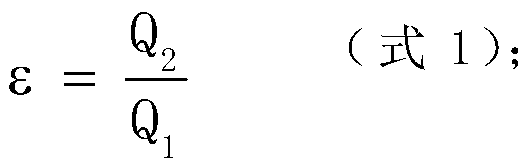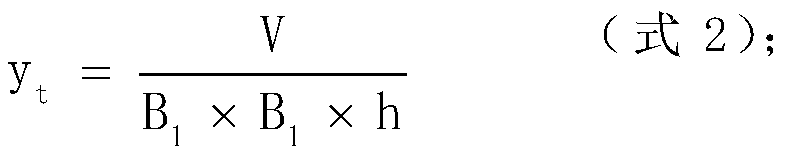A Method for Calculating the Critical Condition of River Blocking by Viscous Debris Flow
A critical condition and debris flow technology, applied in calculation, design optimization/simulation, instrumentation, etc., can solve problems such as poor universality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for calculating the critical condition of viscous debris flow blocking the river, comprising the following steps:
[0038] a. Calculate the single-width discharge ratio ε between the tributary ditch and the main river according to formula 1;
[0039]
[0040] Among them, Q 1 Single-width discharge of the main river, unit m 2 / s, Q Z Main river flow, unit m 3 / s, according to the survey, combined with the relevant national norms and design tasks to obtain Q Z , B 1 The average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries, in m, obtained by field measurement B 1 ;Q 2 is the single-width flow rate of the tributary, in m 2 / s, Q n is the debris flow flow rate, unit m 3 / s, according to the survey, combined with the relevant national norms and design tasks to obtain Q n , B 2 The average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary,
[0041] The unit is m, and B is obtained by ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] A method for calculating the critical condition of viscous debris flow blocking the river, comprising the following steps:
[0056] a. Calculate the single-width discharge ratio ε between the tributary ditch and the main river according to formula 1;
[0057]
[0058] Among them, Q 1 Single-width discharge of the main river, unit m 2 / s, Q Z Main river flow, unit m 3 / s, according to the survey, combined with the relevant national norms and design tasks to obtain Q Z , B 1 The average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries, in m, obtained by field measurement B 1 ;Q 2 is the single-width flow rate of the tributary, in m 2 / s, Q n is the debris flow flow rate, unit m 3 / s, according to the survey, combined with the relevant national norms and design tasks to obtain Q n , B 2 The average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary,
[0059] The unit is m, and B is obtained by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com