A method and device for allocating PRB resources in a carrier
A technology of resource allocation and carrier, applied in the field of data communication, which can solve the problems of idle channel, low data transmission bandwidth, interference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
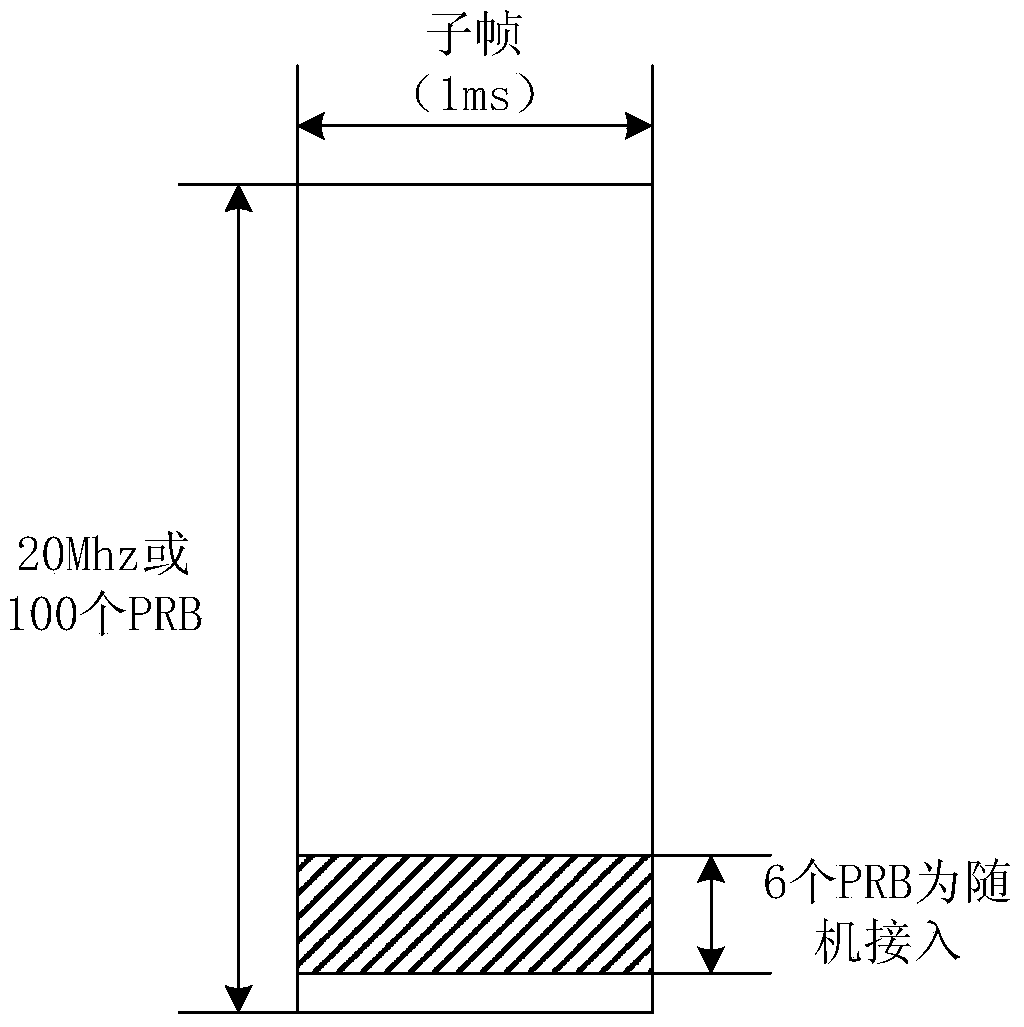
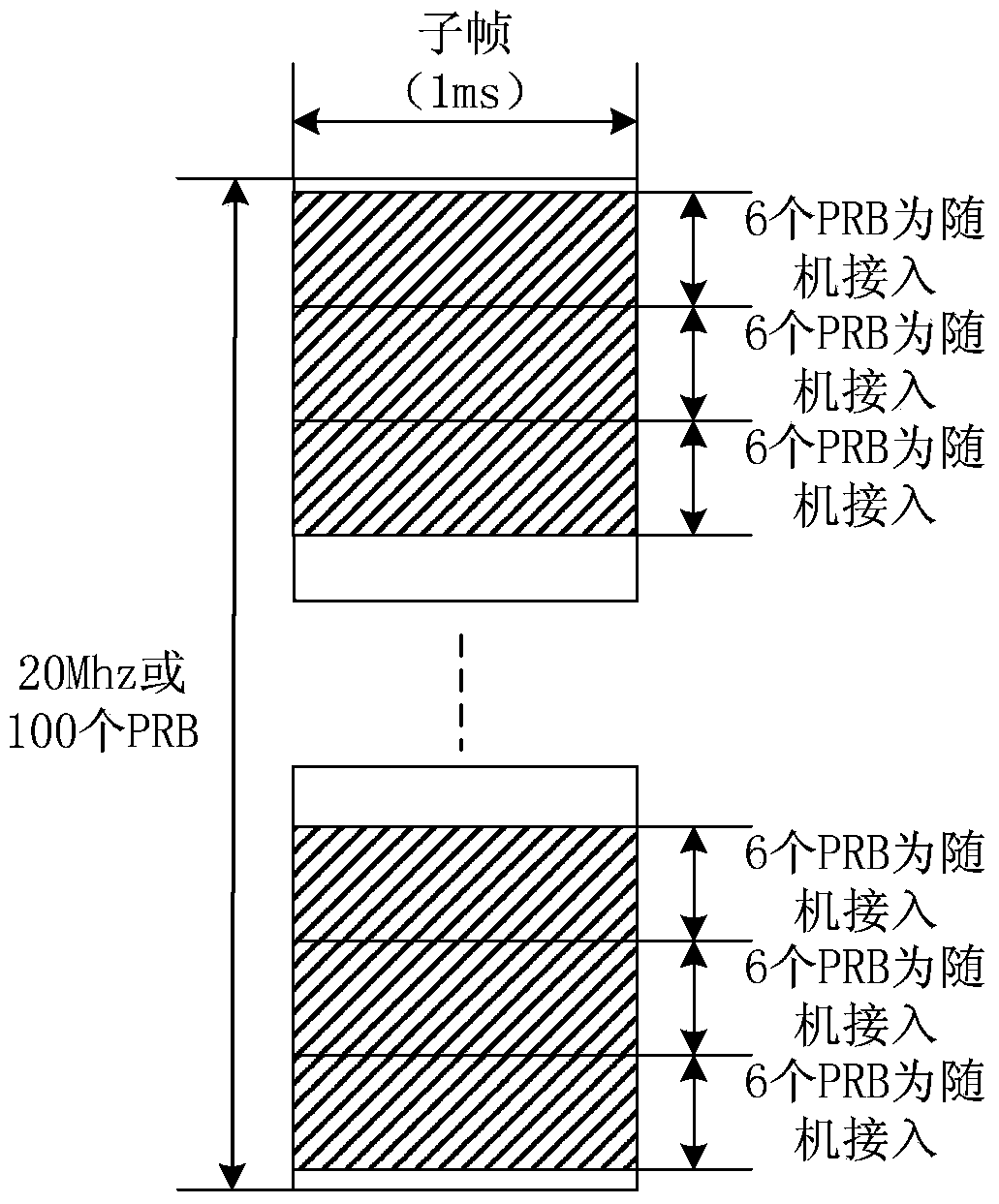
[0242] When 6 groups of PRB resources for random access are allocated in a subframe, and each group uses 6 PRB pairs, then 36 PRB pairs are required, and the PRB resources are allocated in the following manner.
[0243] The allocation of 36 PRB pairs is performed using the following equation:
[0244]
[0245] in,
[0246] is the total number of uplink PRB pair resources.
[0247] The value range is It is the number of the PRB pair in the frequency domain in the system bandwidth, which may be notified by high-level signaling or through DCI.
[0248] K is a cluster of adjacent clusters (cluster numbers are both odd or even, if the interval between two clusters with an even cluster number and an odd cluster number can be K or not K) between PRB pairs at the same position The interval, calculated by PRB pair, can be obtained according to the power spectral density of the signal in the carrier (for example, assuming that the entire bandwidth and the PRB pair numbers in ...
Embodiment 2
[0260] Increase the number of PRB pairs for each group of random access in the subframe, for example, increase from the original 6 to 10. In this way, the random access resources can be better dispersed in the frequency domain, and better meet the 80% bandwidth occupied by the equipment sending signals.
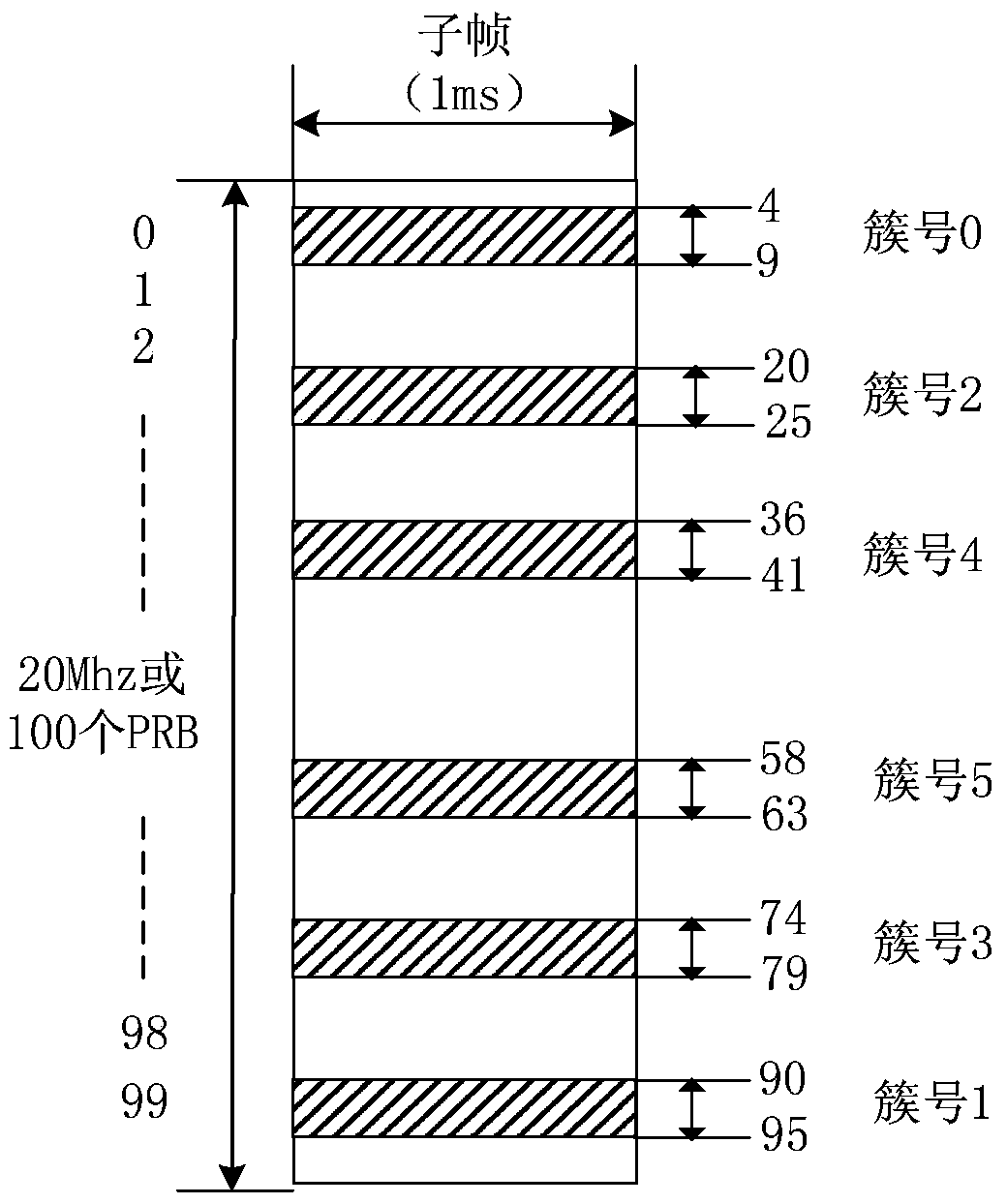
[0261] At this time, the above-mentioned idea of PRB resource allocation is still used, but some improvements are needed. At this time, the K value needs to be adjusted to a value range, for example, the value of K is about 10, for example, 10. At this time, when 10 clusters need to be allocated, f RA The value is 0~9, which is the serial number of the cluster.
[0262]
[0263]Example 1, assuming that the system bandwidth is 20MHz, when calculating the PRB allocation, it corresponds to 100 PRB pairs (the actual 20MHz system has 110 PRBs, numbered from 0 to 109), numbered from 0 to 99, and the following PRB pair resources can be obtained . The value of K is 10 (11 an...
Embodiment 3
[0275] The subcarrier spacing when the existing random access sequence is sent is modified, for example, from the existing 1.25KHz to 2.5KHz, and then 12 PRB pairs are determined for each group of random access.
[0276] The allocation of candidate PRB pairs still follows the above implementation 2, that is, 72 PRB pairs are generated for random access. It needs to be divided into 12 clusters to generate, and then a PRB pair is selected from each cluster to form 12 PRB pairs for random access.
[0277] At this time, the K value needs to be adjusted in a value range, for example, the value of K is about 8, for example, 8. At this time, when 12 clusters need to be allocated, f RA The value is 0 to 11, which is the serial number of the cluster.
[0278]
[0279] Example 1, assuming that the system bandwidth is 20MHz, when calculating the PRB allocation, it corresponds to 100 PRB pairs (the actual 20MHz system has 110 PRBs, numbered from 0 to 109), numbered from 0 to 99, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com