Method for promoting the growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali land with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer
A technology of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and sweet sorghum, applied in organic fertilizers, botany equipment and methods, applications, etc., to achieve the effects of promoting plant growth, alleviating saline-alkali stress, and changing rhizosphere physical and chemical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Utilize the method for the growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali land by Phylopodium moses, described Phylopodium moses is Funneliformis mosseae, this bacterial classification is common bacterial classification, provided by China Agricultural University, described The method includes the following steps:
[0035] Step 1, preparation of moses stipe fungus agent
[0036] The initial inoculant is a soil sample containing Funneliformis mosseae spores, hyphae and infected root segments;
[0037] Air-dry the farmland soil and organic fertilizer separately, pass through a 2mm fine screen, sterilize by high-pressure steam at 121°C for 1 hour, take out after high-pressure steam sterilization and cool to room temperature, and then put the farmland soil and organic fertilizer cooled to room temperature according to volume Ratio 2:1 mixing and stirring to form a matrix evenly;
[0038] Adopt mixed application method to inoculate described initial inoculant in matrix, inoculum ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Utilize the method that rhizophysis internae promotes the growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali land, except that the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus bacterial classification and sweet sorghum kind are different from embodiment 1, all the other are the same;
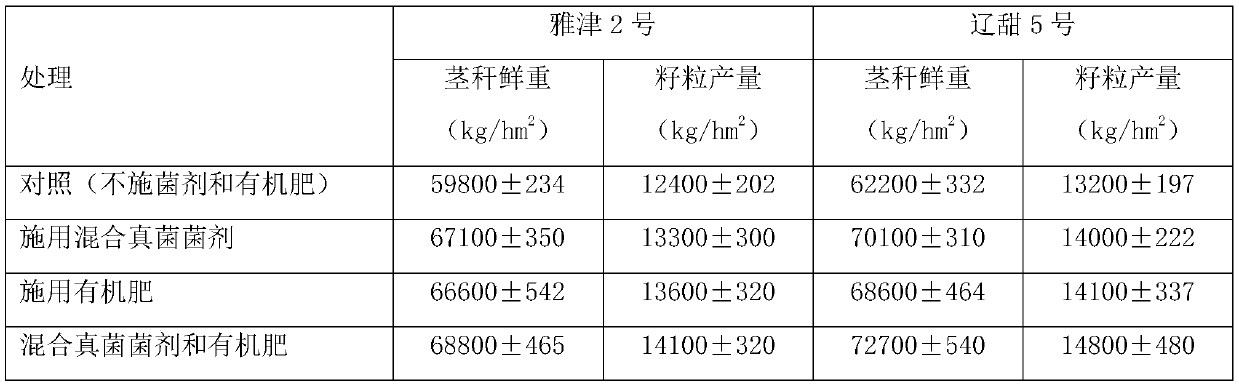
[0050] The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus is Rhizophagus intraradices, provided by China Agricultural University; the sweet sorghum variety is Liaotian 5, which is purchased from the market; the biological yield of sweet sorghum is measured after maturity As in Table 2:
[0051] Table 2 Effects of rhizomatous fungal agents and organic fertilizers on the fresh weight and grain yield of sweet sorghum (Liaotian No. 5)
[0052] deal with Fresh weight of stalks (kg / hm 2 )
[0053] It can be seen from Table 2 that the average fresh weight of the stalks in the control treatment was 62200kg / hm 2 , the average biological yield of the stalks was 68500kg / hm under the treatment of applying the fungus fungus in t...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Utilize Phylopodium scoliticum to promote the growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali land, except that the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus strains are different from Example 1 and two sweet sorghum varieties are adopted, all the other are the same;
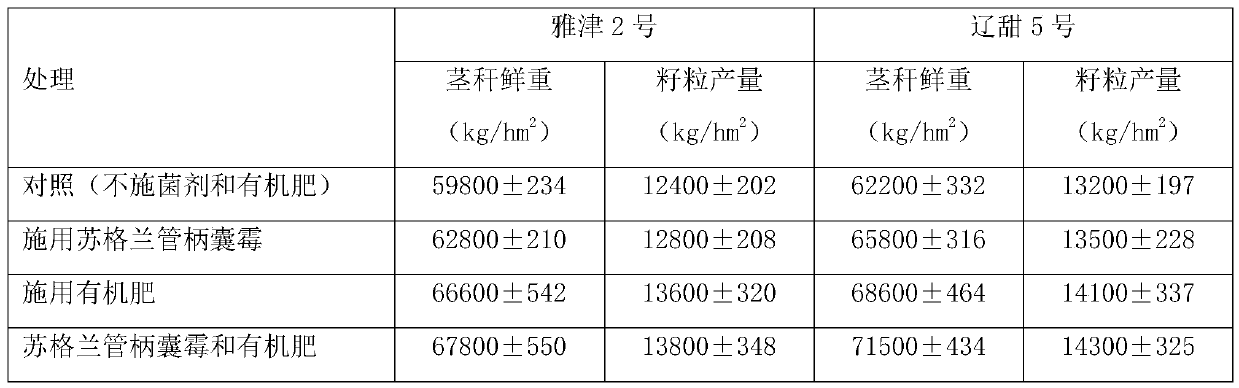
[0056] The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus was Funneliformis caledonium, provided by the Nanjing Soil Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences; the sweet sorghum varieties were Yajin 2 and Liaotian 5, both of which were purchased from the market; The measurement results of the yield are shown in Table 3:
[0057] Table 3 Effects of Scotch stalk fungi and organic fertilizers on sweet sorghum (Yajin 2 and Liaotian 5) stalk fresh weight and grain yield
[0058]
[0059] It can be seen from Table 3 that for Yajin No. 2 sweet sorghum, the average fresh weight of the stalks treated with Phylopodium scotidica, organic fertilizer, and bacterial agent and organic fertilizer were respectively 62800kg / hm 2 、66600kg / hm ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com