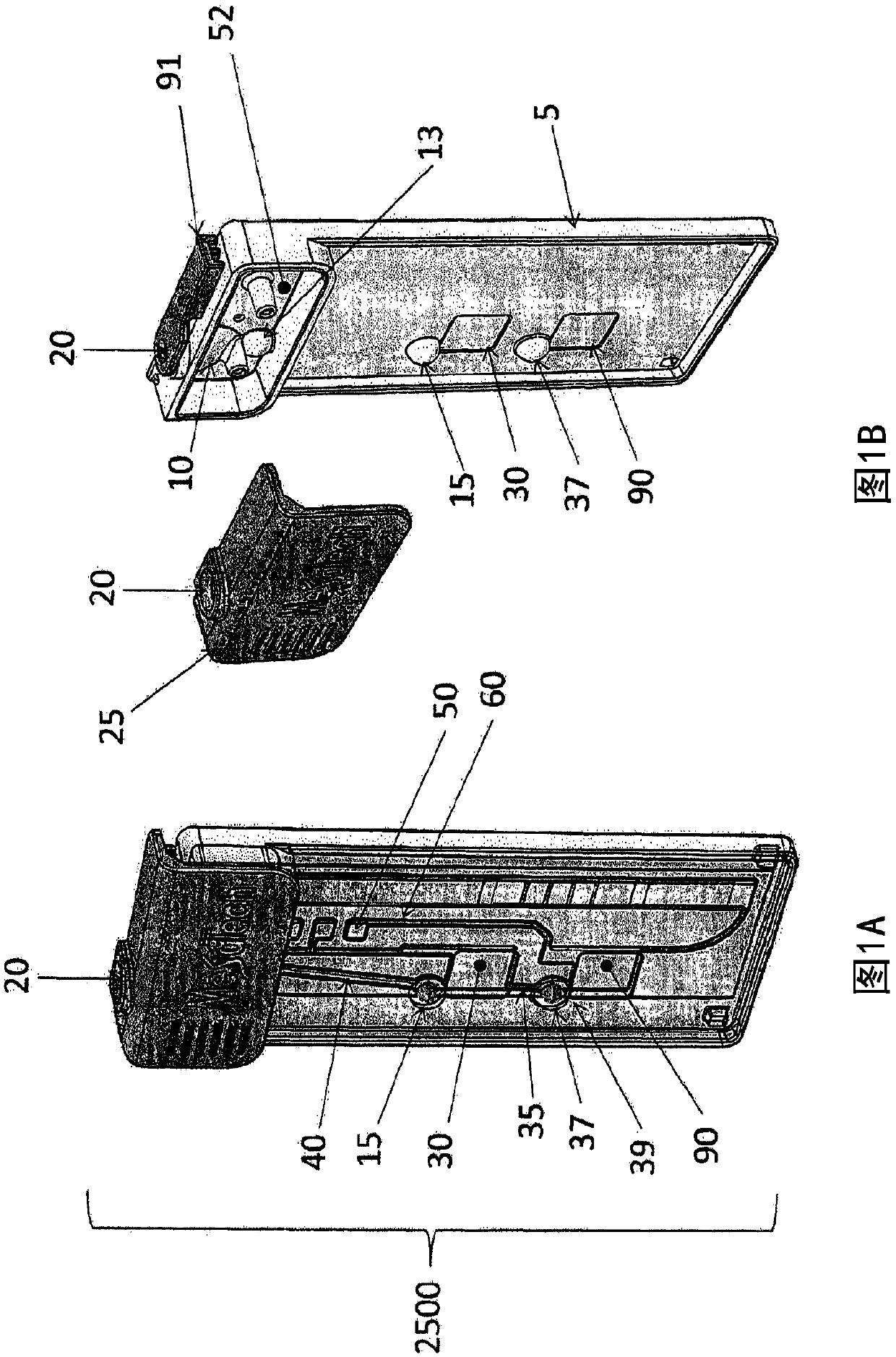
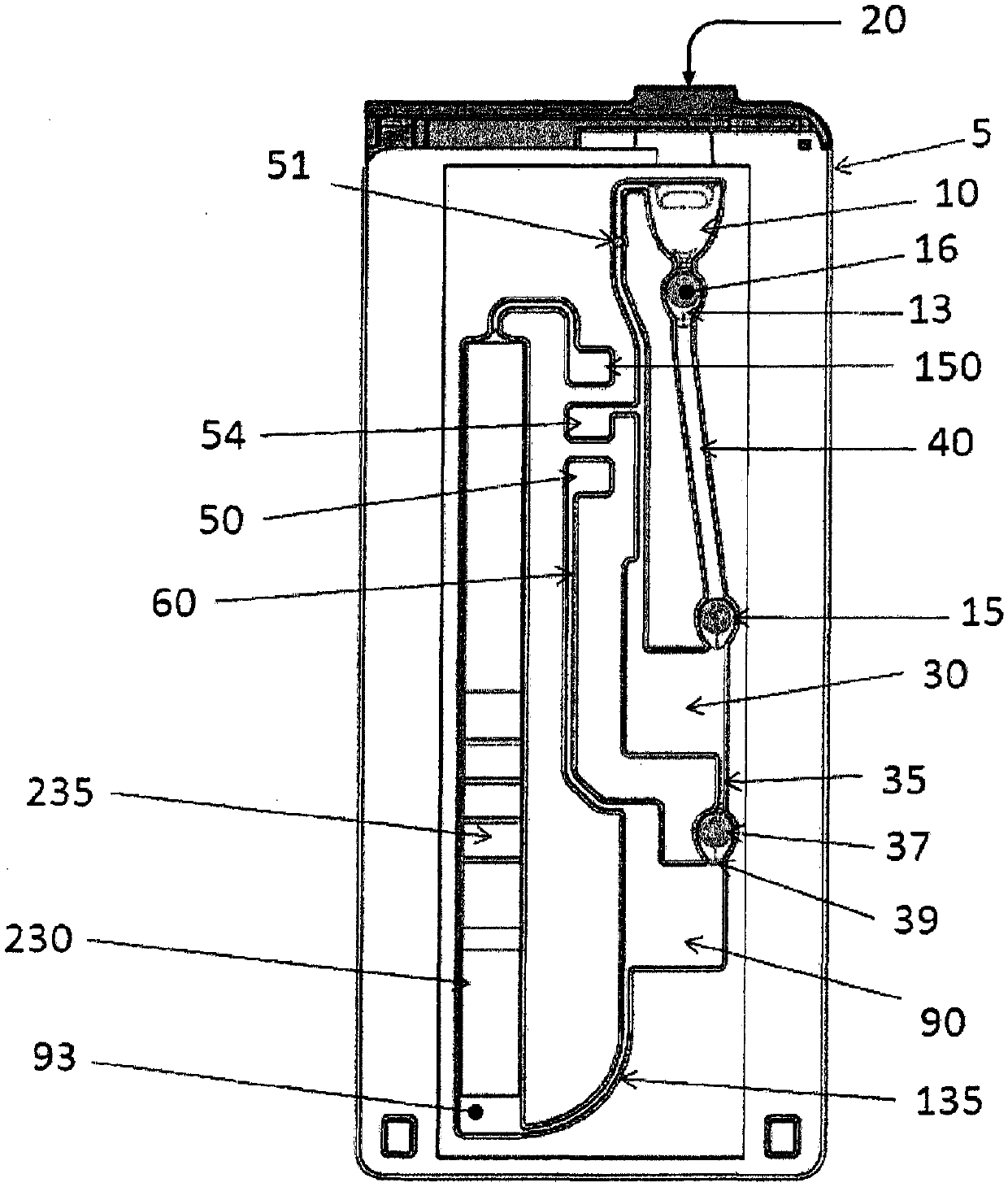
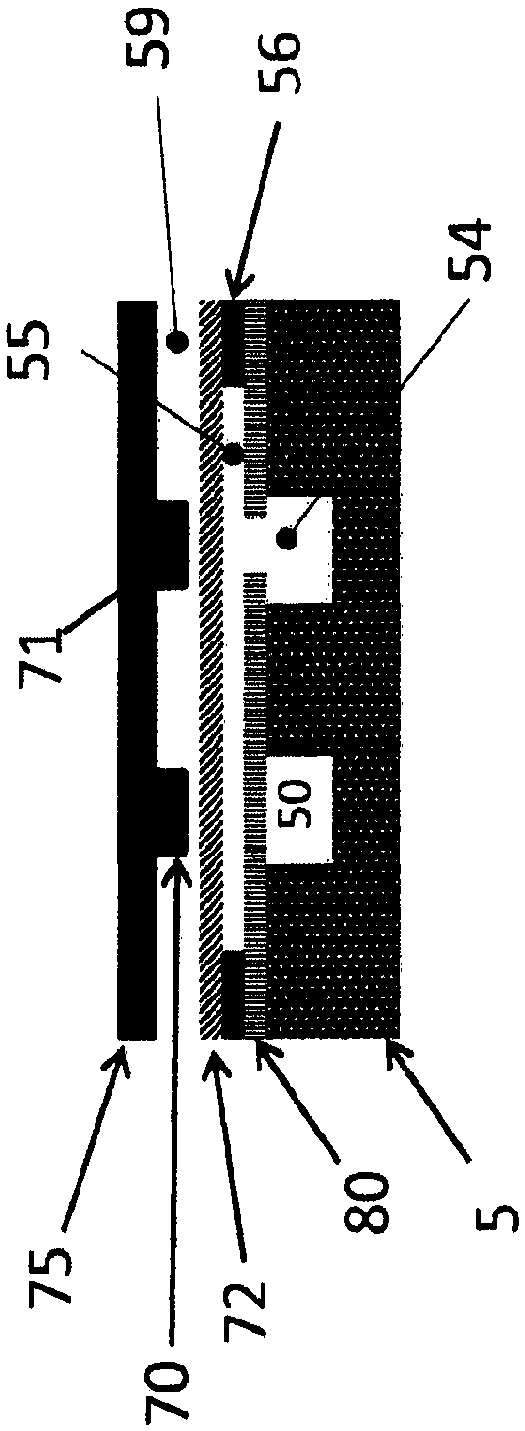
Fluidic test cassette
A technology for fluids and test strips, applied in the direction of fluid controllers, microbiological determination/inspection, laboratory containers, etc., can solve the problem of increasing storage and transportation complexity, operation and manufacturing complexity, and does not allow programming or electronics. control issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0199] Example 1: Multiplexing of Purified Viral RNA (Influenza A / Influenza B (inf A / B)) and Internal Positive Control Virus Multiplexing Amplification and Detection Methods
[0200] Position the Influenza A and Influenza B test cartridges in the docking unit. Add 40 µL of sample solution to the sample port. The sample solution includes a concentration equal to 5000TCID 50 / mL of purified A / Puerto Rico influenza virus RNA at a concentration equal to 500 TCID 50 / mL of purified B / Brisbane influenza virus RNA or molecular grade water (no template control sample). Upon entering the sample port, 40 μL of sample was mixed with the lyophilized beads as they flowed into the first chamber of the assay cartridge. Lyophilized beads consisted of MS2 bacteriophage virus particles (as a positive internal control) and DTT. In the first chamber of the assay cartridge, the samples were heated to 90 °C for 1 min to promote virus cell lysis, and then cooled to 50 °C before opening the e...
example 2
[0202] Example 2: Multiplexed Amplification and Detection Method of Viral Lysate and Internal Positive Control Virus in Buffer Law
[0203] Position the Influenza A and Influenza B test cartridges in the docking unit. Add 40 µL of sample solution to the sample port. The sample solution includes a concentration equal to 5000TCID 50 / mL of A / Puerto Rico influenza virus at a concentration equal to 500 TCID 50 / mL of B / Brisbane influenza virus or molecular grade water (no template control sample). Upon entering the sample port, 40 μL of sample was mixed with the lyophilized beads as they flowed into the first chamber of the assay cartridge. Lyophilized beads consisted of MS2 bacteriophage virus particles (as a positive internal control) and DTT. In the first chamber of the assay cartridge, the samples were heated to 90 °C for 1 min to promote virus cell lysis, and then cooled to 50 °C before opening the exhaust port connected to the second chamber. Opening the vent connec...
example 3
[0205] Example 3: Multiplicity of Influenza Virus (Purified) and Internal Positive Control Virus Spiked into Negative Clinical Nasal Samples Multiplexed Amplification and Detection Methods
[0206] Nasal swab samples collected from human subjects were placed in 3 mL of 0.025% TritonX-100, 10 mM Tris, pH 8.3 and tested for influenza A and B using an FDA-approved real-time RT-PCR assay exist. Samples were confirmed to be negative for influenza A and influenza B prior to use in this study. Spike concentration equal to 5000 TCID in confirmed influenza negative nasal samples 50 / mLA / Puerto Rico influenza virus, or use as a negative control without added virus. Add 40 μL of the resulting spiked or negative control sample to the sample ports of the Influenza A and B assay cartridges. Upon entering the sample port, 40 μL of sample was mixed with the lyophilized beads as they flowed into the first chamber of the assay cartridge. Lyophilized beads consisted of MS2 bacteriophage ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com