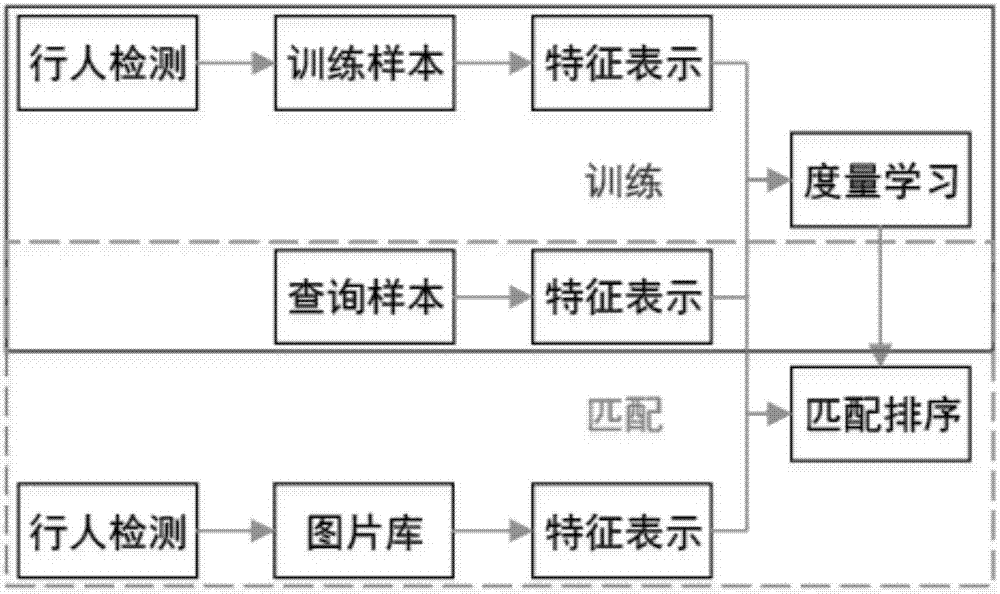
Pedestrian re-identification method based on unsupervised local measurement learning and reordering
A pedestrian re-identification and metric learning technology, applied in the field of pedestrian re-identification based on unsupervised local metric learning and reordering, can solve the problems of limited training data and large differences between different pedestrians, and achieve low time complexity, feasibility and The effect of improving usability, enhancing usability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
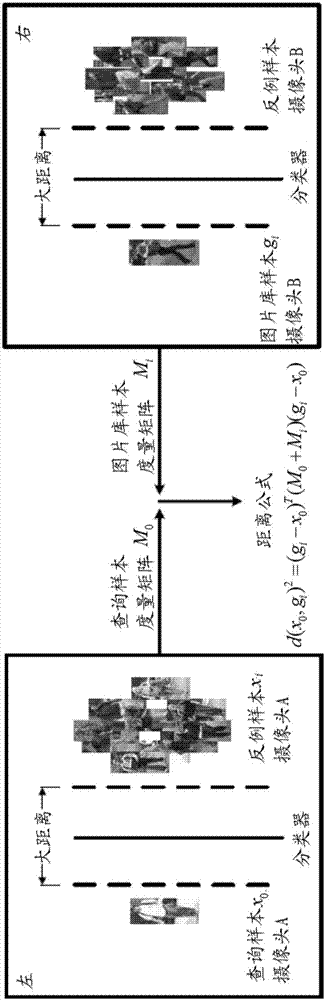
[0090] In this implementation, it is only necessary to obtain the local metric matrix M corresponding to the sample in the image library i , to calculate the similarity.
[0091] In a further preferred embodiment, query samples x are used respectively 0 The local metric matrix M of and the sample g in the image library i The corresponding local metric matrix M i , calculate the similarity between the query sample and the sample in the image library, and add the two similarities to get the final similarity.
[0092] The similarity is expressed in the form of distance as follows:
[0093] d(x 0 , g i ) 2 =(g i -x 0 ) T (M 0 +M i )(g i -x 0 ) Formula (4-3).
[0094]Through formula (4-1), formula (4-2), and formula (4-3), the distance between the query sample and the sample in the picture library can be calculated, and the similarity ranking can be obtained. The shorter the distance, the higher the ranking and the greater the similarity.
[0095] Using the local me...
Embodiment 1
[0115] 1. Database and sample classification
[0116] The pedestrian re-identification detection is carried out by adopting the method of the invention. For the accuracy and comparability of the experiment, the widely used public data VIPeR, CUHK01 and PRID2011 databases in the field of person re-identification are used.
[0117] VIPeR dataset: It consists of 1264 pictures of 632 people under two cameras, each person has only one picture under each camera, and the pictures are normalized to 128*48 pixel values. In addition to the different viewing angles of the two cameras in this dataset, the lighting conditions vary greatly, which brings great difficulty to re-identification. In the experiment, we use 316 samples under camera a as the training sample set, the remaining 316 samples under camera a as query samples, and 316 samples under camera b corresponding to the query samples as the image library.
[0118] CUHK01 dataset: Contains a total of 971 people, each with two ima...
Embodiment 2
[0131] 1. Database and sample classification
[0132] The VIPeR, CUHK01 and PRID2011 databases were used for experiments. The VIPeR and CUHK01 data sets are divided on the basis of Example 1, and the number of query samples is reduced to half of the original, respectively 158 and 243 query samples, and the division of the training sample set remains unchanged.
[0133] In the PRID2011 data set: 100 samples from 200 pairs of cameras a are randomly selected as query samples, the remaining 100 samples from camera a are used as training sample sets, and 649 samples (100+549) from all remaining cameras b are used. as a photo gallery. At this time, there are many negative samples in the image library, and the interference ability is strong.
[0134] 2. Performance evaluation criteria
[0135] Make a CMC curve and consider the matching accuracy at rank-1 as an index to measure the effectiveness of the method.
[0136] For each query sample and sample in the picture library, calcu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com