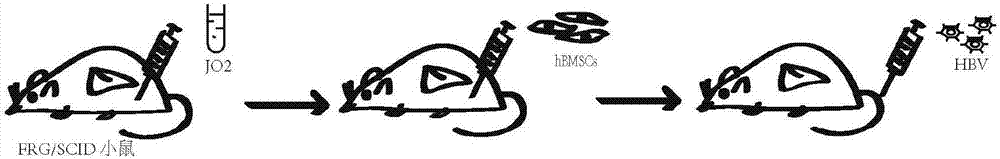Method for constructing humanized chronic hepatitis B mouse model by means of stem cell
A stem cell and mouse model technology, applied in the fields of clinical medicine, regenerative medicine and virology, and experimental medicine, can solve problems such as difficulty in establishing research models, long experimental periods, and limiting the optimization of treatment plans.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: figure 1 Schematic diagram for the construction of a humanized FRGS mouse model of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) were transplanted into FRGS mice with fulminant liver failure to establish a humanized FRGS mouse model of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
[0046] 1. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells hBMSCs were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum.
[0047] 2. FRGS mice gradually reduced the drug 2-(2-nitro-4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-cyclohexane-1,3-dione (NTBC) and injected 0.2mg / kg anti-Fas antibody (JO2), to establish a mouse model of liver failure.
[0048] 3. Inject 500ul 1×10 through the portal vein 6 hBMSCs.
[0049] 4. Continuous JO2 injection at 2, 5, and 8 days after transplantation.
[0050] 5. Inject each mouse with type A, B, C, and D 1*10 through the tail vein 6 Hepatitis B virus.
[0051] 6. After 1 week, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks after the injection of hepatiti...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: figure 2 Schematic diagram for the construction of an embryonic stem cell humanized uPA mouse model. Human embryonic stem cell lines were transplanted into homozygous uPA mice to establish an embryonic stem cell humanized uPA mouse model.
[0054] 1. Culture human embryonic stem cells in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum.
[0055] 2. Obtain a homozygous uPA / SCID mouse model.
[0056] 3. Inject 500ul 1×10 via the spleen at 8 weeks of birth 6 Human embryonic stem cells.
[0057] 4. Inject 1*10 per mouse via the tail vein 7 Hepatitis C virus.
[0058] 5. After 1 week, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks after the injection of hepatitis C virus, the viral load and liver function status were detected every 4 weeks to confirm the successful establishment of the model.
[0059] figure 2 Using uPA mice, uPA will spontaneously form liver damage, and then use human embryonic stem cell transplantation to differentiate into liver cells, and finally inject hepatitis C ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3, image 3 Schematic diagram for the establishment of a normal mouse model of induced pluripotent stem cell humanized galactosamine. Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) were injected into normal immune fulminant liver failure mice to establish a normal mouse model of induced pluripotent stem cell humanization.
[0061] 1. Introduce certain transcription factors into animal or human somatic cells through gene transfection technology, so that the somatic cells can be directly restructured into pluripotent stem cells, and cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum.
[0062] 2. Each mouse was intraperitoneally injected with 1.5 g / kg of galactosamine to establish a mouse model of liver failure.
[0063] 3. Inject 500ul 1×10 through the liver 6 Human induced pluripotent stem cells.
[0064] 4. Inject 1*10 per mouse via the tail vein 5 Hepatitis E virus.
[0065] 5. After 1 week, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks after the injection of hepatitis E viru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com