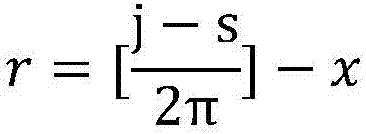Force moment zero-searching method for elastic drive joint
An elastic drive and joint technology, applied in the direction of manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of high price, increased production cost, and small maximum rotation speed of absolute position sensors, so as to reduce production costs and simplify the structure. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
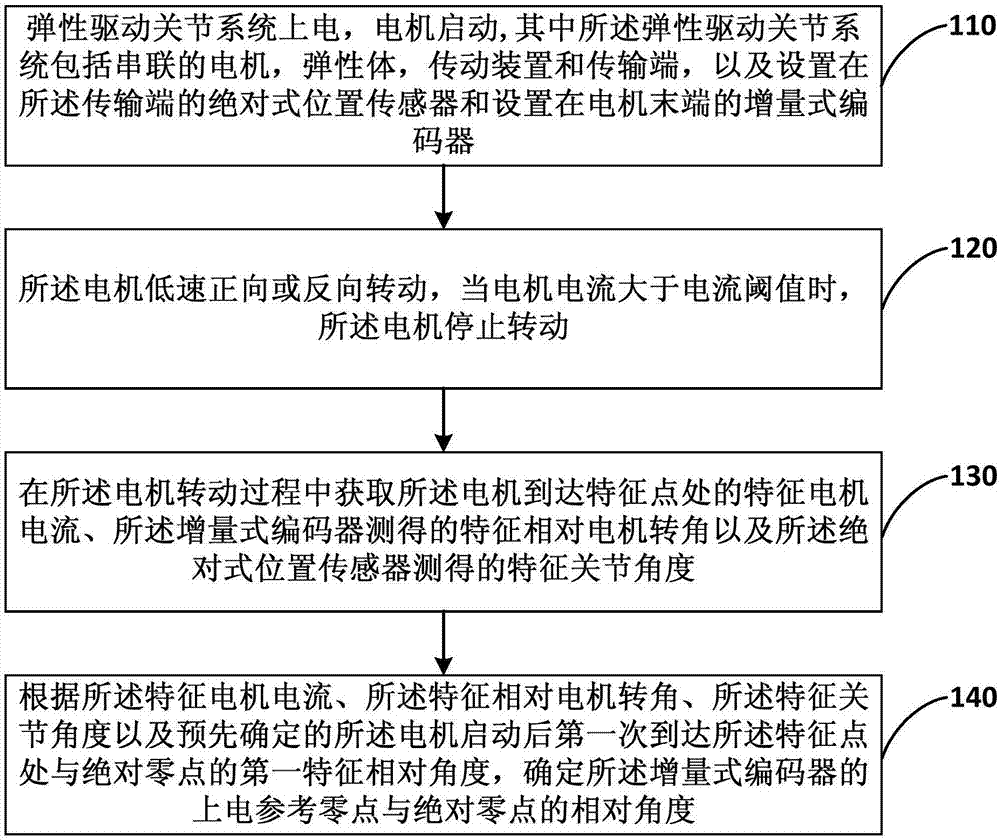
[0025] figure 1 It is a flow chart of a torque zeroing method for an elastically driven joint provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This embodiment is applicable to the case of measuring joint torque. This method can be performed by a SEA joint, and specifically includes the following steps:
[0026] Step 110, the elastically driven joint system is powered on, and the motor is started, wherein the elastically driven joint system includes a series motor, an elastic body, a transmission device and a transmission end, and an absolute position sensor arranged at the transmission end and an absolute position sensor arranged at the end of the motor incremental encoder;
[0027] Among them, the elastic drive joint system can be linear or rotary, and the rotary elastic drive joint system can also be disc type, cylinder type, etc.; the motor is the drive source of the elastic drive joint system, and the motor can be at any position Start; the elastic body can be a torsion...
Embodiment 2
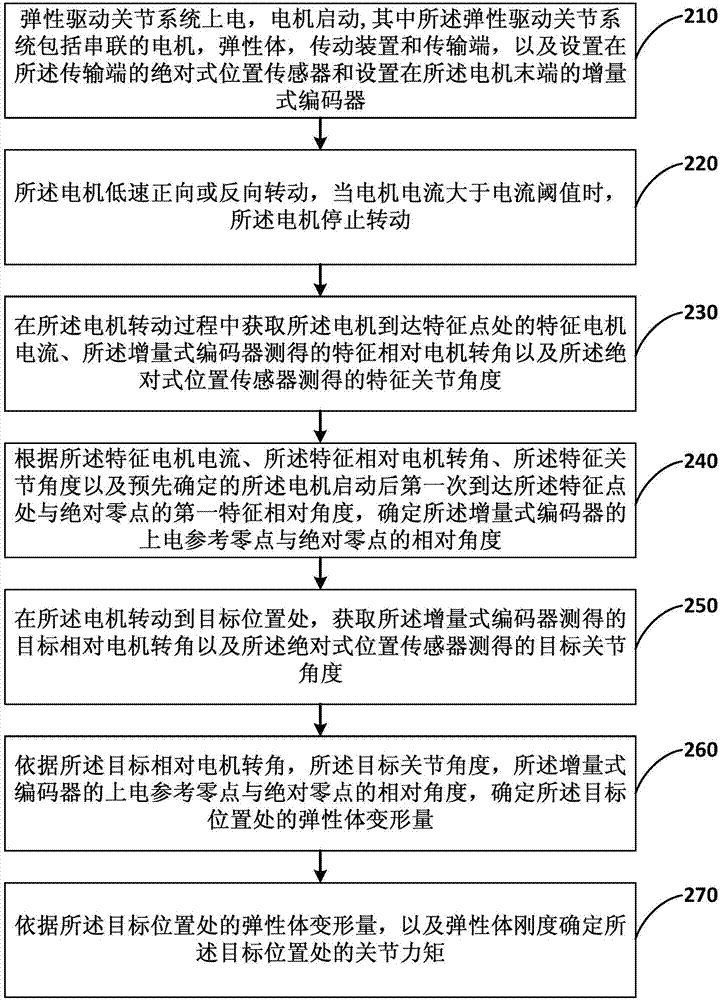
[0058] figure 2 It is a flow chart for measuring joint torque in a torque homing method of an elastically driven joint provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This embodiment is optimized on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments. After determining the relative angle between the power-on reference zero point and the absolute zero point of the incremental encoder, it also includes, when the motor rotates to the target position, obtaining the The target relative motor rotation angle measured by the incremental encoder and the target joint angle measured by the absolute position sensor; according to the target relative motor rotation angle, the target joint angle, the upper position of the incremental encoder The relative angle between the electrical reference zero point and the absolute zero point is used to determine the deformation amount of the elastic body at the target position; and the joint moment at the target position is determined according to the def...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com