 Vg and 3 Validators in the system ;
[0045] Step S2: if figure 1 , in the Pre-Prepare process, randomly select a Validator from the Validator Set as Vg, Vg packs the collected transactions, generates a Merkle tree from the transaction list, and then broadcasts the list of Merkle roots and transaction hashes as a Pre-Prepare message To the other 3 Validators in the Validators Set;
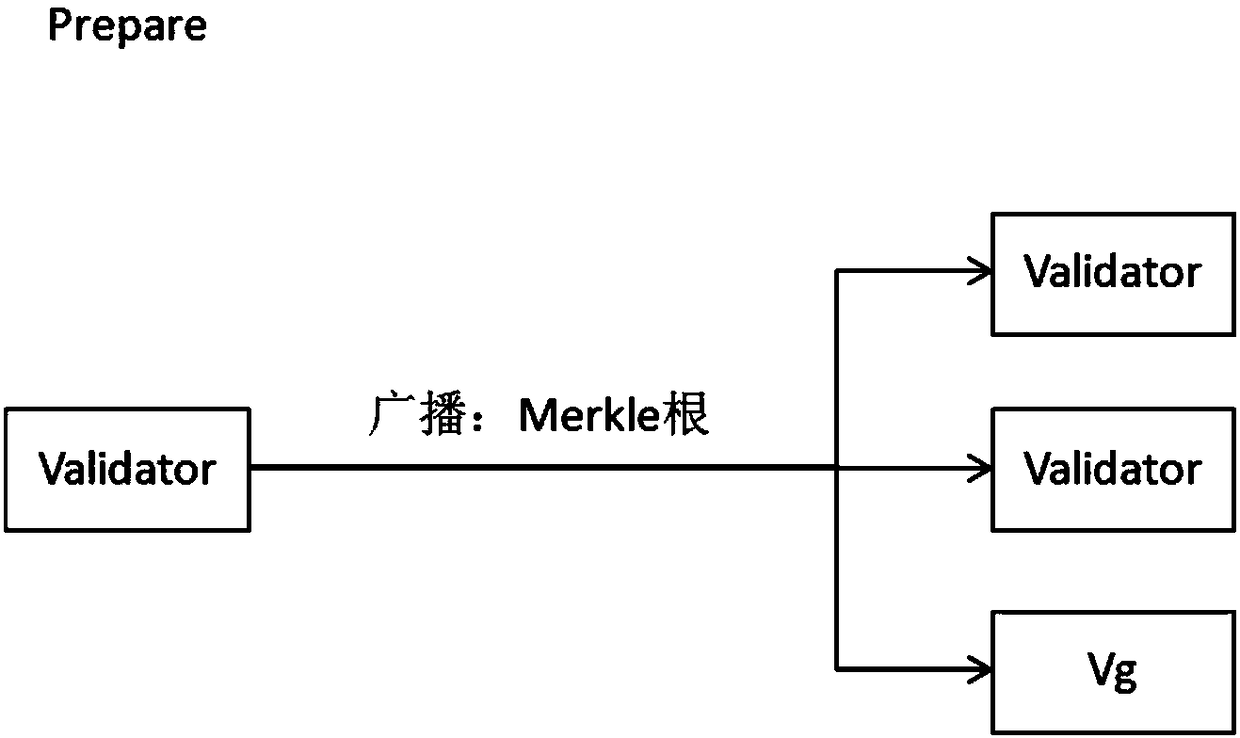
[0046] Step S3: if figure 2 , in ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3: This embodiment exemplifies the process of judging legality, such as Figure 4 :
[0050] After the block chain system generates Block(H), when the next round of consensus generates Block(H+1), N Validators will be randomly selected to vote on the validity of Block(H); if the Validators have different Opinions, then continue to randomly select different Validators to vote until there are N votes from the Validators holding a certain opinion, at which point the legitimacy of Block(H) can be determined.
[0051] The blockchain system sets N to be 5:
[0052] If all 5 Validators think Block(H) is legal, then Block(H) is legal;
[0053] If 5 Validators have different opinions, if 3 Validators think that Block(H) is legal, and 2 Validators think that Block(H) is illegal, then continue to randomly select 2 different Validators to vote for Block(H); these 2 Validators Among them, if 2 Validators think that Block(H) is legal, at this time there are 5 Validators...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com