An RT-qPCR method for the direct quantitative detection of circulating miRNAs
A quantitative detection and detection method technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of incomplete RNA precipitation and recovery, time-consuming RNA extraction process, RNA loss, etc., to achieve excellent transcription efficiency, improve sensitivity and accuracy, and easy operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1 Direct S-Poly(T)Plus method compares the circulating miRNA content in plasma and serum
[0054] In this example, the same volunteer serum and plasma were used as templates at the same time, and a total of 10 pairs of serum and plasma samples from the same healthy volunteer were collected. Use the DirectS-Poly(T)Plus method in the present invention to detect the miRNA expression levels in the same amount of serum or plasma samples respectively. Specifically include the following steps:
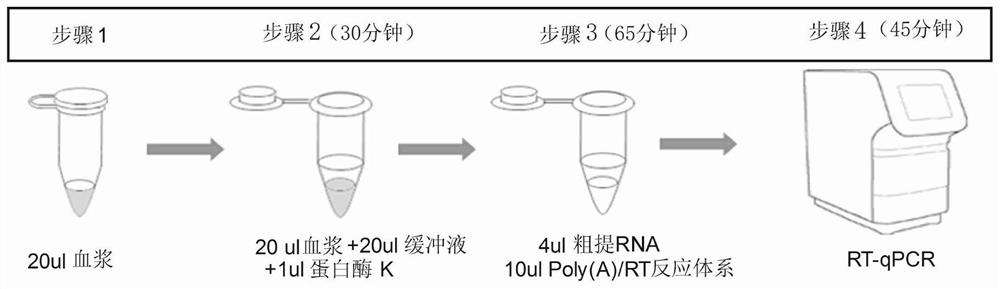
[0055] S1, cracking and centrifuging, the specific steps are:
[0056] 1) Mix 20uL plasma / serum with 20uL 2×lysis buffer, add 1uL proteinase K, treat at 50°C for 20 minutes, then keep at 95°C for 5 minutes, and place on ice;
[0057] 2) Centrifuge at 13,000g at 4°C for 5 minutes; absorb the supernatant (crude RNA) and transfer it to another new centrifuge tube or use it directly in S2;
[0058] S2. Reverse transcription with tailing: poly(A) tailing and reverse transcript...
Embodiment 2
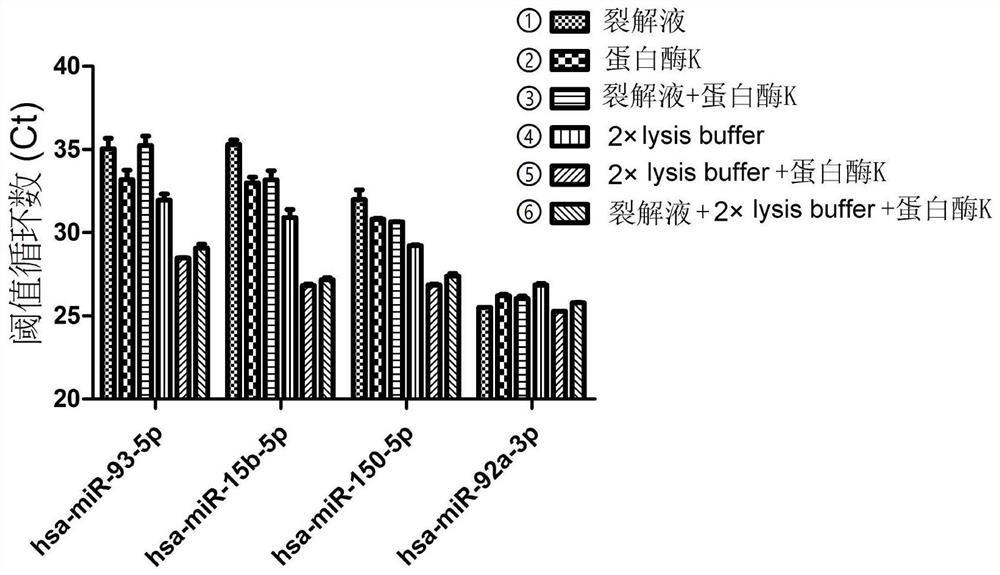
[0088] Embodiment 2 Comparison of the effects of different cracking schemes in the Direct S-Poly (T) Plus (DSPP) method of the present invention
[0089] In the Direct S-Poly(T)Plus method, any of the following six treatments can be used to cleavage the miRNA from the protein complex:
[0090] ① Lysis system: 20ul lysate, 20ul sample; lysis condition: keep at 75°C for 5 minutes;
[0091] ② Lysis system: 20ul RNase-free water, 1ul proteinase K, 20ul sample; lysis conditions: treat at 50°C for 20 minutes, then keep at 95°C for 5 minutes;
[0092] ③ Lysis system: 20ul lysate, 1ul proteinase K, 20ul sample; lysis conditions: treat at 50°C for 20 minutes, then keep at 95°C for 5 minutes;
[0093] ④ Lysis system: 20ul 2×lysis buffer, 20ul sample; lysis condition: keep at 75°C for 5 minutes;
[0094] ⑤ Lysis system: 20ul 2×lysis buffer, 1ul proteinase K, 20ul sample; lysis conditions: treat at 50°C for 20 minutes, then keep at 95°C for 5 minutes;
[0095] ⑥ Lysis system: 10ul 2×ly...
Embodiment 3
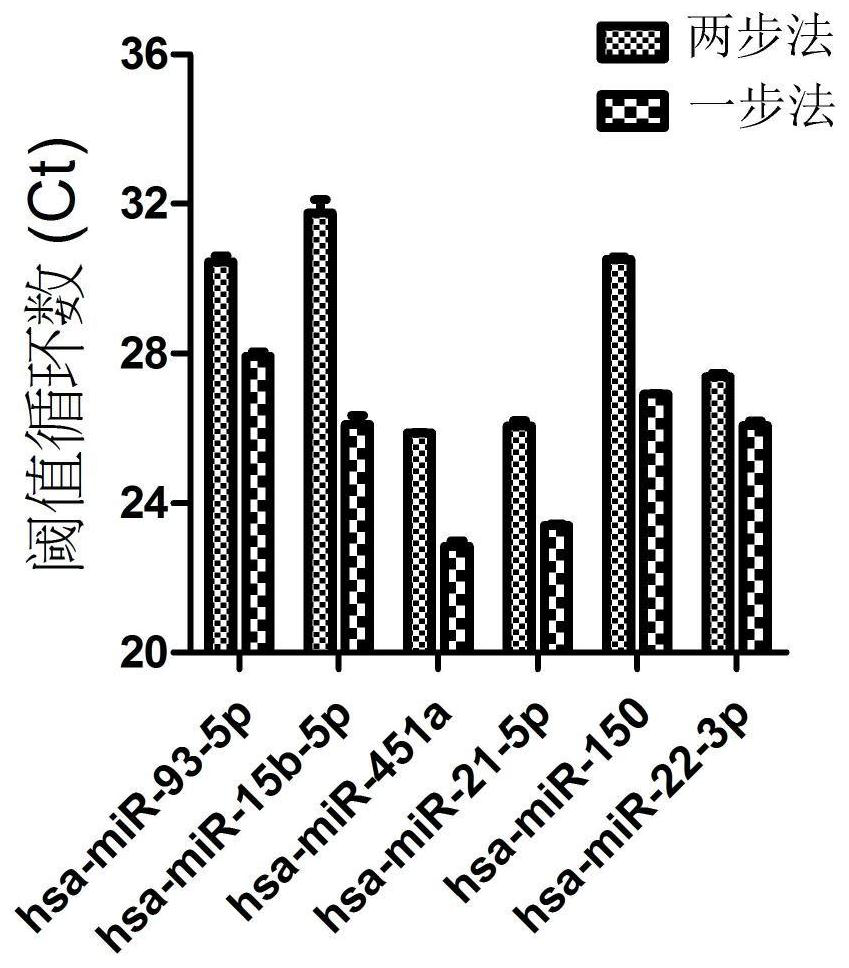
[0099] One-step method and two-step method sensitivity contrast in embodiment 3 Direct S-Poly (T) Plus method
[0100] In the previously invented S-Poly(T)Plus method (patent application number: 201510558101.5), using purified RNA as a template, the sensitivity of the one-step method is greatly improved compared with the two-step method. The two-step method means that miRNA Poly(A) tailing is completed before reverse transcription; the one-step method means that miRNA Poly(A) tailing and reverse transcription are performed in the same reaction. In this invention, using crudely extracted RNA as a template, the operation is the same as in Example 1, and the sensitivity of the two-step method and the one-step method are compared again. Such as image 3 Shown, in Direct S-Poly (T) Plus method, the scheme of the present invention makes the sensitivity of one-step method improve 2.5~52 times (1.7~5.7 Ct value difference) than its two-step method ( image 3 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| percent by volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com